Measuring piston height
| Measuring piston height |
| Choice of cylinder head gasket |
| • |
The thickness of the cylinder head gasket depends on how far the piston protrudes above the sealing surface of the cylinder block.
|
|
| • |
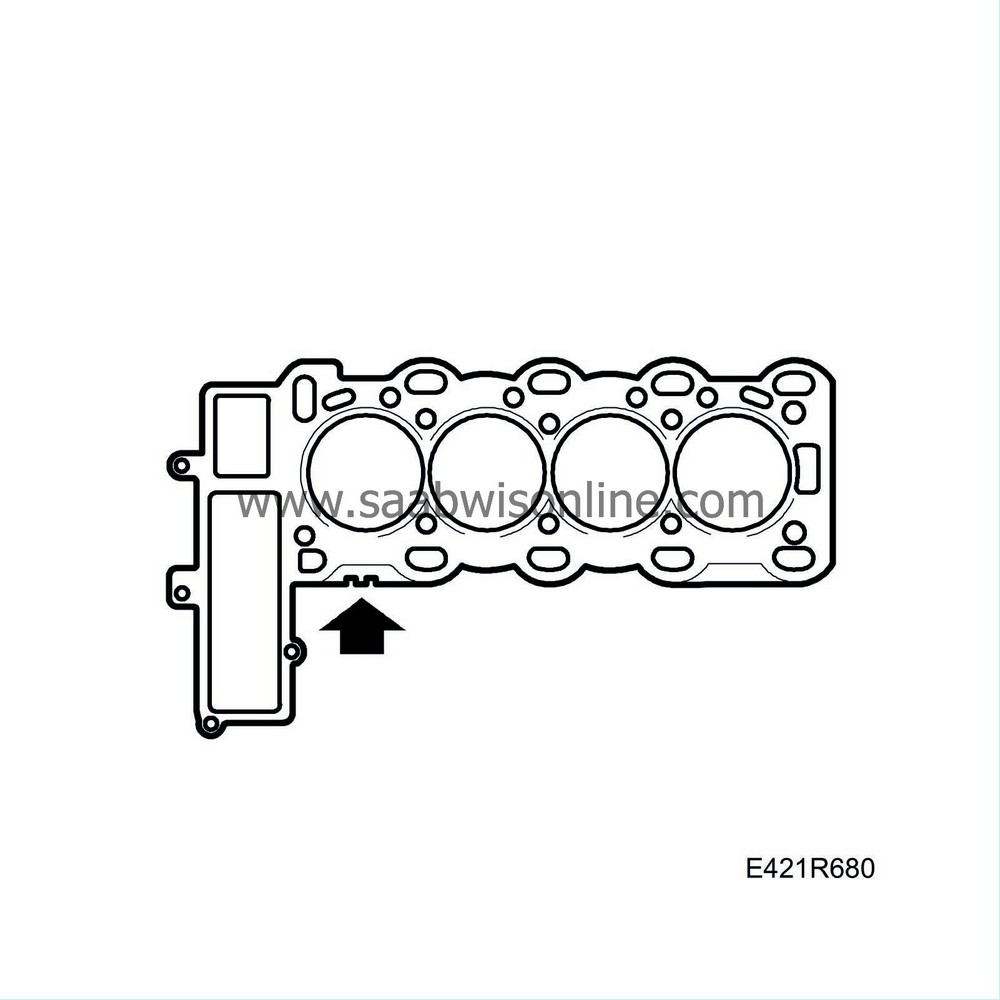
There are three gasket thicknesses available. Refer to the table in
Engine block
|
|
| • |
Before taking measurements, the surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned from soot residue, etc.
|
|
| • |
The height of each piston must be measured in two different places.
|
|
| • |
Make sure each piston is at top dead centre before being measured as follows:
|
|
| 1. |
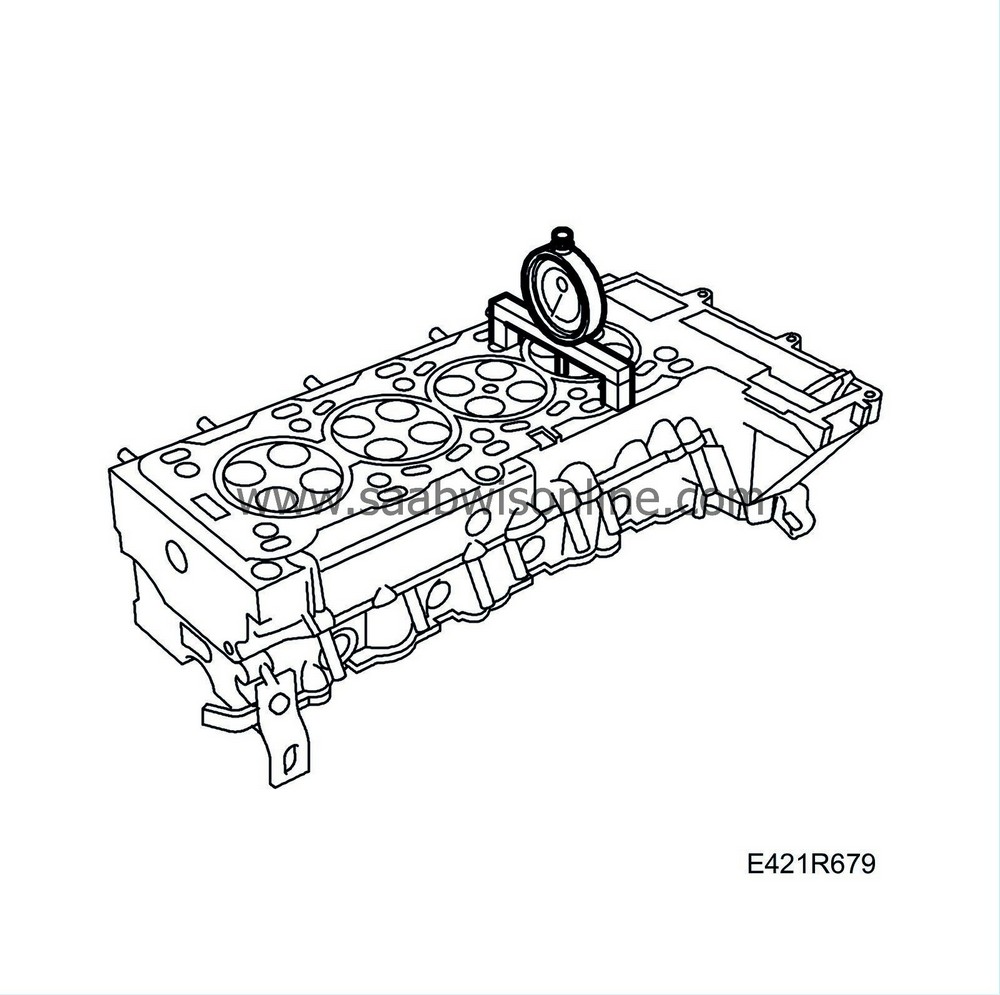
Fit a
78 40 622 Dial indicator
in a
Measuring jig
.
|
|
| 2. |
Place the measuring jig on the cylinder block sealing surface so that the point of the dial indicator makes contact with the block.
|
|
| 3. |
Zero the dial indicator.
|
|
| 4. |
Place the measuring jig over one of the piston measuring points, see illustration.
|
|
| 5. |
Turn the crankshaft in the direction of rotation while reading the dial gauge. Note the highest value shown on the dial before the pointer starts to go back.
|
|
| 6. |
Repeat the previous step on the other piston measuring points.
|
|
| 7. |
Calculate the average value for each piston.
|
|
| 8. |
Note the maximum value for each of the three pistons in each cylinder bank.
|
|
| 9. |
Select a gasket thickness from the table, see
Engine block
depending on the obtained maximum value.
|
|


