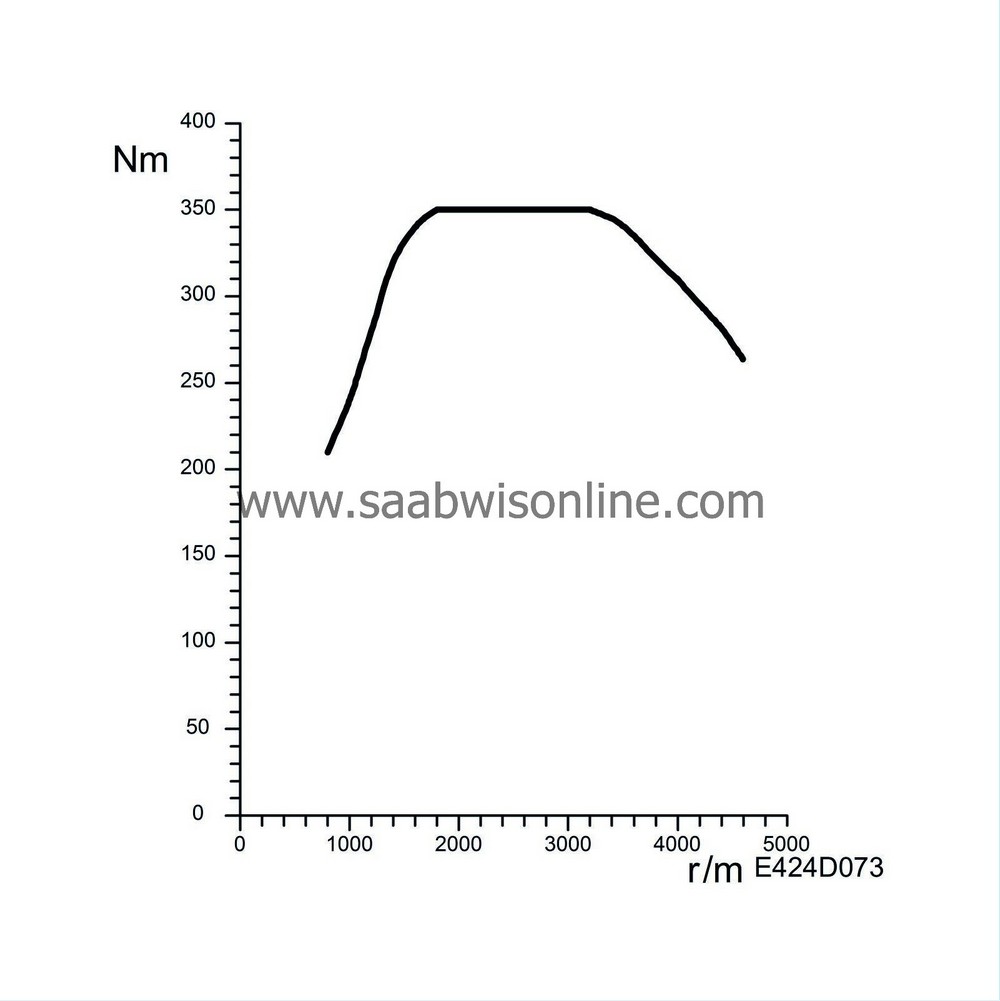
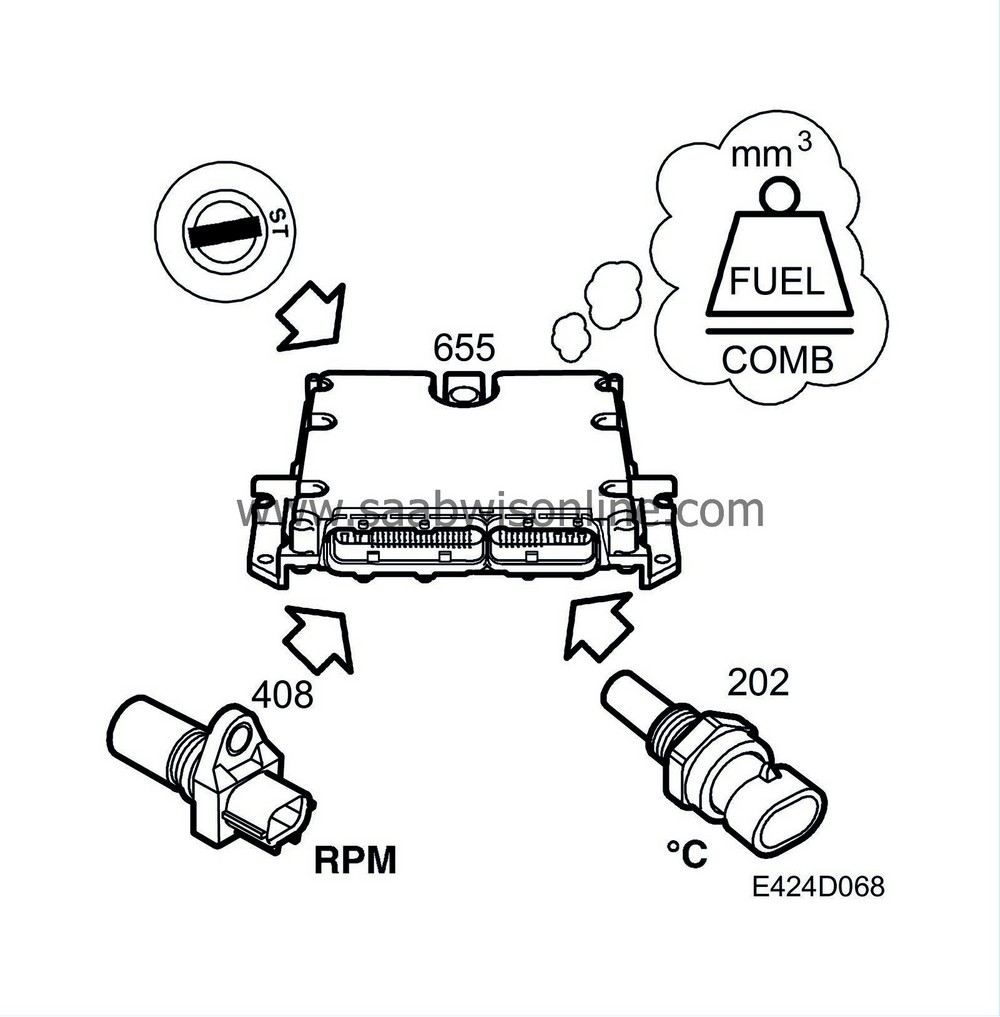
Fuel calculation
| Fuel calculation |
If the temperature exceeds 8°C, the engine will be started with the "pilot injection amount" and the "main injection amount". Once the engine has started, i.e. when the engine speed exceeds 400 rpm, the fuel amount will be reduced gradually until a stable idling speed has been attained.
During normal running, the total amount of fuel is always one pilot injection and one main injection.
During normal running, the accelerator pedal potentiometer is one of the most important input signals to ECM for calculating the fuel amount together with the engine speed and engine temperature.
Temperature compensation
When the engine is cold, an enrichment will be necessary to ensure good driveability.If the engine is about to overheat on the other hand, this function will be activated to reduce the fuel quantity.
Information to control this comes from:
| • |
Coolant temperature sensor
|
|
| • |
Fuel temperature sensor
|
|
Quantity compensation with Tech 2
Due to variations in fuel quality, it can have different densities, which means that at a lower density, the car will not be as powerful as expected or, if the diesel fuel has a high density, the car will tend to smoke more from the exhaust pipe. In order to compensate for this, there is a quantity compensation function.Quantity compensations are made for limitation values by multiplying by a value between 0.95 and 1.05 mm 3 /combustion.
The quantity compensation can be adjusted by 5% with the diagnostic instrument.
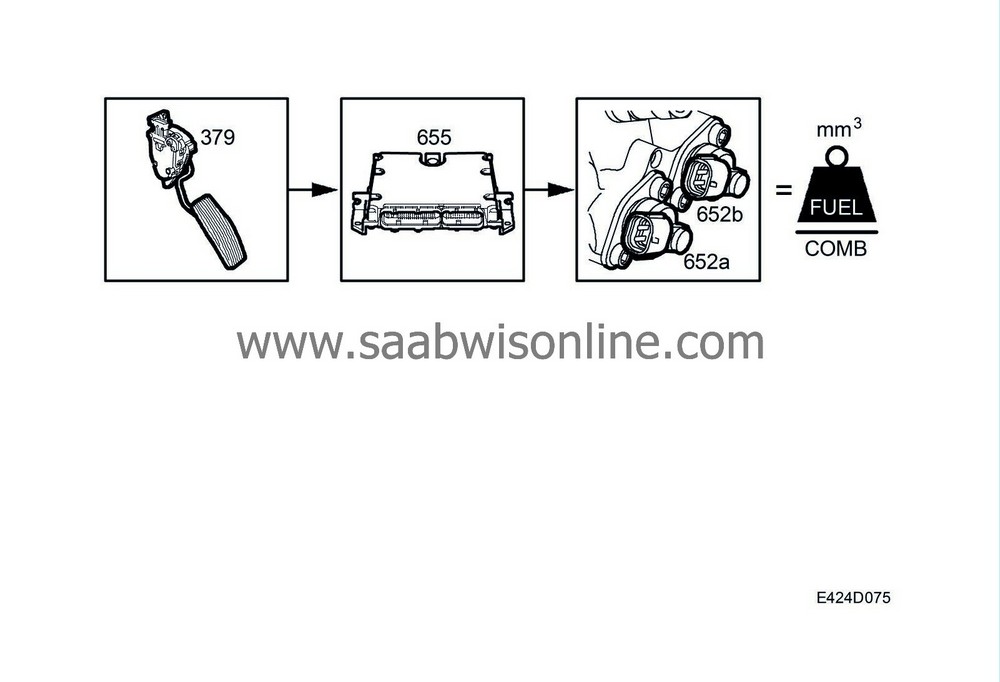
Requested quantity from accelerator pedal position sensor
The requested torque goes from the pedal position sensor to the engine control module. The control module adjusts the quantity of fuel/combustion so that it agrees with the requested torque.The pedal position sensor value is filtered for both increasing and reducing acceleration.
Compensation for A/C compressor cut-in
This function is engaged when the A/C compressor starts and compensates the extra torque that the A/C compressor takes from the engine with an extra fuel quantity/combustion.The compensation quantity from the "compensation of A/C compressor cut-in" function is added to the value from "requested quantity from pedal position sensor". The compensation fuel quantity depends on the pressure in the A/C system and is about 2-3 mm 3 /combustion.
ECM reads the A/C pressure from the bus.
Control module calculations
All the calculations made by ECM are converted to signals for opening the injectors but also to the turbo control valve for regulating the input air to the combustion chamber.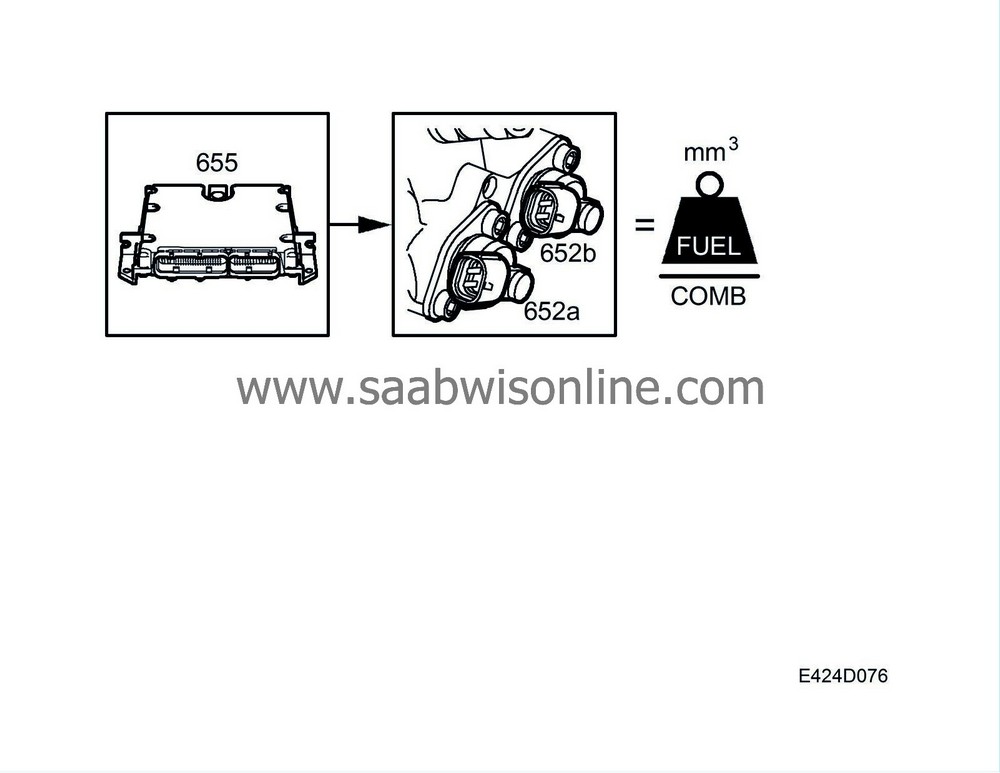
| Limiting fuel quantity |
Smoke limitation
To avoid smoke, there is a smoke limiting function. This is based on the fuel quantity, air mass, atmospheric pressure, engine speed and engine temperature. A new total fuel quantity is calculated 60 times/sec to avoid smoke.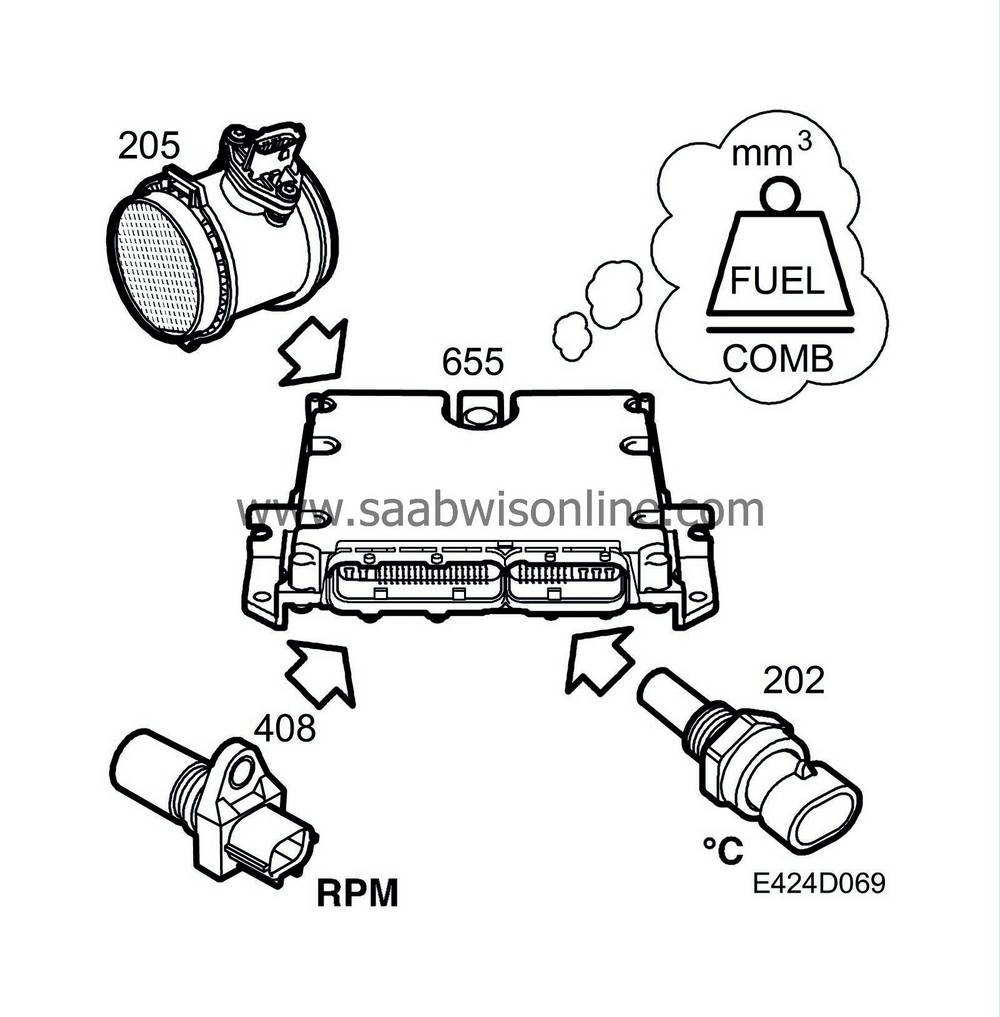
Fuel rail pressure
Based on engine speed and requested torque from the accelerator pedal potentiometer and the present pressure.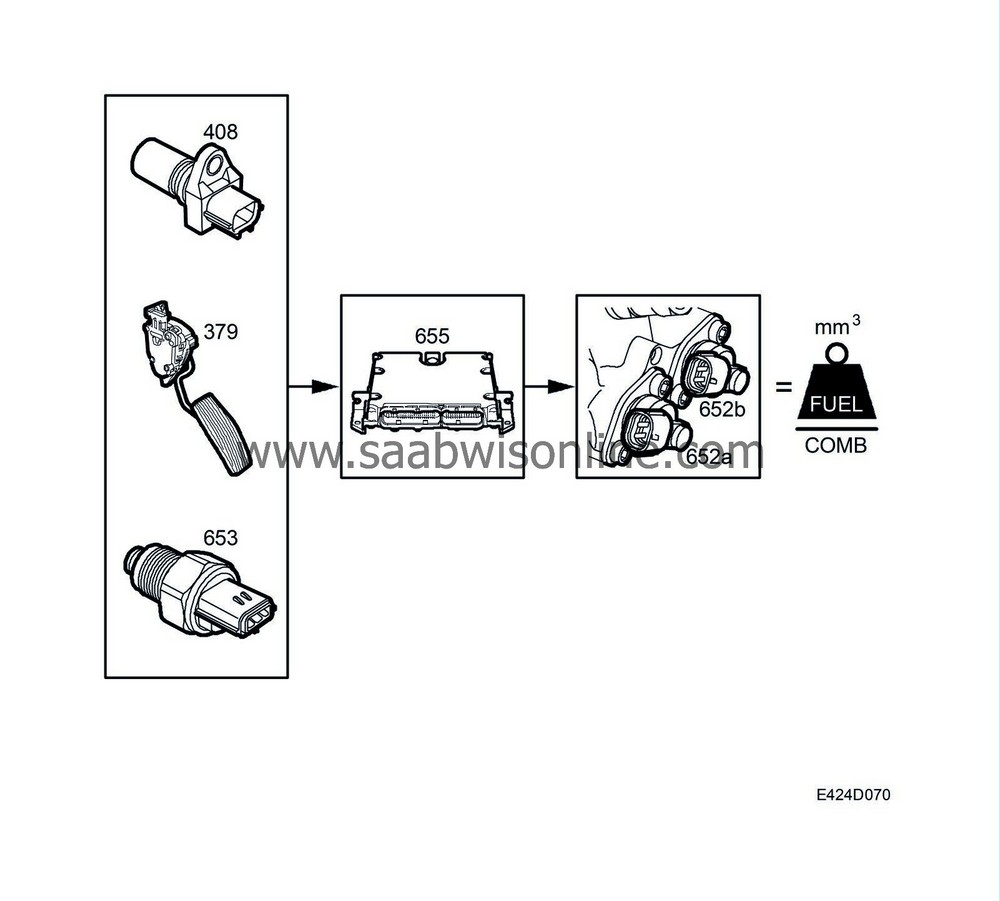
Overheating protection
This regulation is dependent on engine speed, gear and engine temperature. At 115°C, ECM starts to reduce the fuel quantity to prevent the engine temperature from rising to 125°C.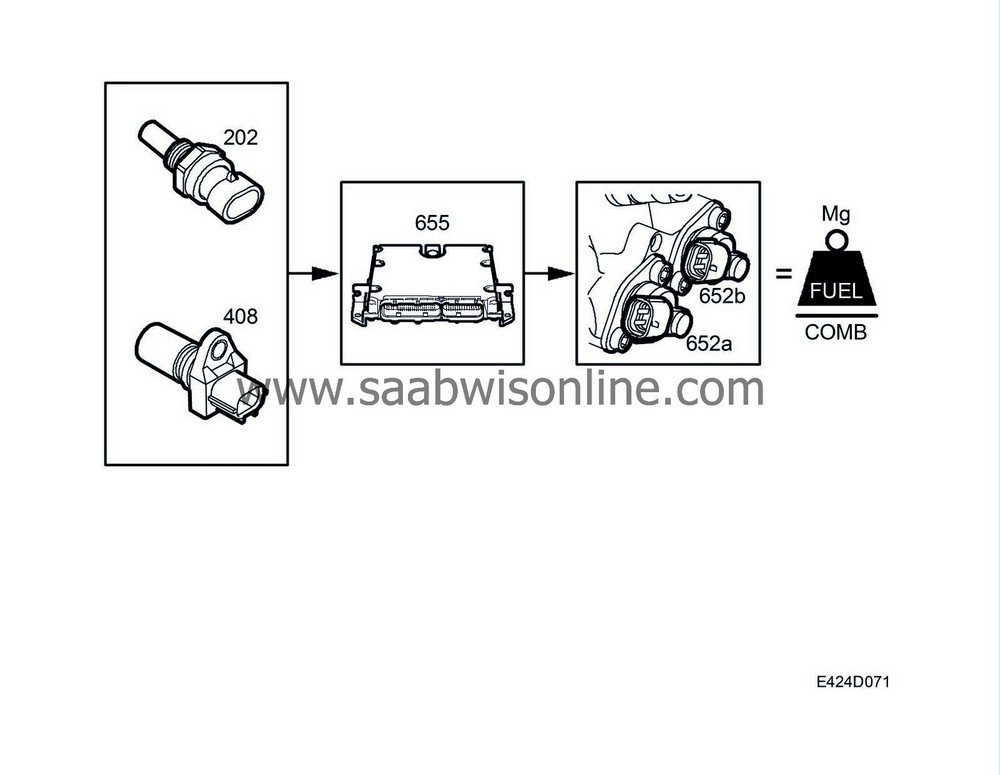
Limp-home
When DTCs have been set in the system, the fuel quantity will be reduced to prevent damage to the engine and its systems. The permitted fuel quantity differs depending on the DTCs that have been set. The more serious the fault, the more the fuel is reduced.ASD (Active Surge Damper)
The fuel quantity is adjusted to counteract jerkiness and vibration during engine braking and gear changing.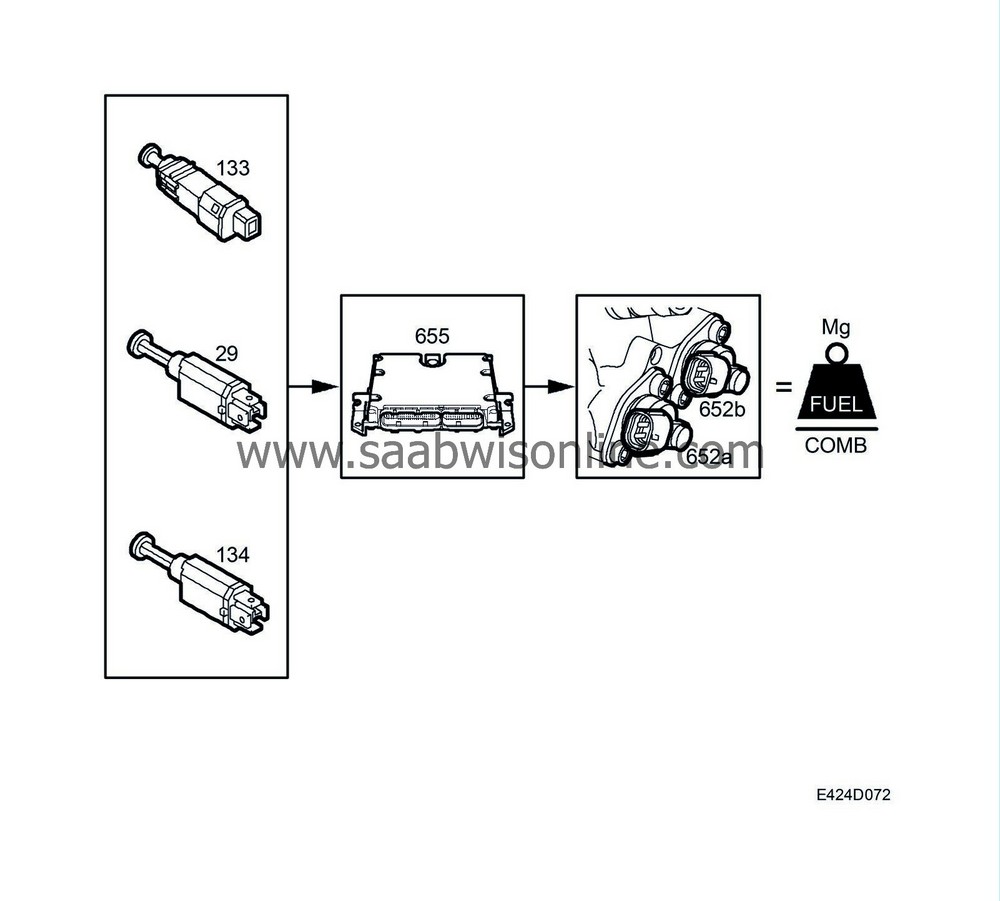
Engine torque limitation
This regulation is a fundamental protection for the basic engine and transmission. In order to avoid damaging these components, the torque available from the engine is limited. This is a preprogrammed value in relation to the requested value from the accelerator pedal potentiometer.