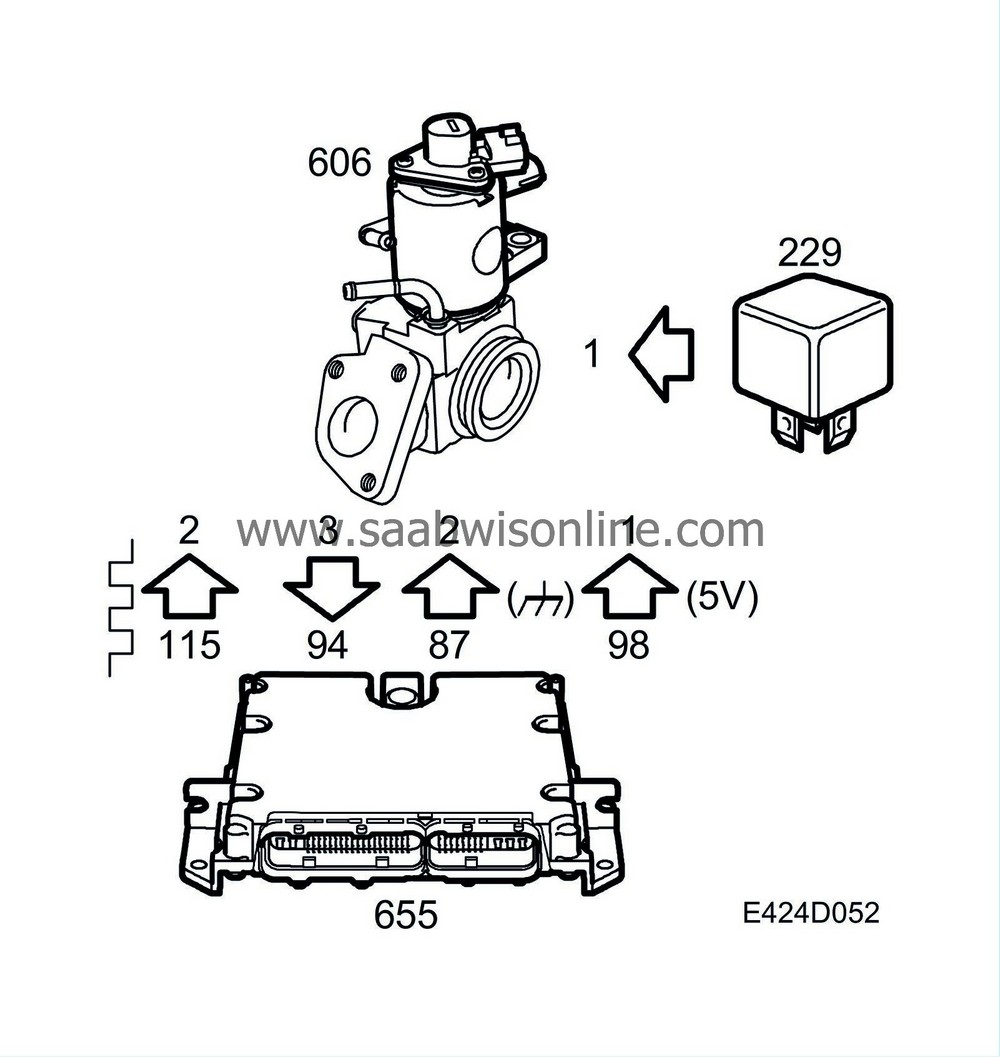
EGR solenoid valve
| EGR solenoid valve |
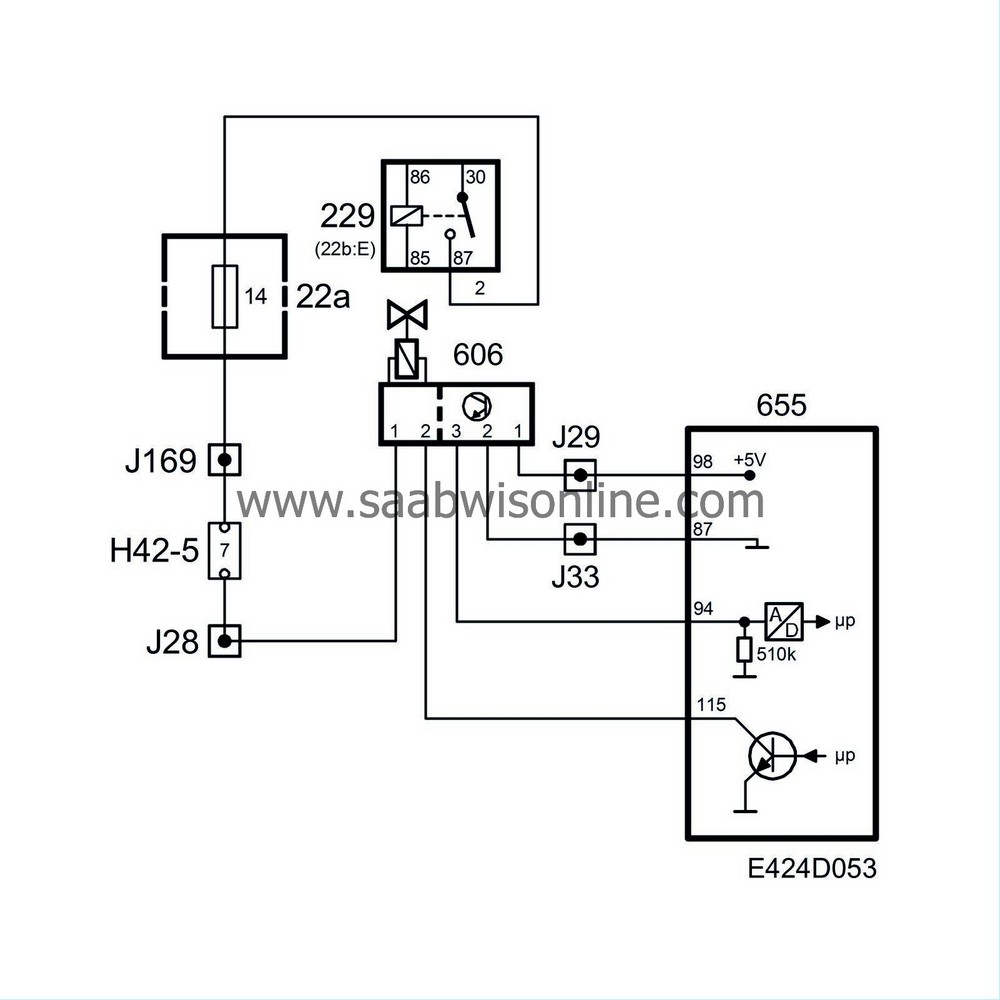
The engine has an EGR valve with feedback potentiometer. When the EGR valve opens, exhaust gas is led into the intake manifold and into the combustion chamber. This exhaust gas lowers the temperature in the combustion chamber and greatly reduces the amount of NO x . The amount the valve opens is determined by the control module and is dependent on engine speed, temperature and load. The EGR valve has a potentiometer that measures how far the valve is open. When the control module requests a larger or smaller EGR opening, the time it takes to change the position of the valve will be very short.
| • |
Potentiometer pin 1 is supplied with power from control module pin 98.
|
|
| • |
Potentiometer pin 2 is grounded from control module pin 87.
|
|
| • |
Potentiometer pin 3 gives feedback of the needle position in the EGR signal to control module pin 94. The feedback signal is also used for diagnosis.
|
|
| • |
EGR valve pin 1 is supplied with B+ via fuse 14.
|
|
| • |
EGR valve pin 2 receives a 140 Hz PWM signal from control module pin 115.
|
|
| • |
If an EGR related DTC is generated, the engine torque will be reduced and the CHECK ENGINE lamp will come on.
|
|
| EGR system function |
The EGR system comprises three sub-functions:
| • |
Desired value calculation
|
|
| • |
Air mass calculation
|
|
| • |
EGR control and monitoring
|
|
| Diagnostics |
If the solenoid valve or corresponding wiring harness is out of order, it can be indicated by the following DTCs being generated:
| • |
P0401
EGR Flow To Low
|
|
| • |
P0402
EGR Flow too High.
|
|
| • |
P0403
EGR Valve PWM Signal Circuit. Short to Ground/Open.
|
|
| • |
P0404
EGR Valve PWM Signal Circuit. Short to B+.
|
|
| • |
P0405
EGR Position Sensor Circuit. Short to Ground/Open.
|
|
| • |
P0406
EGR Position Sensor Circuit. Short to B+.
|
|
| • |
P1403 EGR position sensor, Low. Malfunction.
|
|
| • |
P1404 EGR position sensor, High. Malfunction.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Exhaust recirculation and boost pressure control are disengaged.
|
|
| • |
The idling speed will be set to 1000 rpm.
|
|
| • |
The following limitations apply: Pedal position sensor adjustable to max 30%, fuel quantity max 30 mm
3
/combustion, fuel rail pressure max 60 M Pa.
|
|
| Desired value calculation |
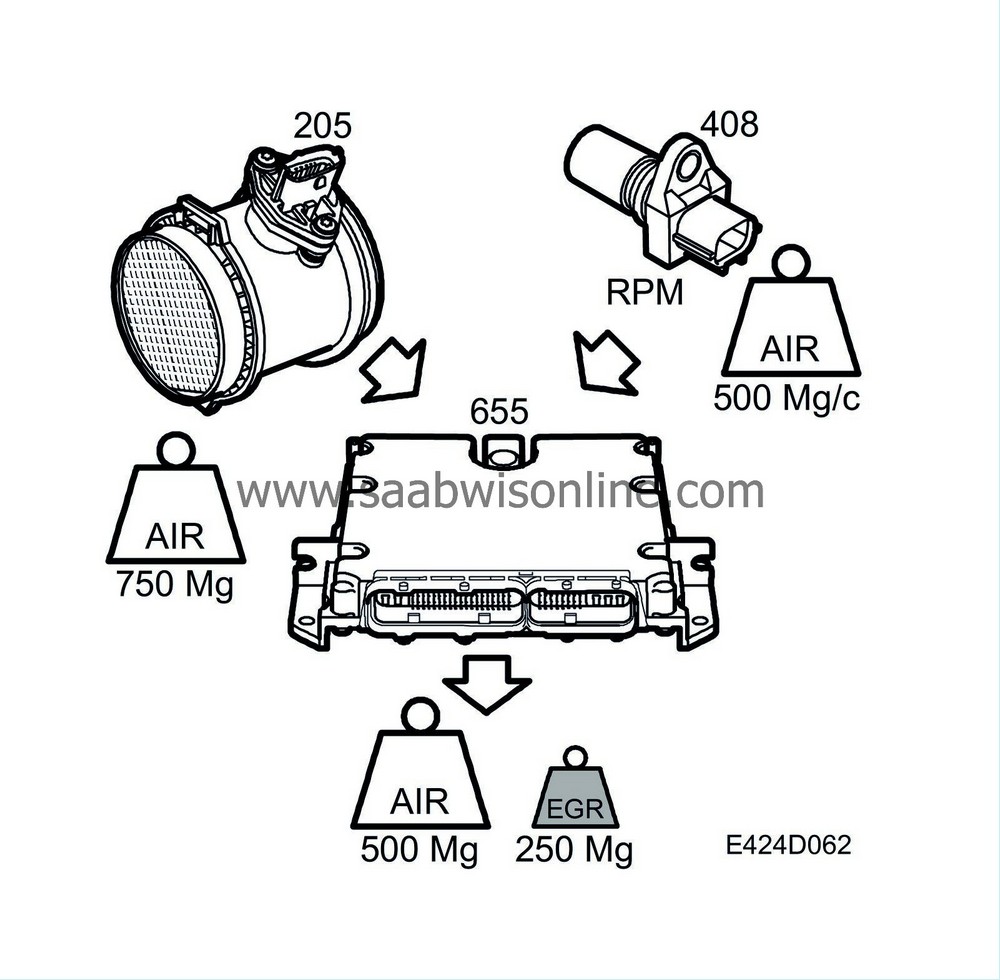
The desired value calculation estimates the air mass/combustion required by the engine on each occasion. The regulating function controls the EGR valve so that this amount of air is always attained. This is achieved by allowing the amount of recirculated exhaust gases to enter the intake manifold that is required to reduce the intake air mass/combustion to the value estimated by the desired value calculation.
Example:
In certain circumstances, the pump can deliver 750 mg air/combustion.
The desired value calculation says that there should be 500 mg air/combustion under these particular circumstances. The result from the desired value calculation is sent to the EGR regulation. The control function will then open the EGR valve enough to allow exhaust gas to enter and prevent 250 mg air/combustion from being drawn into the engine.
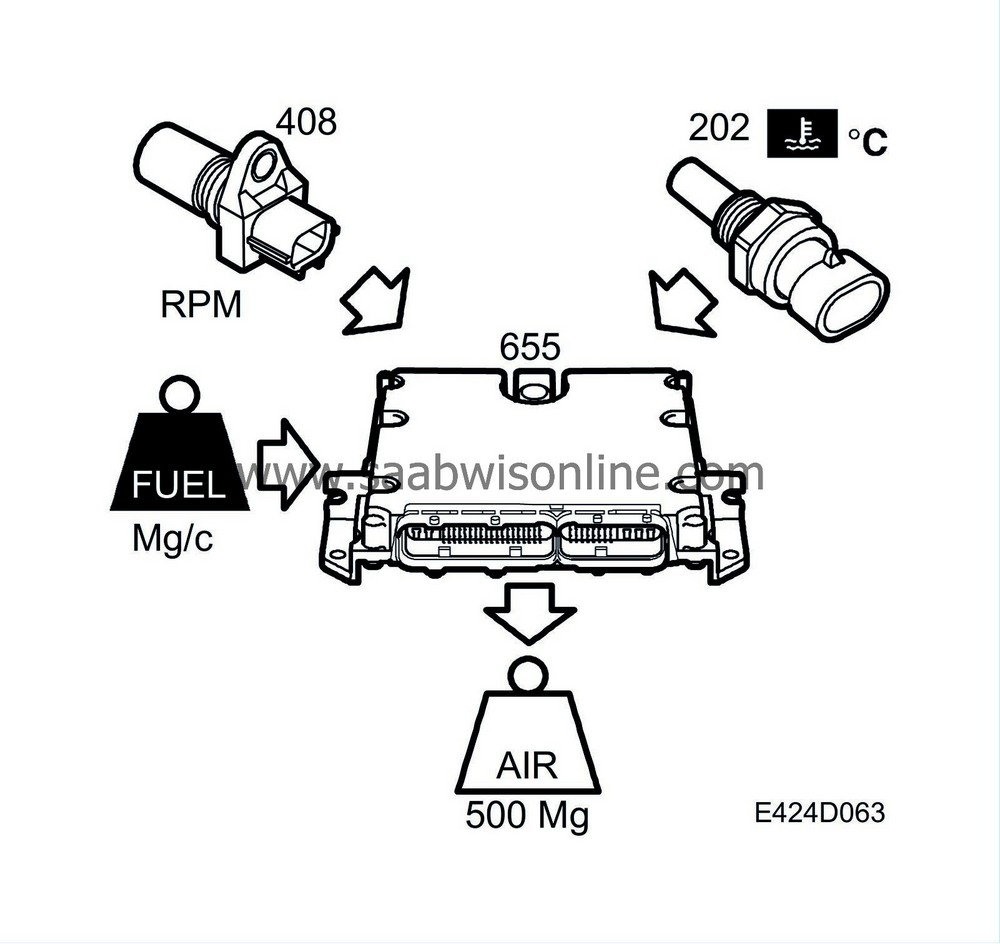
The desired value is a function of:
| • |
Requested torque
|
|
| • |
Engine speed
|
|
| • |
Calculated fuel quantity
|
|
| • |
Engine coolant temperature
|
|
| • |
Atmospheric pressure
|
|