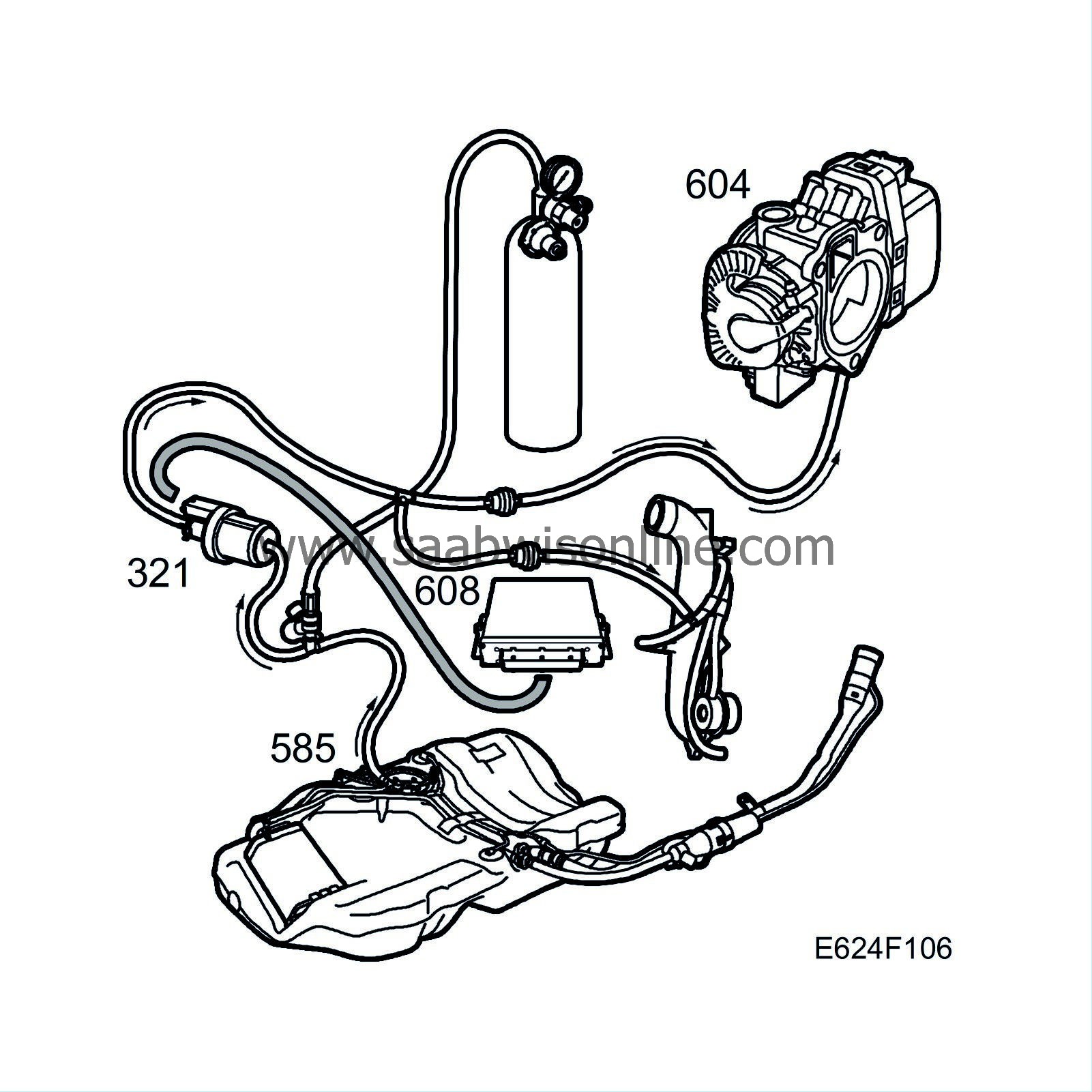
P0456
Read the instructions below then start the fault diagnostic procedure.
Symptom: CHECK ENGINE. Possible smell of petrol.
| P0456 |
Fault symptoms
| • |
CHECK ENGINE.
|
|
| • |
Possible smell of petrol.
|
|
On-Board Diagnostics
Type of diagnosis:| - |
Once per driving cycle. Interrupted when fault criteria fulfilled or OK reported. Restarts next driving cycle.
|
|
Test 1, Stationary idling speed
Enable criteria:
| - |
Run the engine at idling speed. Max one status change for brake light switch. Venting adaptation higher than 7%. Intake air pressure is at least 20 kPa lower than ambient pressure. The fuel volume in the tank is between 11 - 60 litres. The battery voltage is between 10 - 16 Volts. Tank pressure between -300 to +100Pa.
When the above criteria have been fulfilled for a duration of 100 ms, the diagnosis can be started. If the diagnosis is interrupted, the speed must be in excess of 45 km/h for 30 s before it can be re-started. The diagnosis is divided into three phases, A-C: Phase A) Evaporation control Shut-off valve is activated (closes) and any venting is interrupted for 8 s. Monitor the tank pressure. A drop in pressure can indicate a leaking evap canister purge valve. A rise in pressure of more than 7 Pa/s may indicate fuel evaporation and the test should be stopped. If the rise in pressure is less than 7 Pa/s, phase A is completed and the diagnosis continues towards a pressure reduction. Phase B) Pressure reduction Shut-off valve still closed, evap canister purge valve pulse ratio is set to 23-24.5 % until the tank pressure has reached -1500 Pa. The duration of the pressure reduction may not exceed 25 seconds. Phase C) Retaining pressure Shut-off valve still closed, evap canister purge valve is closed. Monitor the tank pressure for approximately 10 seconds. |
|
Test 2, Driving
Enable criteria:
| - |
The following criteria must be fulfilled for a duration of 3 seconds before the diagnosis can be started: Speed between 70-130 km/h. Venting adaptation higher than -6%. Tank pressure is between -300 to +100 Pa. Intake air pressure is at least 20 kPa lower than ambient pressure. The fuel volume in the tank is between 11-60 litres. The battery voltage is between 10-16 Volts. The tank pressure gauge diagnostic should not have reported an incorrect value.
When the above criteria have been fulfilled for a duration of more than 3 seconds, the diagnosis can be started. The diagnosis should be stopped if the venting adaptation exceeds 6 %. If the diagnosis is interrupted, the speed must exceed 50 km/h for 1 minute before the diagnosis can be re-started. The diagnosis is divided into three phases, A-C. Phase A) Evaporation control Shut-off valve is activated (closes) and any venting is interrupted for 10s. Monitor the tank pressure and stop the diagnosis if the pressure drops. A rise in pressure of more than 5 Pa/s may indicate fuel evaporation and the test should be stopped. If the rise in pressure is less than 5 Pa/s, phase A is completed and the diagnosis continues to phase B (pressure drop). Phase B) Pressure reduction Shut-off valve still closed, evap canister purge valve pulse ratio is set to 40 % until the tank pressure has reached -2000 Pa. The duration of the pressure reduction may not exceed 23 seconds. Phase C) Retaining pressure Shut-off valve is still closed and the evap canister purge valve closes. Monitor the tank pressure for approximately 14 seconds. |
|
Fault criteria:
| - |
Phase A) If evaporation control
shows that the pressure rises by more than 5 Pa/s, the diagnosis should be stopped due to substantial fuel evaporation. In order to re-start the diagnosis, the car must be moving. If the increase in pressure is under 5 Pa/s, the diagnosis continues to phase B.
|
|
| - |
Phase B) Pressure reduction
If it is not possible to reduce the pressure in three 8-second stages of approximately -500 Pa each, a large leak has been discovered. (24 s total)
|
|
| - |
Phase C) Retaining pressure
An increase in pressure indicates a small or large leak.
|
|
Fault code generation
| - |
Diagnostic trouble codes are generated when the above fault criteria are fulfilled and the dependents are OK.
P0455, P1455 are set if faults are reported during Phase B P0442, P0456, P1442 or P1456 are set if faults are reported during Phase C. |
|
Dependents:
| - |
P0444, P0445, P0501, P0502, P0506, P0507, P1444, P1445, P1576 and P1577.
|
|
OK report:
| - |
Test 1
or
Test 2 performed once and fault criteria not fulfilled.
|
|||||||
Fault handling:
| - |
Type III.
|
|
Diagnostic help
Fault diagnosis concerns a leak.Functions in the diagnostic tool related to the fault:
| • |
Diagnostic status for the diagnosis.
|
|
| • |
Activate EVAP diagnosis.
|
|
For more information, see Fault tracing strategy for electronic systems