EGR valve, exhaust gas recirculation
| EGR valve, exhaust gas recirculation |
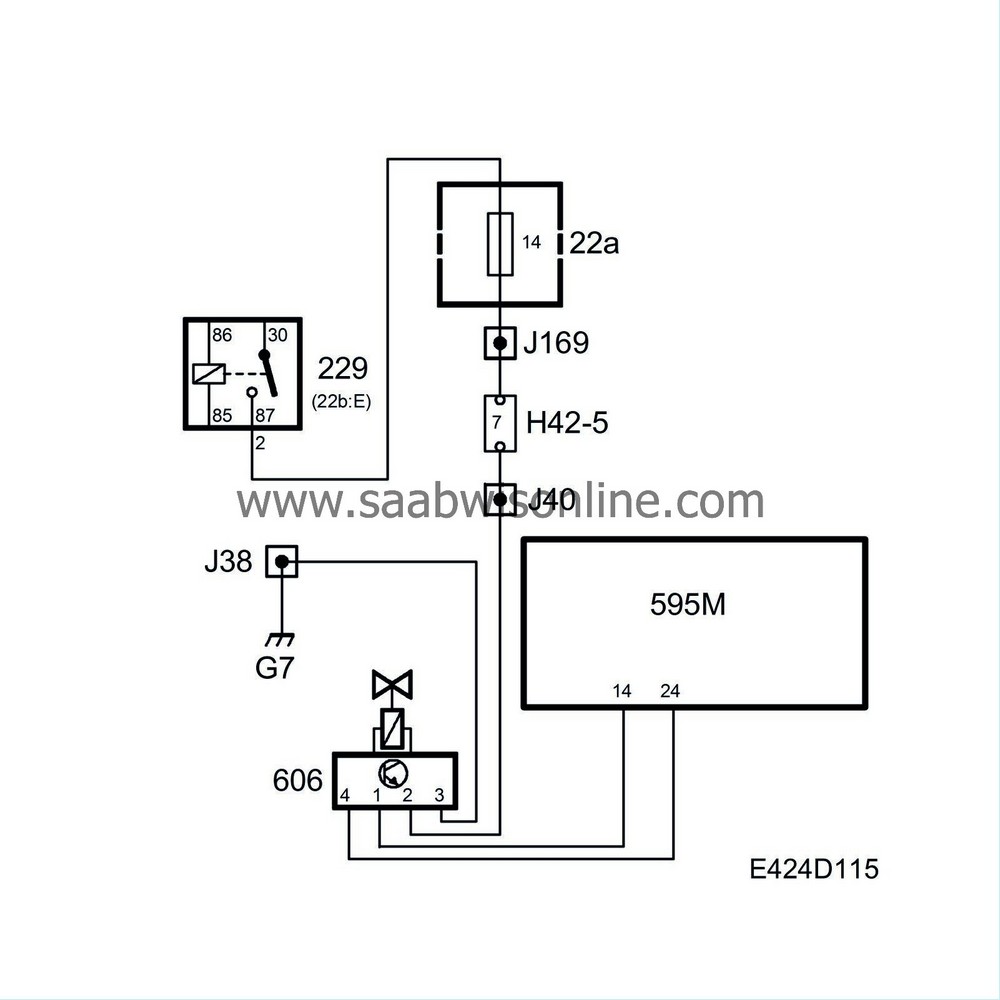
The engine is equipped with a water-cooled, electronically-controlled EGR valve, which leads some of the engine's exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. The exhaust gases reduce the temperature of combustion, which reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides. The EGR valve has its own processor which keeps constant track of how far open the valve is. This means that when the PSG 16 signals how much to open or close the valve, the reaction time is very short. Valve opening also changes quickly in order to keep combustion temperature as low as possible.
| • |
If an DTC related to the EGR valve is generated, engine torque is reduced and the CHECK ENGINE lamp comes on.
|
|
| • |
The EGR function is deactivated after 1 minute of idling to reduce the build-up of carbon deposits.
|
|
| • |
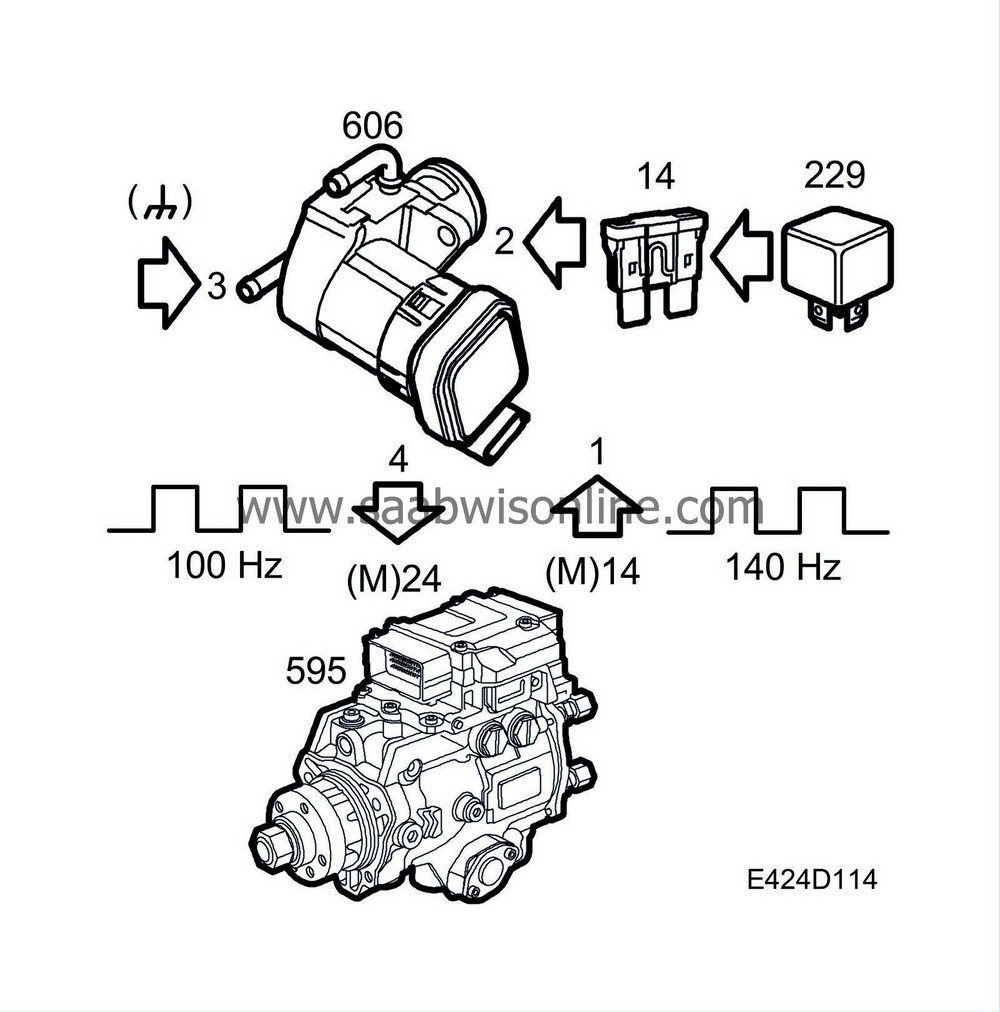
Pin 1 of the EGR valve receives a 140 Hz PWM signal.
|
|
| • |
Pin 2 of the of the EGR valve is fed with B+ via fuse 27.
|
|
| • |
Pin 3 of the of the EGR valve is grounded to G7P.
|
|
| • |
The EGR valve diagnostic lead (PWM 100 Hz from EGR) connects pin 4 on the EGR valve to pin M24 on the engine control module.
|
|
| EGR system functions |
The EGR function comprises three sub-functions:
| • |
Desired value calculation
|
|
| • |
Air mass calculation
|
|
| • |
EGR control and monitoring
|
|
| Desired value calculation |
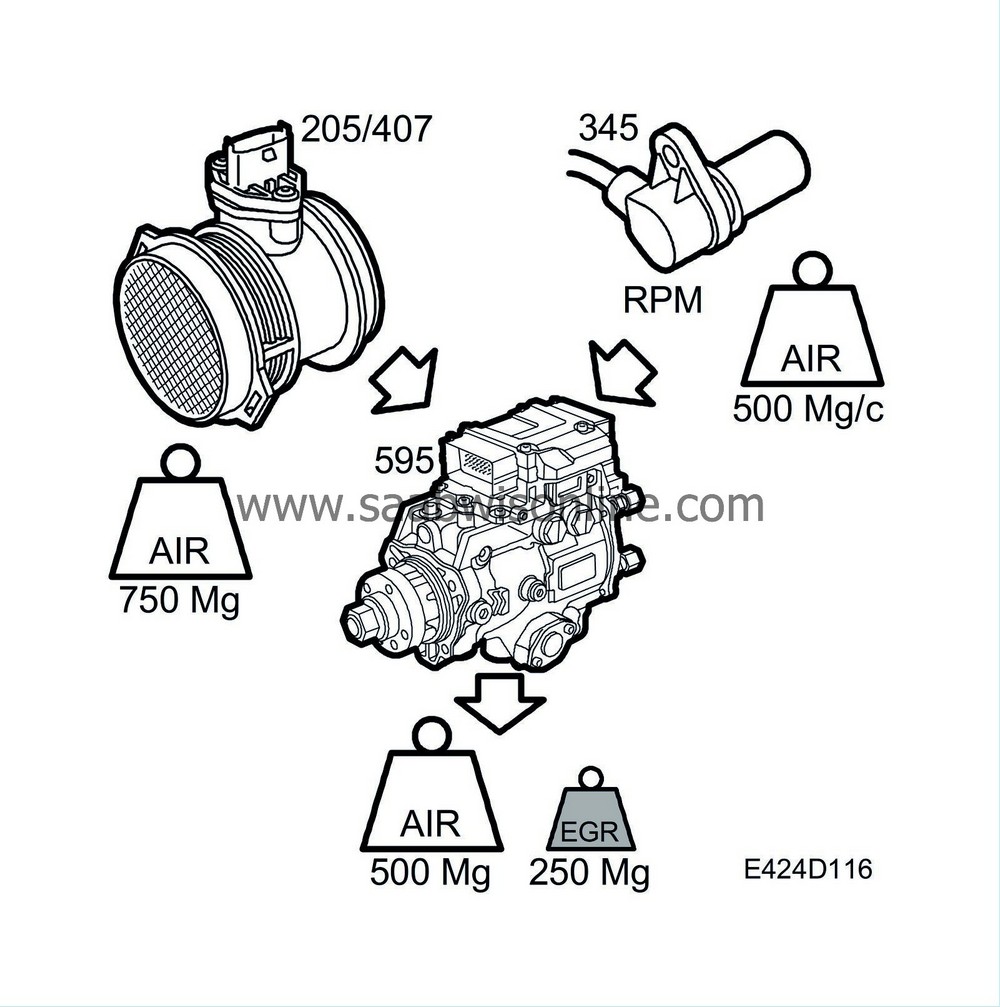
The calculation of the desired value determines the air mass/combustion required by the engine. The EGR control valve is controlled so that the desired quantity of air is obtained. This is achieved by allowing the quantity of recirculated exhaust gas into the intake that is required to reduce the intake air mass/combustion to the value calculated by the desired value function.
Example:
At a certain moment, the engine can pump through 750 mg air/combustion.
The desired value calculation says that it should be 500 mg air/combustion for these particular operating conditions. The control function will then open the EGR valve to allow just enough exhaust gas to enter to prevent 250 mg air/combustion from entering the engine.
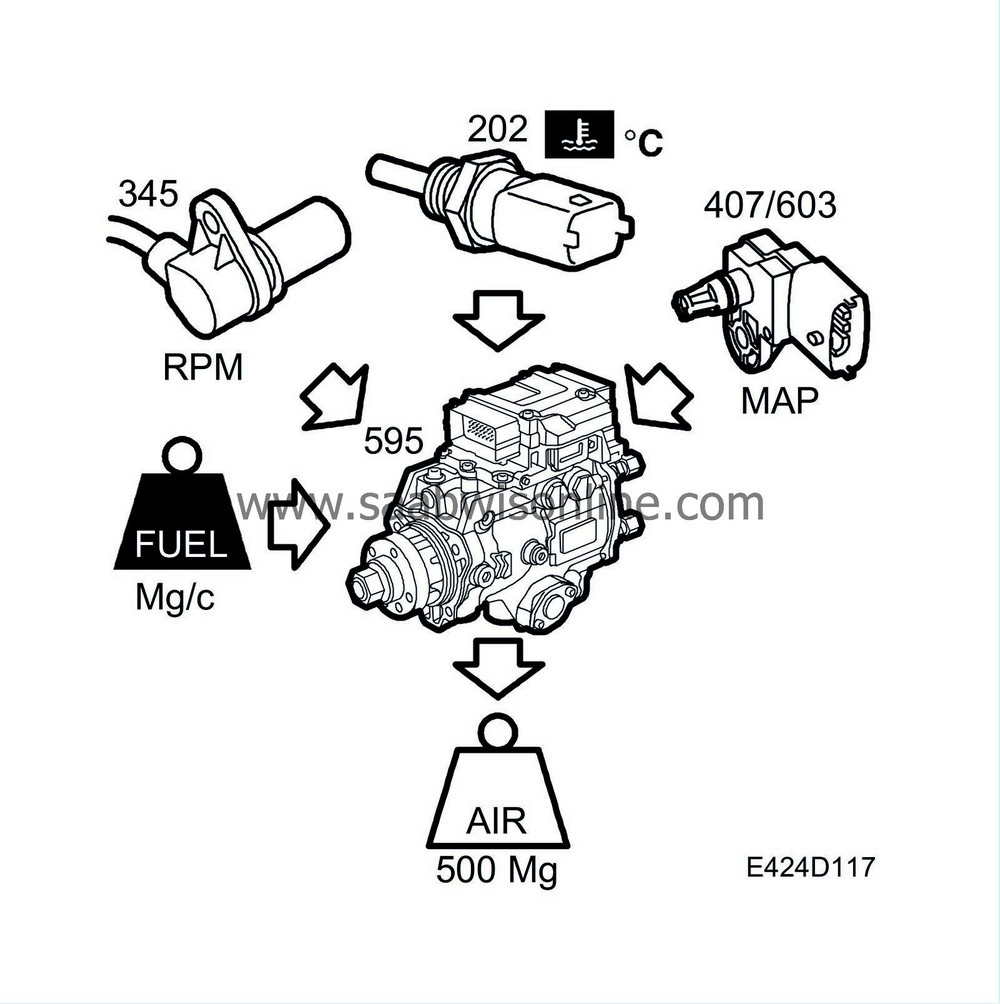
The desired value calculation determines the desired air mass/combustion and makes it available for the other EGR functions. The desired value is a function of:
| • |
Engine RPM
|
|
| • |
Injected fuel quantity
|
|
| • |
Coolant Temperature
|
|
| • |
Atmospheric pressure
|
|
The result of the desired value calculation is carried forward to EGR control.
| Air mass calculation |
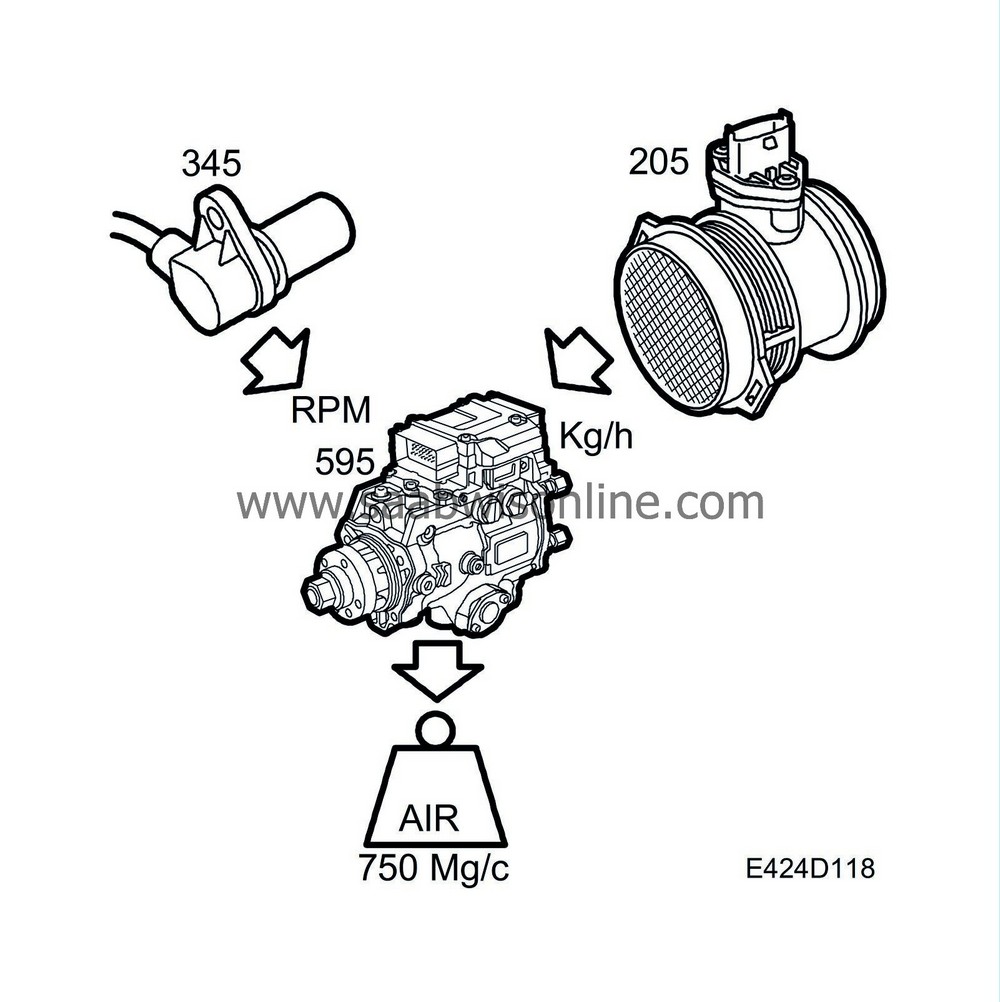
The current air mass available for combustion is calculated using the variables engine speed, intake air mass from the mass air flow sensor and air temperature in the mass air flow sensor.
The signal from the mass air flow sensor is filtered and the reading converted from kg/h to mg/combustion.
When the air mass has been converted to mg/combustion, a plausibility check is performed by comparing the engine speed with the intake air mass. Information on the intake air mass/combustion is made available to the fuel quantity calculation.
| EGR control |
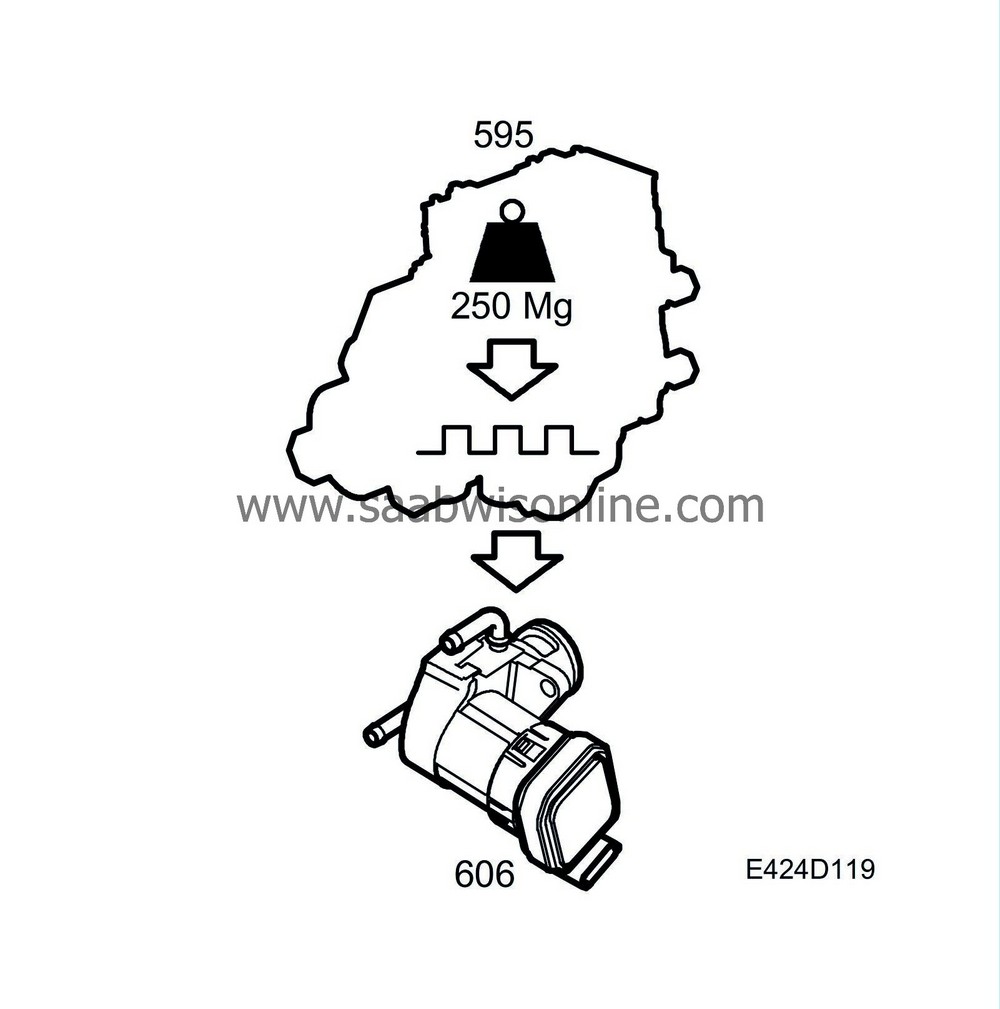
The EGR valve has it own processor which keeps track of how far open the valve is. Thus, when a 140 Hz signal arrives, the reaction time is very short. An internal processor also means that the valve is self-diagnosing. The valve sends signals back to the engine control module on the same lead as it receives orders. The signal from the valve is a 100 Hz PWM signal. When the EGR valve cannot fulfil what is requested it informs PSG 16. EGR control is deactivated after 1 minute of idling to reduce the build-up smoke in the exhaust gases. When the value on Tech 2 is 95%, the EGR valve is fully closed.
System reaction to a fault
| • |
A DTC is generated and PSG 16 will limit engine torque.
|
|
| • |
Reduction of power output due to a reduction in torque.
|
|
| • |
The regulatory functions for EGR, swirl throttle and charge air are switched off.
|
|
| Diagnostics |
P0400 is generated if the control deviation is more than 20% from the requested EGR position for 3 seconds.
P0401 is generated if the flow of exhaust gas through the EGR valve is so low that a control deviation of more than 75 mg air/combustion has been present for more than 7.5 seconds.
P0402 is generated if the flow of exhaust gas through the EGR valve is so high that a control deviation of more than 75 mg air/combustion has been present for more than 7.5 seconds.
P0403 is generated if the EGR circuit is shorted to ground for more than 0.6 second.
P0404 is generated if the EGR circuit is shorted to B+ for more than 0.6 second.
P0405 is generated if there is an electrical fault on the circuit between pin 24 on the control module and pin 4 on the EGR valve, that is a short circuit to ground or open circuit and the feedback signal from the EGR is less than 5% PWM for more than 0.6 seconds.
P0406 is generated if there is a short to B+ (constant high) on the circuit between pin M24 on the control module and pin 4 on the EGR valve
P0409 is generated if the feedback signal is faulty.
P1400 is generated if there is an internal fault in the EGR valve.
P1404 is generated if there is a break in the EGR circuit for more than 0.6 seconds.