Description of operation, engine management system
| Description of operation, engine management system |
| Calculation, starting fuel quantity |
The starting fuel quantity is the amount of fuel allowed when starting the engine. The function is activated when starting the engine is possible and is terminated at engine speeds above 750 rpm. If starting from cold, the function is deactivated at a considerably higher engine speed.
The fuel quantity is calculated using the following sub-functions:
Base value
A base value is retrieved for which the starter motor speed and engine coolant temperature are the input values.Starting quantity correction
The starting quantity correction is calculated from the current engine speed. The max. correction is 5 mg/combustion and it decreases with the engine speed (0 mg/combustion at 750 rpm).Starting quantity enrichment
Starting quantity enrichment ensures problem-free starting at all temperatures. Enrichment is calculated from the pump temperature, engine speed and the time it takes for the engine to start. Different parameters are selected for cold starting enrichment depending on whether the pump temperature is above or below 10°C.The results of these calculations are totalled and form the total starting fuel quantity.
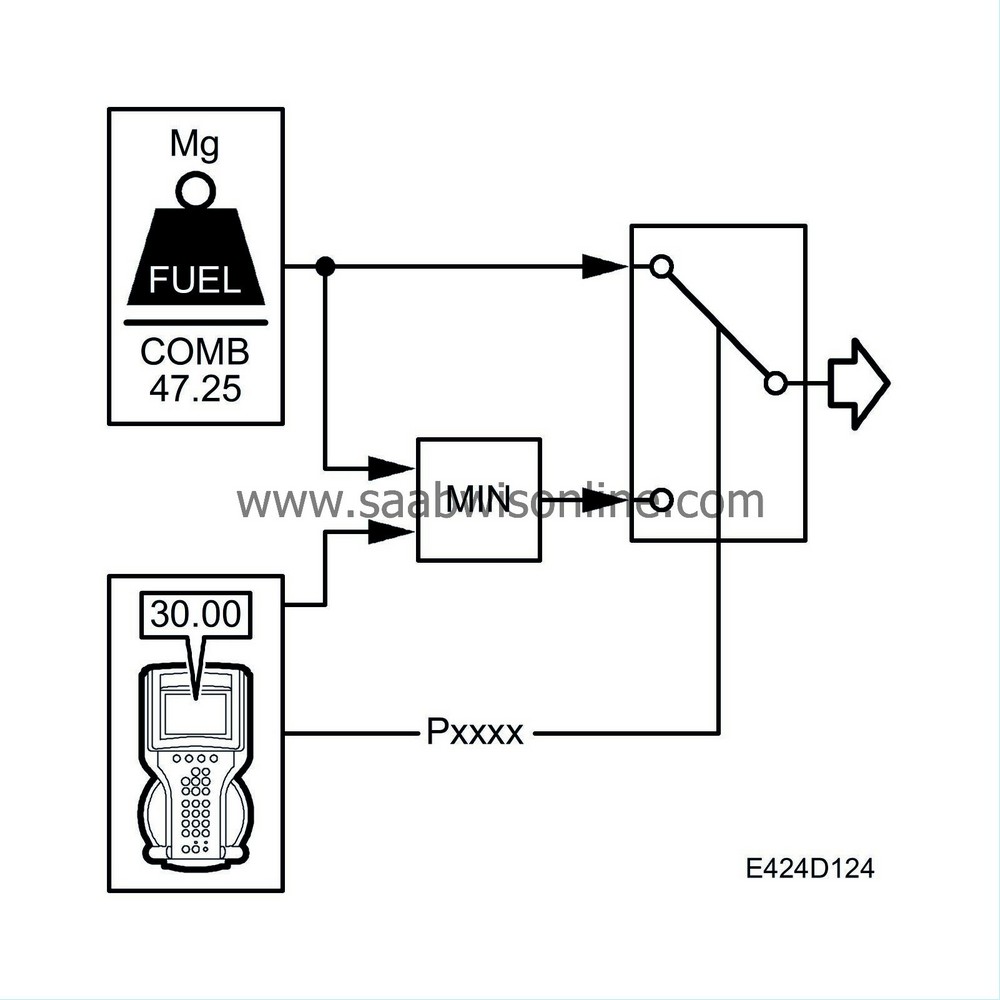
The starting fuel quantity can be decreased or increased by 5 mg/combustion with the diagnostic tool.
| Limit quantities |
The sub-functions under limit quantities calculate the largest permitted injection quantity in mg/combustion for the current operating conditions. The calculated limit quantity is used to limit the requested quantity from the pedal position sensor and the cruise control if it should be necessary. The calculation is performed at fixed time cycles, independent of the engine speed.
| 1. |
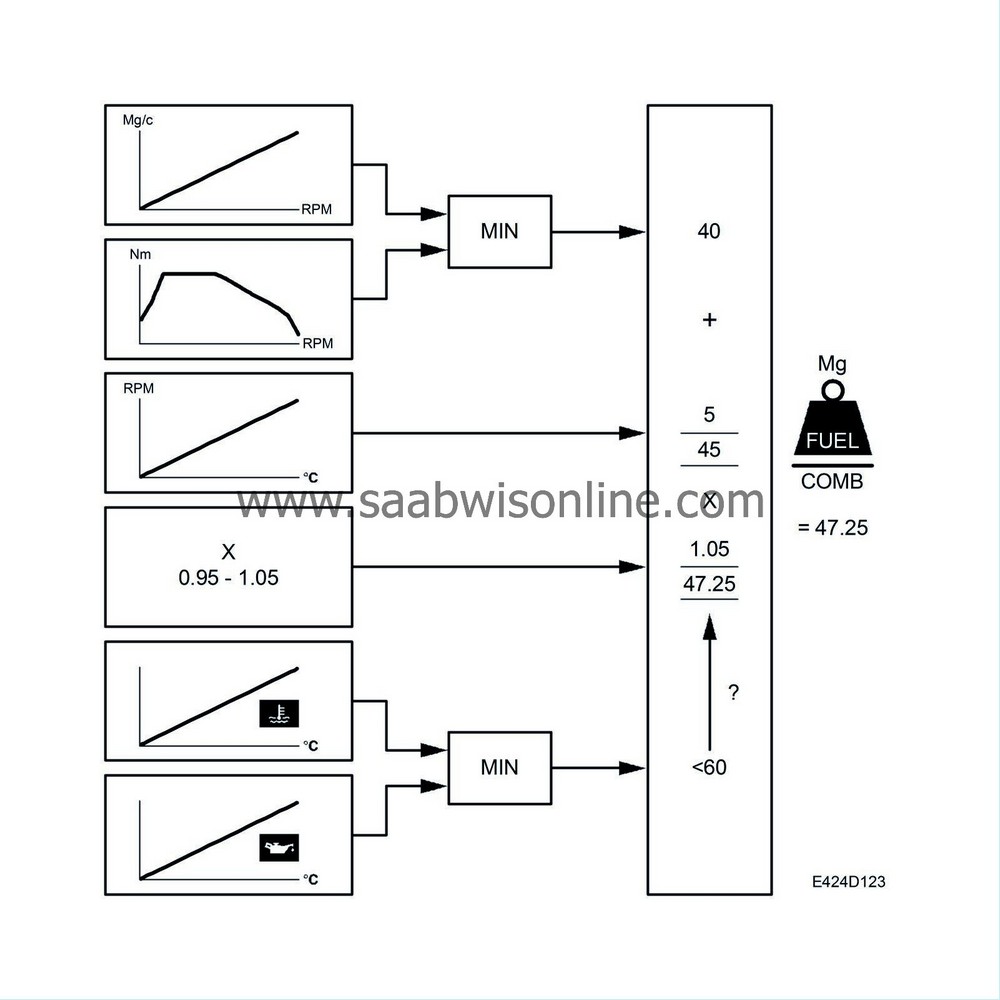
The results of the calculations in the smoke limitation and torque limitation sub-functions are compared and the function that gives the lowest injection quantity is the value that is carried forward.
Example: The result of smoke limitation is 40 mg/combustion and the result of the torque limitation is 60 mg/combustion. This means that the value from the smoke limitation (40 mg/combustion) is carried forward. |
|
| 2. |
The result of the temperature compensation is added to the result of the calculation above.
Example: 40 mg/combustion + 5 mg/combustion = 45 mg/combustion. |
|
| 4. |
However, if there is a system fault, 45 mg/combustion is compared with the limit quantity on system fault (rpm dependent, max. 30 mg/combustion), and the lowest value is carried forward as the limit quantity.
|
|
Smoke limitation
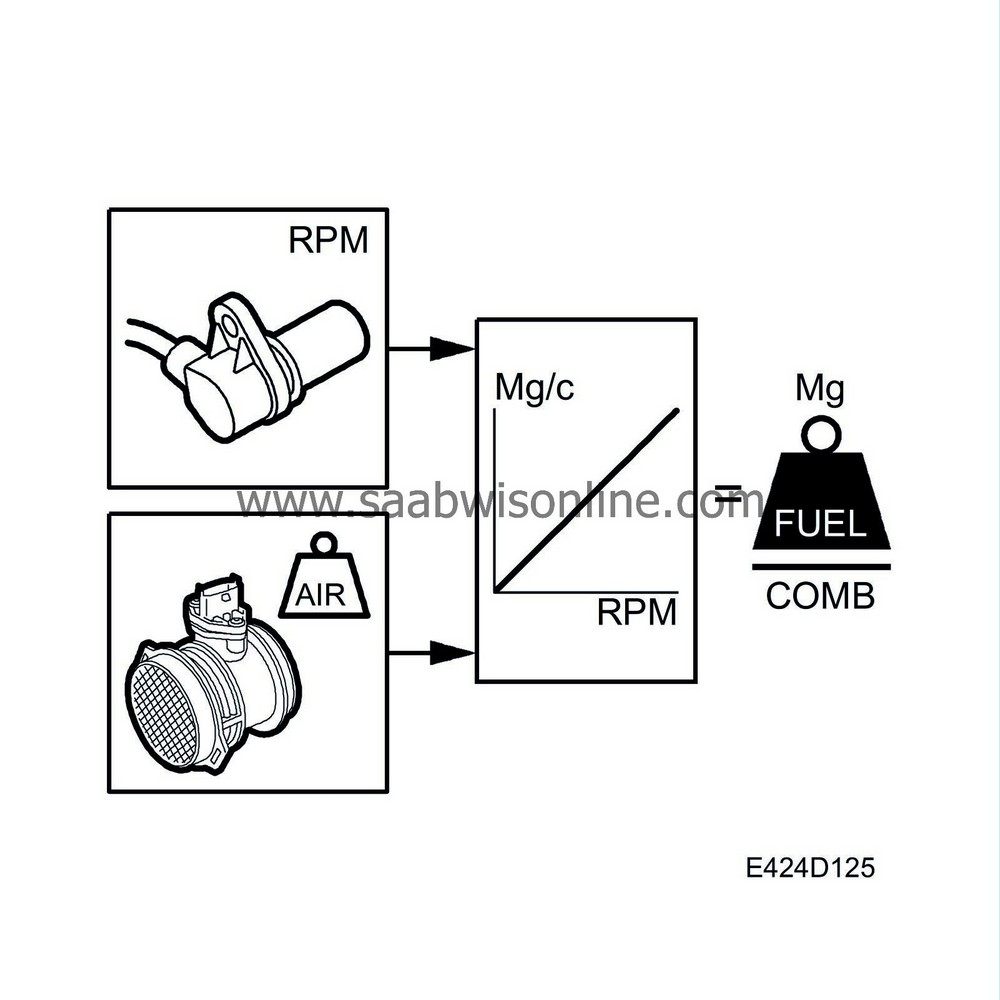
There is a smoke limitation function to prevent the formation of large amounts of smoke.Smoke limitation is calculated from the engine speed, absolute pressure and the intake air mass in mg/combustion. The function is tested so that the fuel quantity in mg/combustion always has sufficient air mass/combustion to prevent smoke formation.
If this is not the case, smoke limitation is activated and the fuel quantity is reduced to a level at which the available air mass is sufficient to burn the fuel without the formation of large amounts of smoke. This takes place when driving at high altitudes for example, as the proportion of oxygen in the air decreases at higher altitudes.
Torque limitation
To adapt the torque of the engine a torque limitation quantity based on the engine speed is obtained. This value is proportional to the value from the throttle potentiometers.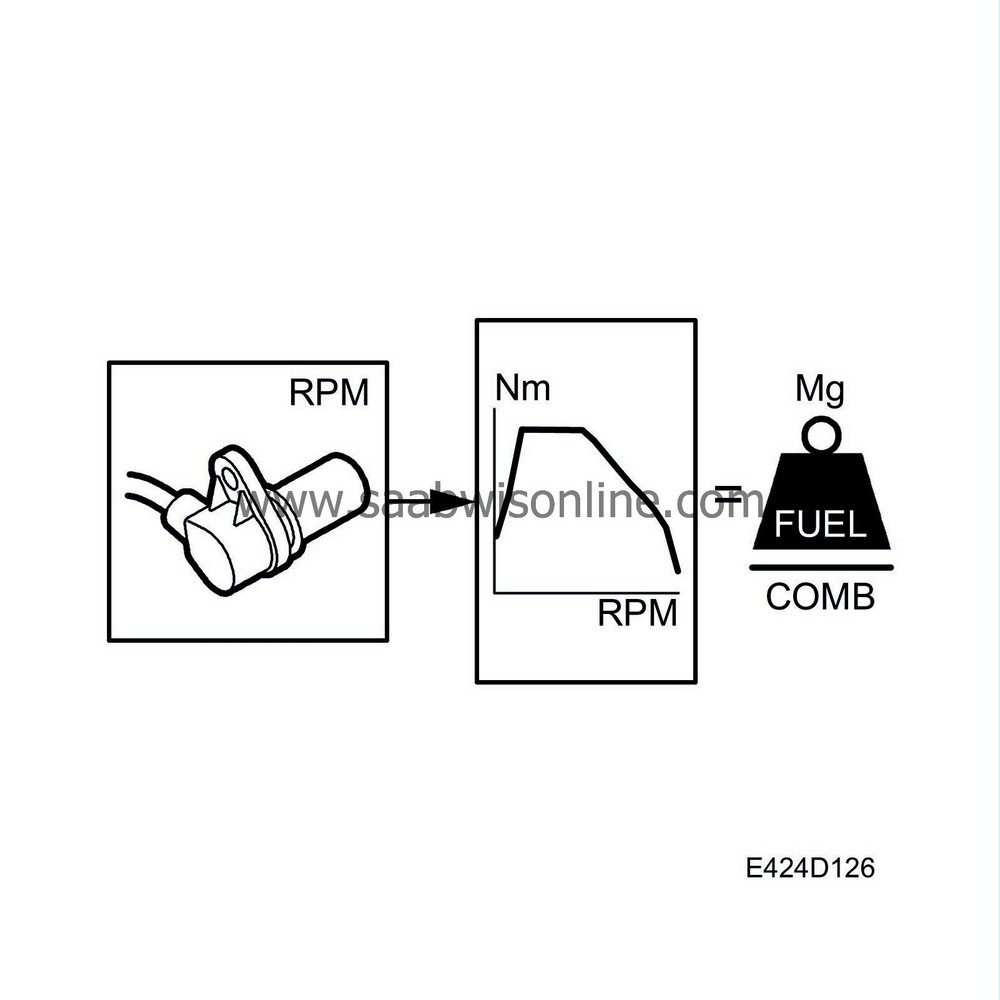
Temperature compensation
Enrichment is required when the engine is cold to ensure good driveability.On the other hand, if the engine is about to overheat, this function is activated to reduce the fuel quantity.
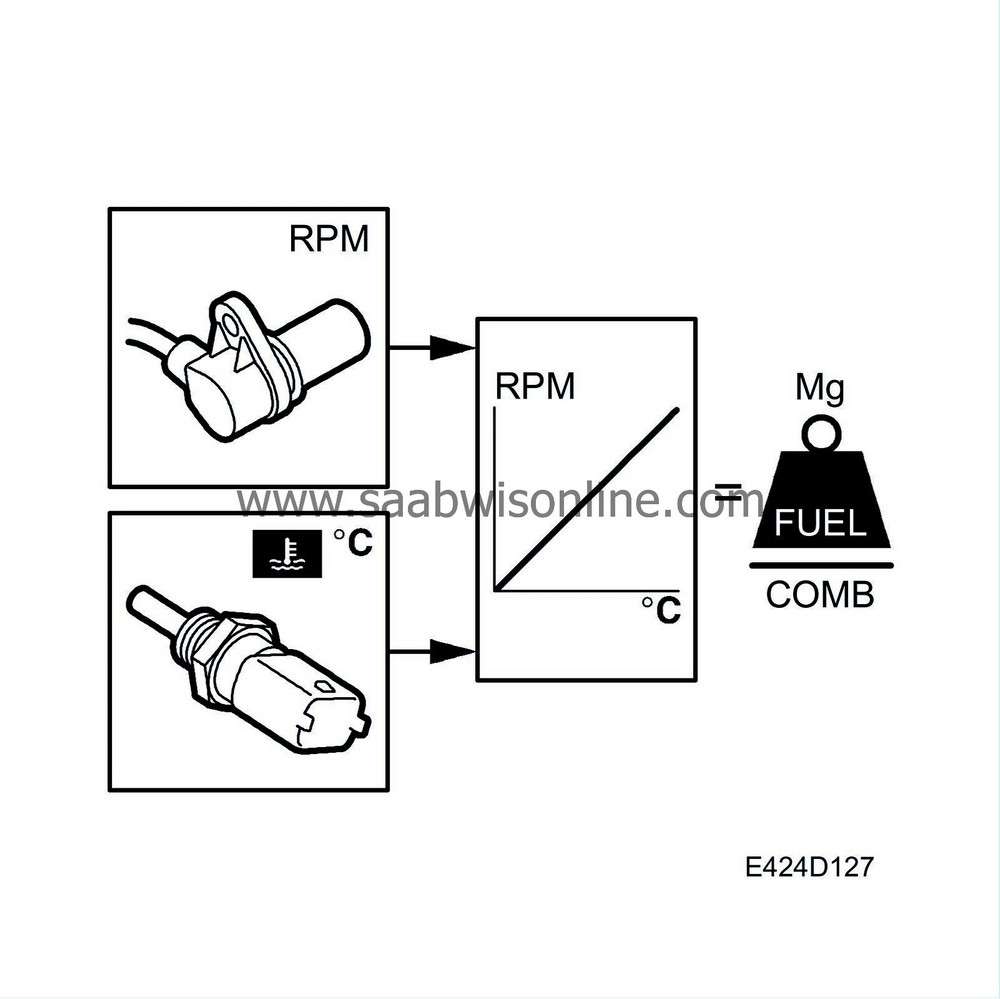
Information used to control this functions comes from:
| • |
Oil temperature sensor
|
|
| • |
Coolant temperature sensor
|
|
| • |
Fuel temperature sensor
|
|
Quantity compensation
Due to variations in the diesel fuel, its density may vary. This means that at lower densities, the car will have less power than expected or, if the diesel fuel has a high density, the car will tend to issue more smoke from the exhaust. To compensate for this, there is a quantity compensation function.The limits are quantity compensated by multiplying them by a value between 0.95 and 1.05 mg/combustion.
Quantity compensation can be adjusted 5% using the diagnostic tool.

Overheating protection
If the engine coolant temperature or engine oil temperature becomes too high, the overheating protection is activated and the permitted fuel quantity is reduced.The overheating protection function reduces the fuel quantity depending on the engine coolant temperature and the vehicle speed, the fuel temperature, or engine oil temperature and the vehicle speed. The limit that results in the smallest injection quantity is the value that is applied.
The reduction is considerable and is clearly noticeable while driving. This occurs so that the engine temperature can be stabilized so that the engine is not damaged. The A/C is switched off.
If overheating protection has been activated, a diagnostic trouble code is generated that can be read on the diagnostic tool. The diagnostic trouble code is cleared after 60 starts with a fault-free system, or with the diagnostic tool.

Requested quantity from accelerator position sensor
The requested torque is sent from the pedal position sensor to the PSG 16 engine control module. The control module adjusts the fuel quantity/combustion so that this agrees with the requested torque.The value from the pedal position sensor is filtered during acceleration and deceleration.

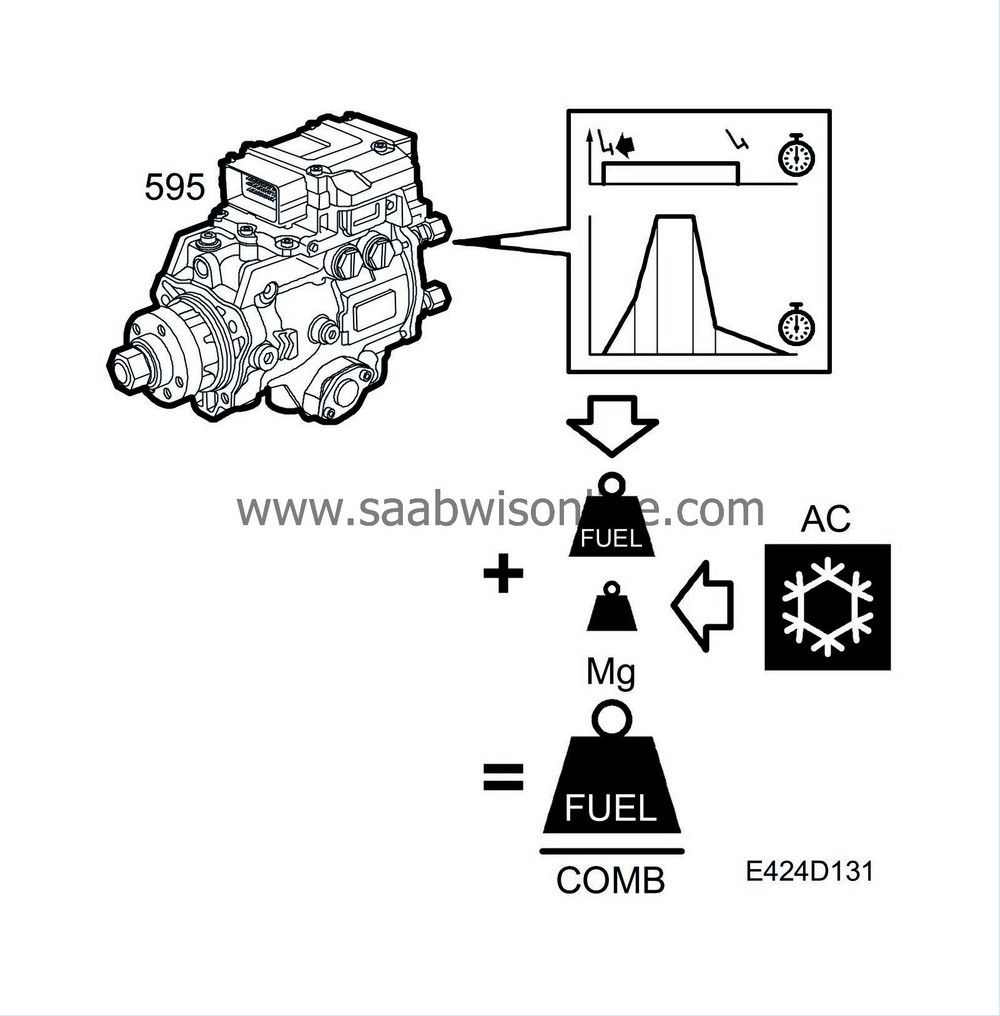
Compensation for A/C compressor operation
This function is activated when the A/C compressor starts, compensating for the extra torque that the A/C compressor takes from the engine with an extra fuel quantity/combustion.The compensatory quantity from the "compensation A/C compressor operation" function is added to the value "requested quantity from pedal position sensor". The compensatory fuel quantity depends on the pressure in the A/C system and is approx. 2-3 mg/combustion.
PSG 16 reads the A/C pressure on the bus.