Rear-wheel sensors
| Rear-wheel sensors |
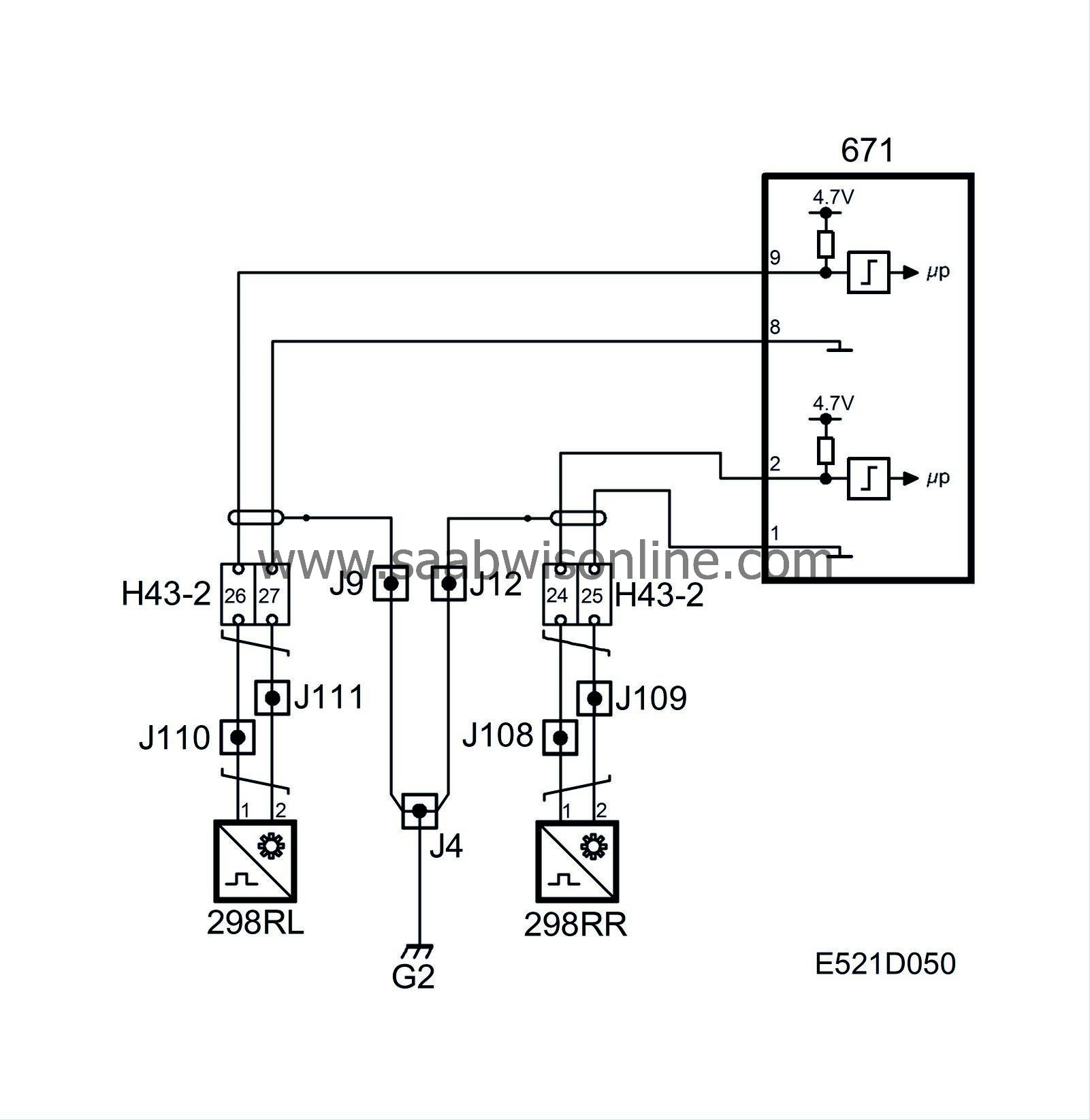
The rear left wheel sensor sends a wheel-speed signal to pin 9 on the control module. The sensor is grounded via pin 8.
The rear right wheel sensor sends a wheel-speed signal to pin 2 on the control module. The sensor is grounded via pin 1.
The wheel sensors are integrated into the wheel hubs and consist of an inductive sensor with 29 teeth.
The inductive sensor works like a small alternator, the sine-wave voltage of which increases with increasing wheel speed. The sine-wave voltage alternates between positive and negative polarity, which is achieved by alternate teeth and gaps on the toothed wheel. By measuring the frequency, the control module can determine the speed of each wheel.
A wheel speed of 20 km/h (12.5 mph) will give approximately 0.8 V AC 70 Hz
The design of the rear-wheel sensor is different to that of the front-wheel sensors and the sensor is less sensitive to play in the wheel bearings.
The ESP control module uses information on wheel speed to calculate the speed of the wheels in relation to each other. If the difference exceeds the limits, the control module will compensate for this by requesting braking and/or a change in engine torque.
Diagnostics
DTC C1382 will be generated for a short/open circuit for the rear left sensor. ESP, TCS and ABS functions will be disabled and ESP OFF and the ABS, foot brake and central warning lamps will come on.DTC C1381 will be generated for a mechanical or operational fault in the rear left sensor. ESP, TCS and ABS functions will be disabled and ESP OFF and the ABS, foot brake and central warning lamps will come on.
DTC C1387 will be generated for a short/open circuit for the rear right sensor. ESP, TCS and ABS functions will be disabled and ESP OFF and the ABS, foot brake and central warning lamps will come on.
DTC C1386 will be generated for a mechanical or operational fault in the rear right sensor. ESP, TCS and ABS functions will be disabled and ESP OFF and the ABS, foot brake and central warning lamps will come on.



