Poor driveability, reduced performance, uneven idling speed.
Symptom: Poor driveability.
Reduced performance
Engine has uneven/low idling speed.
Surge or hesitation upon acceleration
|
|
Poor driveability, reduced performance, uneven idling speed.
|
Fault symptom
Poor driveability.
Reduced performance
Engine has uneven/low idling speed.
Surge or hesitation upon acceleration
Conditions
The car may have certain fault symptoms without a diagnostic trouble code being generated. This can be due to an air leak in the intake system.
If diagnostic trouble codes arise then each fault diagnosis must be used at first. If the fault cannot be located via normal fault diagnosis then the following method is supplementary.
Diagnostic procedure
|
1.
|
Remove the upper engine cover.

|
|
2.
|
Detach the crankcase ventilation hose clamp at the rear section of the camshaft cover using 30 07 739 Hose pinch-off pliers and block the hose with a suitable plug, Ø 25mm.
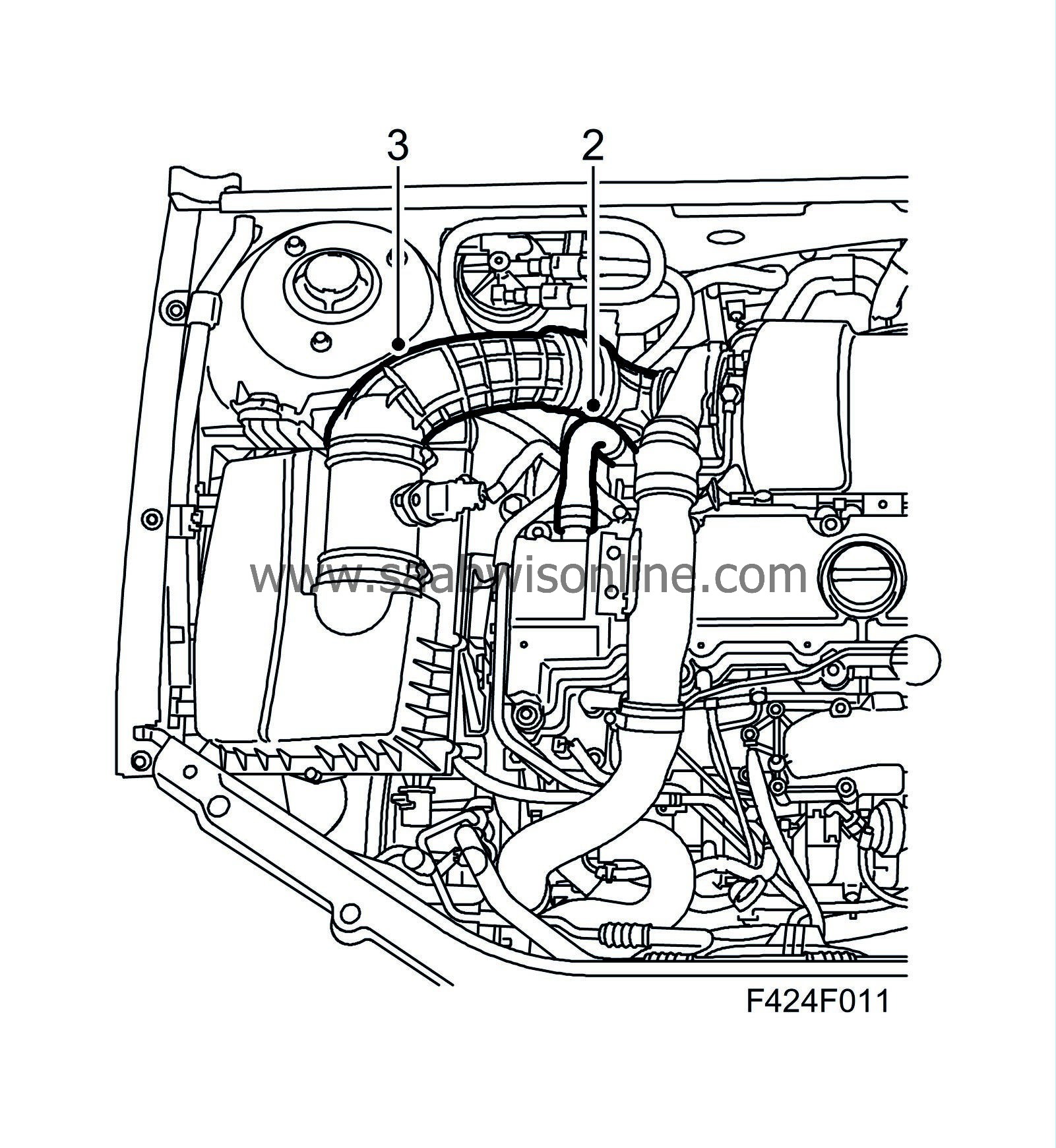
|
Important
|
|
Do
not
plug the hole in the camshaft cover. The air that leaks past the pistons down in the crankshaft during test pressurising must be evacuated through this hole.
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
Undo the intake hose by the mass air flow sensor. Fit the plug from kit 83 95 659 in the hose and then connect the pressure regulator to an external compressed air outlet.
|
Important
|
|
Close the pressure regulator before connecting it to the air pressure outlet.
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Connect Tech 2, set the ignition key to the "ON" position and select "Read values" for the engine type in question. Scroll on through the list until "Charge pressure sensor" in "V" can be seen.
|
Important
|
|
When pressure increases, DTCs P0106 and P1106 will be generated due to the difference between boost pressure and atmospheric pressure. When the DTCs are generated "Boost pressure" will indicate 101 kPa, which is the default value. Boost pressure must therefore be read off directly from the voltage signal.
|
|
|
|
|
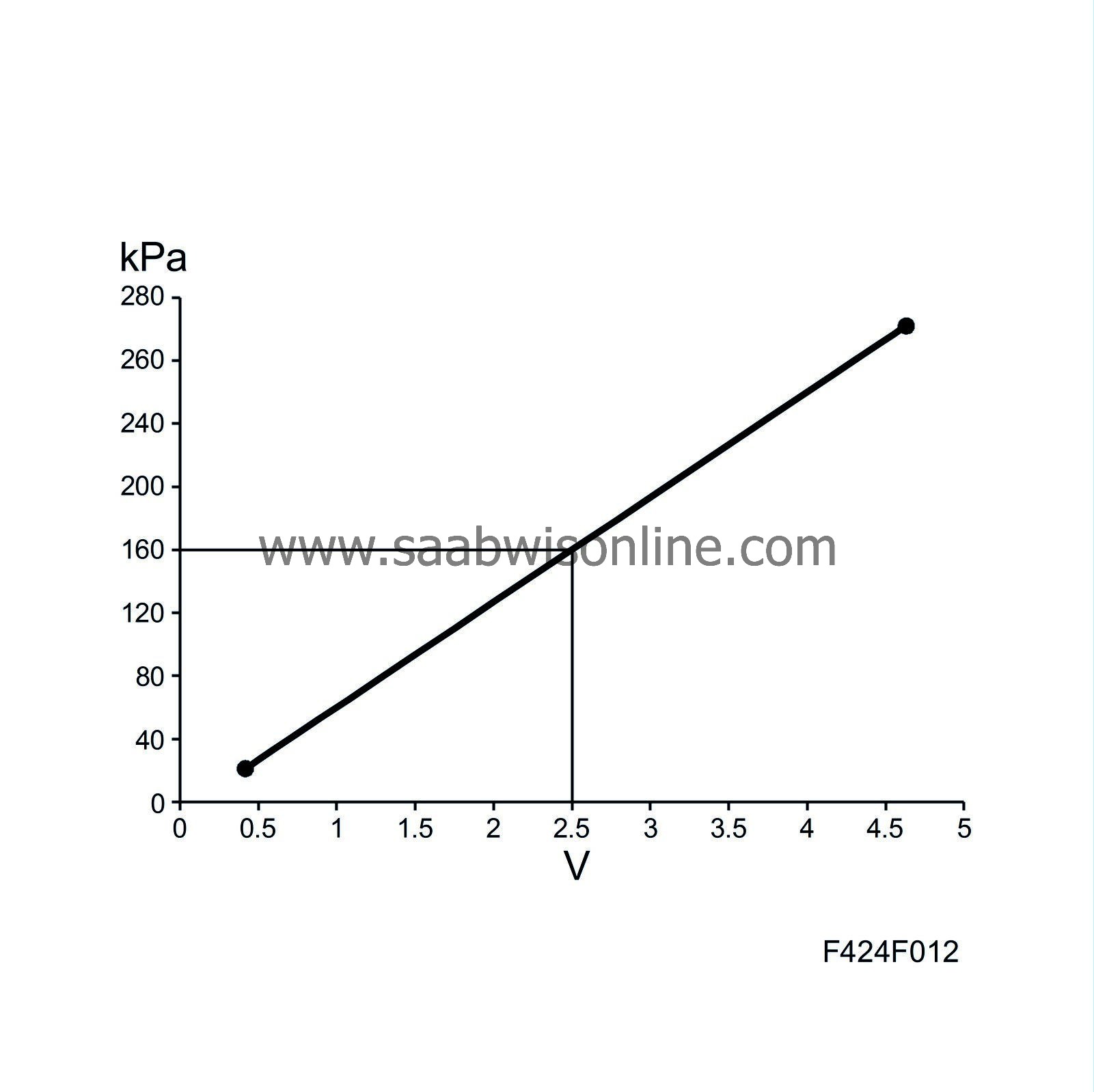
5.
|
Read off the voltage from the charge pressure sensor using Tech 2 and pressurise the intake system by carefully turning the pressure regulator until a maximum of 2.5V is reached.
1.6 V corresponds to approx. 100 kPa (atmospheric pressure)
2.5 V corresponds to approx. 160 kPa (60 kPa overpressure)
|
|
6.
|
The whole intake system is pressurised in this way and leaks can be located using leakage spray or soapy water which foams around the leak. Check all components, hoses and connections and rectify any leaks.

|
|
|
6.3.
|
Mass air flow sensor
|
|
|
6.6.
|
Three way catalytic converter
|
|
|
6.10.
|
Oil trap for crankcase ventilation (integrated in engine)
|
|
|
6.12.
|
Swirl throttle regulator
|
|
|
6.13.
|
Solenoid valve, swirl throttle
|
|
|
6.15.
|
Charge air control valve
|
|
|
6.20.
|
Motor
|
Important
|
|
Only large leaks affect the function of the engine management system. When leakage spray or soap water is used, even small leaks will be detected. Several small leaks can be grouped together and viewed as one large leak.
|
|
Individual tiny leaks need not be remedied.
|
|
|
|
|
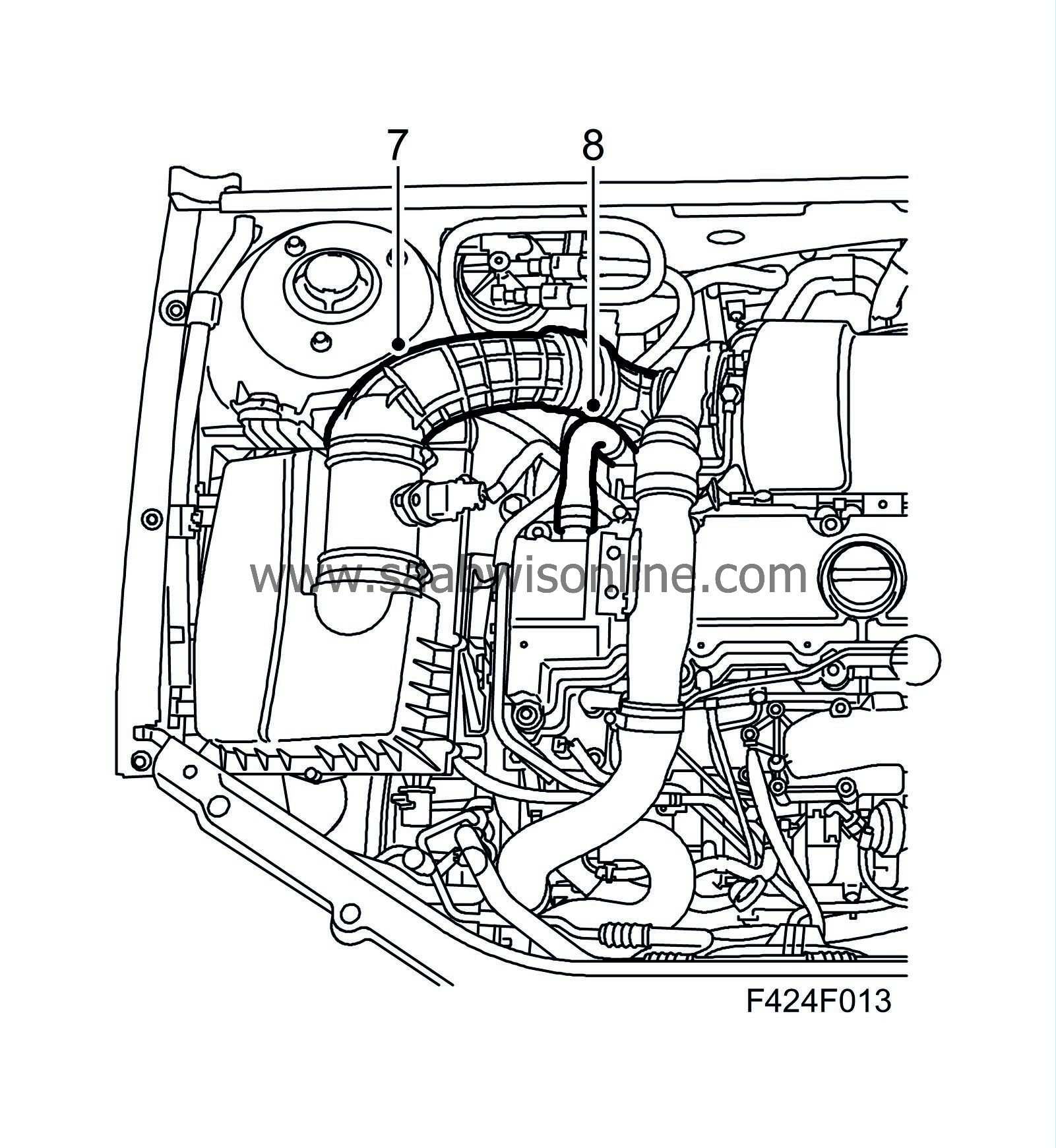
7.
|
Remove the plug from the intake hose. Connect the hose to the mass air flow sensor.
|
|
8.
|
Remove the plug from the crankcase ventilation hose. Connect the hose to the camshaft cover.
|
|
9.
|
Fit the upper engine cover.
|
|
10.
|
Read the control module software version using Tech 2. If there is a later software version in TIS2000 then this must be programmed into the control module.
|
|
11.
|
If the problems are not resolved then complete the following checklist and contact the importer's technical support. Have the checklist ready.
|
|
1.
|
Describe the fault symptom .......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
|
|
3.
|
Turn off A/C or ACC and let the engine idle. Coolant temperature should be over 80°C.
|
Note
|
|
Diagnostic trouble codes must not be erased.
|
|
|
4.
|
Read and note any diagnostic trouble codes: .......................................................................................................................
|
|
5.
|
Select "Engine" - "Engine management system" - "Read values / Activate" in Tech 2. Read and note the following values:
|
|
|
Unit
|
Turn Ignition On
|
Idle
|
Desired value
|
Engine speed
|
rpm
|
-------------
|
|
700-1000
|
Fuel mass/Combustion
|
mg/c
|
-------------
|
|
3 - 20
|
Air mass/Combustion **
|
mg/c
|
-------------
|
|
200 - 400
|
Requested air mass/Combustion **
|
mg/c
|
-------------
|
|
200 - 400
|
EGR valve PWM **
|
%
|
-------------
|
|
5 - 95
|
EGR valve feedback signal
|
%
|
-------------
|
|
85 - 95
|
Mass air flow sensor
|
V
|
|
|
0.85 - 1.15
|
Coolant temperature
|
°C
|
|
|
80-100
|
Oil temperature, engine
|
°C
|
|
|
60 - 120
|
Fuel temperature
|
°C
|
|
|
0 - 80
|
Intake air temperature
|
°C
|
|
|
20 - 60
|
Atmosphere Absolute Pressure
|
kPa
|
|
|
90-115
|
Charge Air Absolute Pressure
|
kPa
|
|
|
90 - 115
|
Additive adaptation
|
mg/c
|
|
|
max. 0.6
|
** Note: EGR is closed after approx. 40-60 seconds after idling speed has been activated. Read off the values with EGR active.
Under “system information” are details on Vehicle Identification Number and version number for PSG16
Vehicle Identification Number
(compulsory)
|
|
Software Module Identifier #1 or Software version
(compulsory)
|
|
Programming date
(compulsory)
|
|








