P1442
Read the instructions below then start the fault diagnostic procedure.
Symptom: CHECK ENGINE. Possible smell of petrol. Possible faulty reading on the fuel gauge in MIU.
| P1442 |
EVAP Purge Valve Circuit. Small leakage in the system at the same time as the fuel level sensor diagnosis has reported a fault.
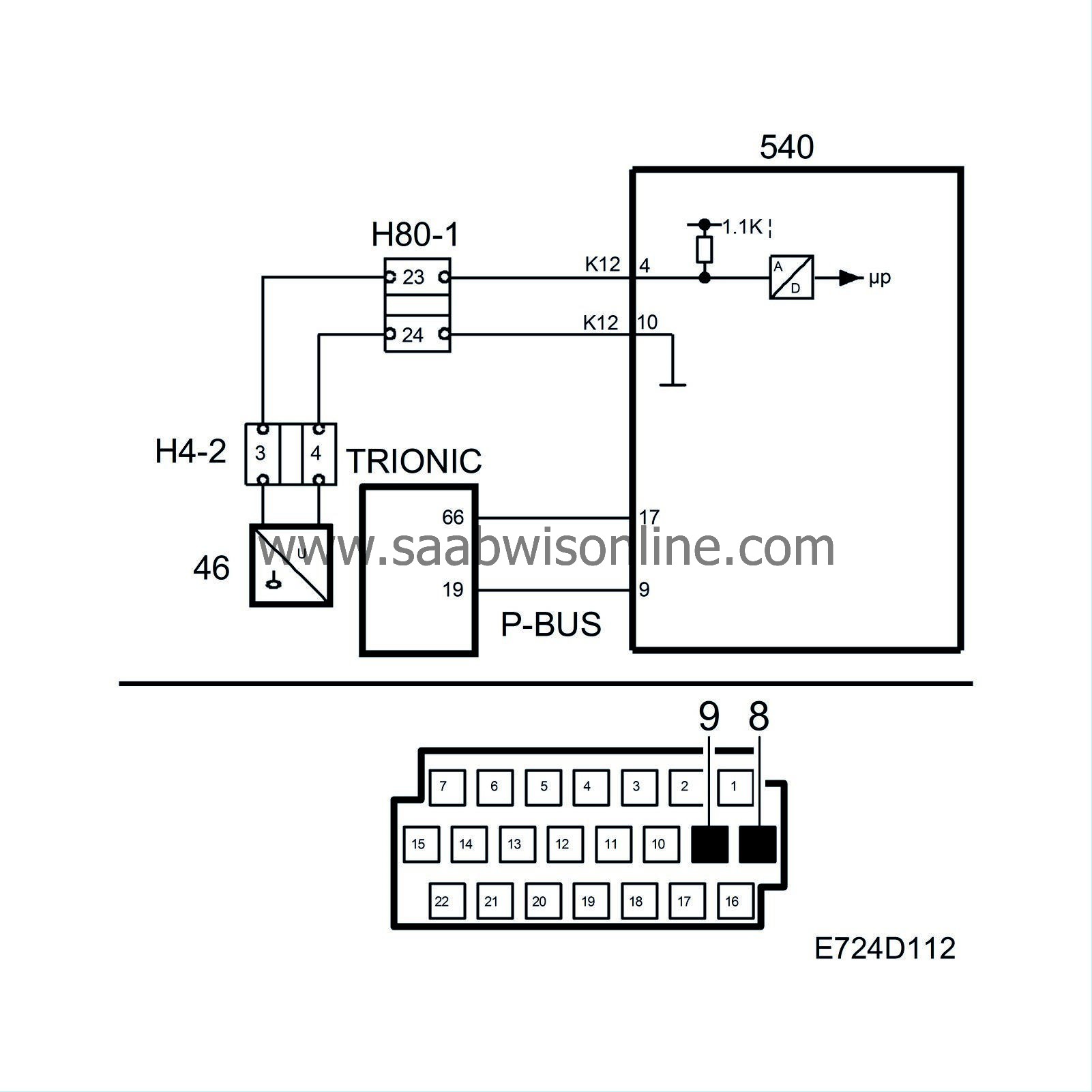
Fault symptoms
| • |
CHECK ENGINE.
|
|
| • |
Possible smell of petrol.
|
|
| • |
Possible faulty reading on the fuel gauge in MIU.
|
|
On-Board Diagnostics
Type of diagnosis:| - |
Once per driving cycle. Interrupted when fault criteria fulfilled or OK reported. Restarts next driving cycle.
|
|
Test 1, Cold start
Enable criteria:
| - |
Coolant temperature at start between 5-40°C. Difference between coolant temperature and intake air temperature less than 5°C.
If the above conditions are not fulfilled, Test 2 will start. Idling speed. Max. one change in status of brake light switch. Purging adaptation higher than -15%. Intake air pressure at least 20 kPa lower than the atmospheric pressure. The vehicle stationary for 5 sec. Fuel volume in tank between 11-54 litres. Battery voltage between 10-16 volts. Tank pressure between -300 to +100 Pa. The diagnosis will start once the above conditions have been fulfilled for more than 5 seconds. If the diagnosis is interrupted then the speed must exceed 0 on one occasion before it is allowed to restart. The diagnosis is divided into 3 phases, A-C: Phase A) Evaporation check The shut-off valve is activated (closed) at the same time as possible purging is stopped for 4.5 sec. Tank pressure is observed, falling pressure reveals leaks in purging valve. Rising pressure of more than 3 Pa/s points to fuel evaporation, in these cases Phase A is repeated. If it becomes apparent that the pressure is rising by more than 3 Pa/s the diagnosis is interrupted, vehicle speed is needed during a certain time for it to be restarted. For pressure increases less than 3 Pa/s then Phase A is complete. The diagnosis continues to Phase B (pressure reduction) Phase B) Pressure reduction Shut-off valve is still closed, the purging valve's pulse ratio is set at 23-24.5% until the tank pressure has reached -600 Pa. This pressure reduction should take no more than max. 30 seconds. Phase C) Pressure retaining The shut-off valve is still closed, the purging valve is closed. The tank pressure is observed for max. 12 seconds. |
|
Test 2, Warm start
Enable criteria:
| - |
The following conditions should be fulfilled for 5 seconds so that the diagnosis can start: Coolant temperature and intake air temperature at start exceeds +40°C and the difference between coolant temperature and intake air temperature is greater than 5°C.
Idling speed. Max. one change in status of brake light switch. Purging adaptation higher than -6%. Tank pressure between -300 to +100 Pa. Inlet air pressure at least 20 kPa lower than the atmospheric pressure. The vehicle stationary. Fuel volume in tank between 11-54 litres. Battery voltage between 10-16 Volts. Tank pressure sensor diagnosis must have reported OK. The diagnosis will start once the above conditions have been fulfilled for more than 5 seconds. The diagnosis is interrupted if the purging adaptation exceeds -8%. If the diagnosis is interrupted then the speed must exceed 0 on one occasion before it is allowed to restart. The diagnosis is divided into 3 phases, A-C: Phase A) Evaporation check The shut-off valve is activated (closed) at the same time as possible purging is stopped for 4.5 sec. Tank pressure is observed, falling pressure reveals leaks in purging valve. Rising pressure of more than 4 Pa/s points to fuel evaporation, in these cases Phase A is repeated. If it becomes apparent that the pressure is rising by more than 4 Pa/s the diagnosis is interrupted, vehicle speed is needed during a certain time to restart. At pressure increases less than 4 Pa/s then Phase A is complete. The diagnosis continues on to Phase B (pressure reduction) Phase B) Pressure reduction Shut-off valve is still closed, the purging valve's pulse ratio is set at 18% until the tank pressure has reached -600 Pa. This fall in pressure should take no more than max. 30 seconds. Phase C) Pressure retaining The shut-off valve is still closed, the purging valve is closed. The tank pressure is observed for max. 12 seconds. |
|
Fault criteria:
Test 1 (Cold start)
| - |
Phase A) Evaporation check
If the pressure falls by more than 27.5 Pa/s then an internal leak in the purging valve has been detected. If the pressure has risen by more than 3 Pa/s then there is major fuel evaporation, Phase A will then be repeated. If it becomes apparent that the pressure is rising by more than 3 Pa/s then the diagnosis is interrupted. For pressure increases less than 3 Pa/s then the diagnosis continues on to Phase B.
|
|
| - |
Phase B) Pressure reduction
If the pressure cannot be reduced to -450 Pa within 15 seconds or if the pressure reaches -450 Pa within 15 seconds but not as high as -600 Pa within a further 15 seconds (30 seconds in total) then a major leakage has been found.
|
|
| - |
Phase C) Pressure retaining
If the pressure rises to -450 Pa within 12 seconds then a small leakage has been found.
|
|
Fault criteria
Test 2 ( Warm start)
| - |
Phase A) Evaporation check
If the pressure falls by more than 27.5 Pa/s then an internal leak in the purging valve has been detected. If the pressure has risen by more than 4 Pa/s then there is huge fuel evaporation, Phase A will then be repeated. If it becomes apparent that the pressure is rising by more than 4 Pa/s then the diagnosis is interrupted. For pressure increases less than 4 Pa/s then the diagnosis continues on to Phase B.
|
|
| - |
Phase B) Pressure reduction
If the pressure cannot be reduced to -450 Pa within 15 seconds or if the pressure reaches -450 Pa within 15 seconds but not as high as -600 Pa within a further 15 seconds (30 seconds in total) then a major leakage has been found.
|
|
| - |
Phase C) Pressure retaining
If the pressure rises to -450 Pa within 12 seconds then a small leakage has been found.
|
|
Fault code generation
| - |
Diagnostic trouble codes are generated when the above fault criteria are fulfilled and the dependents are OK.
Fuel level, Plausibility diagnosis: Because fuel level is used as an enable criteria in certain diagnosis, then the control module must know that fuel level value is plausible. It works in such a way that Trionic receives the bus message ”Fuel level XX litre" from MIU. While driving Trionic observes the value and as the vehicle is driving it is consuming petrol, Trionic sees that the fuel level value will fall. In Trionic there is a number of filtrations of the value so as to avoid inaccuracies due to for example splashing fuel in the tank and hill starts. The fuel level diagnosis can be said to be a support diagnosis, it does not generate its own diagnostic trouble codes, but if for example the EVAP valve diagnosis has reported a small leakage in the purging valve then DTC P0442 is normally generated. If on the other hand the integrity diagnosis has reported the same fault and the fuel level diagnosis at the same time has also reported a fault then DTC P1442 is generated instead. In addition for Test 2 (Warm start) the intake air temperature has not been below 5°C. P0441, P1441 are generated if faults are reported during Phase A P0455, P1455 are generated if faults are reported during Phase B P0442, P1442 are generated if faults are reported during Phase C |
|
Dependents:
| - |
P0444, P0445, P0501, P0502, P0506, P0507, P1444, P1445, P1576 and P1577.
|
|
OK report:
| - |
Test 1
or
Test 2 performed once and fault criteria not fulfilled.
|
|||||||
Fault handling:
(For more information, see “Fault diagnosis, general".)
| - |
Type III.
|
|
Diagnostic help
Fault diagnosis concerns a leak.Functions in the diagnostic tool related to the fault:
| • |
Diagnostic status for the diagnosis.
|
|
| • |
Activate EVAP diagnosis.
|
|
For more information, see “Fault diagnosis, general”.
| Note | ||
|
During the final check of a rectified fault, the diagnostic tool activation command must be used so that Test 1 (cold start) is initiated irrespective of starting temperature. |


