Engine block
| Engine block |
The total swept volume of 2.2 litres provides a high engine torque even at low engine speeds, which is an advantage when driving in normal traffic conditions.
The balancer shafts are used to absorb any vibration and other forces coming from the moving parts of the engine and reduce unwanted engine noise.
| Cylinder block |
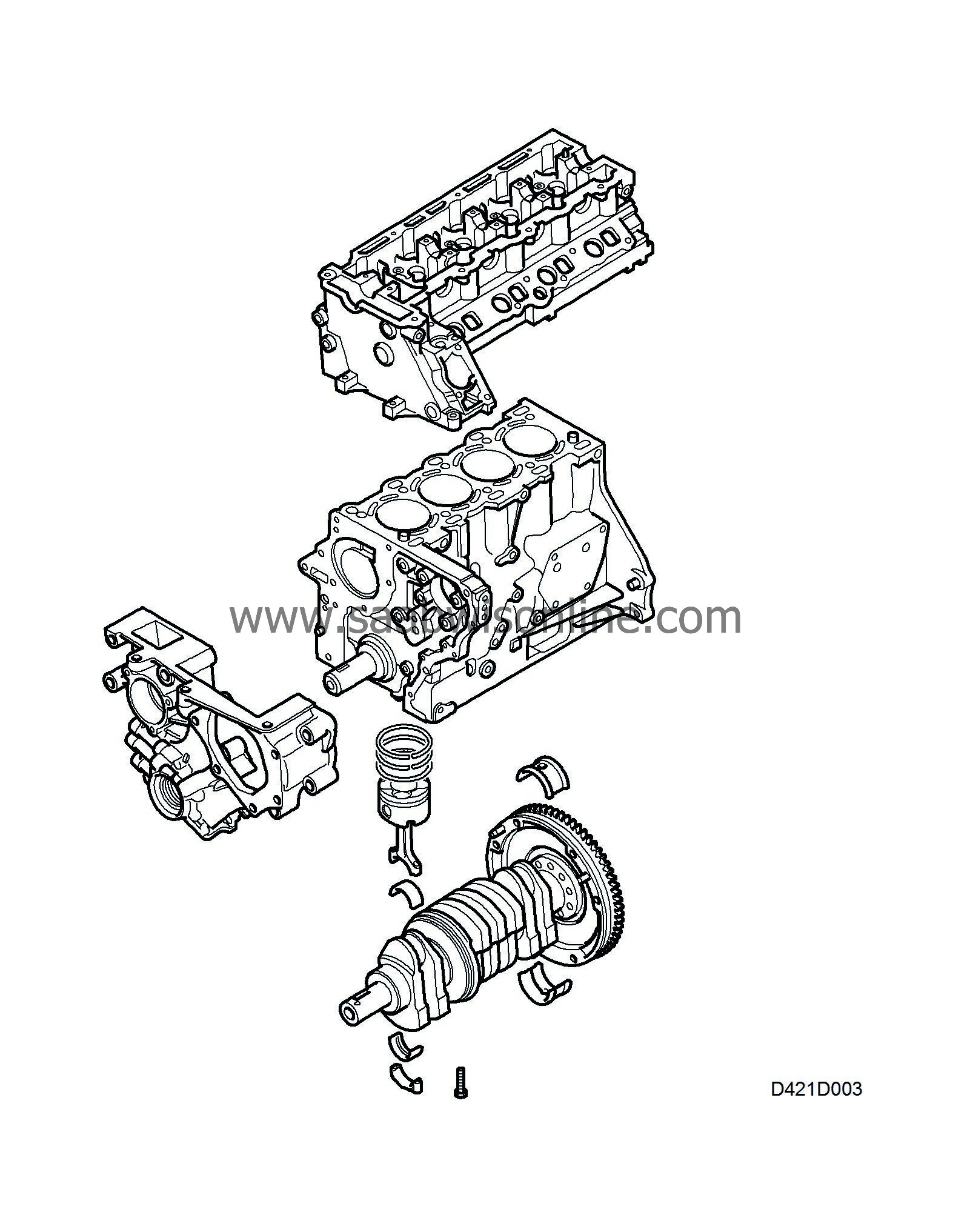
The cylinder block is a special one-piece casting with the cylinder bores drilled directly into the block. Special oilways for the lubricating system are also drilled into the block.
The balancer shafts are mounted in a separate unit under the crankshaft and are chain-driven by the crankshaft.
| Cylinder head |
The cylinder head is precision-cast in light alloy and bolted onto the cylinder block. There are 4 valves per cylinder with the injectors located centrally. The intake passages are double but the engine management system controls only one throttle, which open and closes one of the intake passages in each cylinder. This method improves the swirl formation in the cylinders and gives a more efficient fuel combustion, i.e. the engine is given a high degree of efficiency. The cylinder heads are sealed with a metal gasket, which is available in several thicknesses.
The engine has been developed for reduced emission and lower fuel consumption and has a torque of 290 Nm. It is reinforced around the cylinder head bolts and valve seats and also has stiffening ribs.
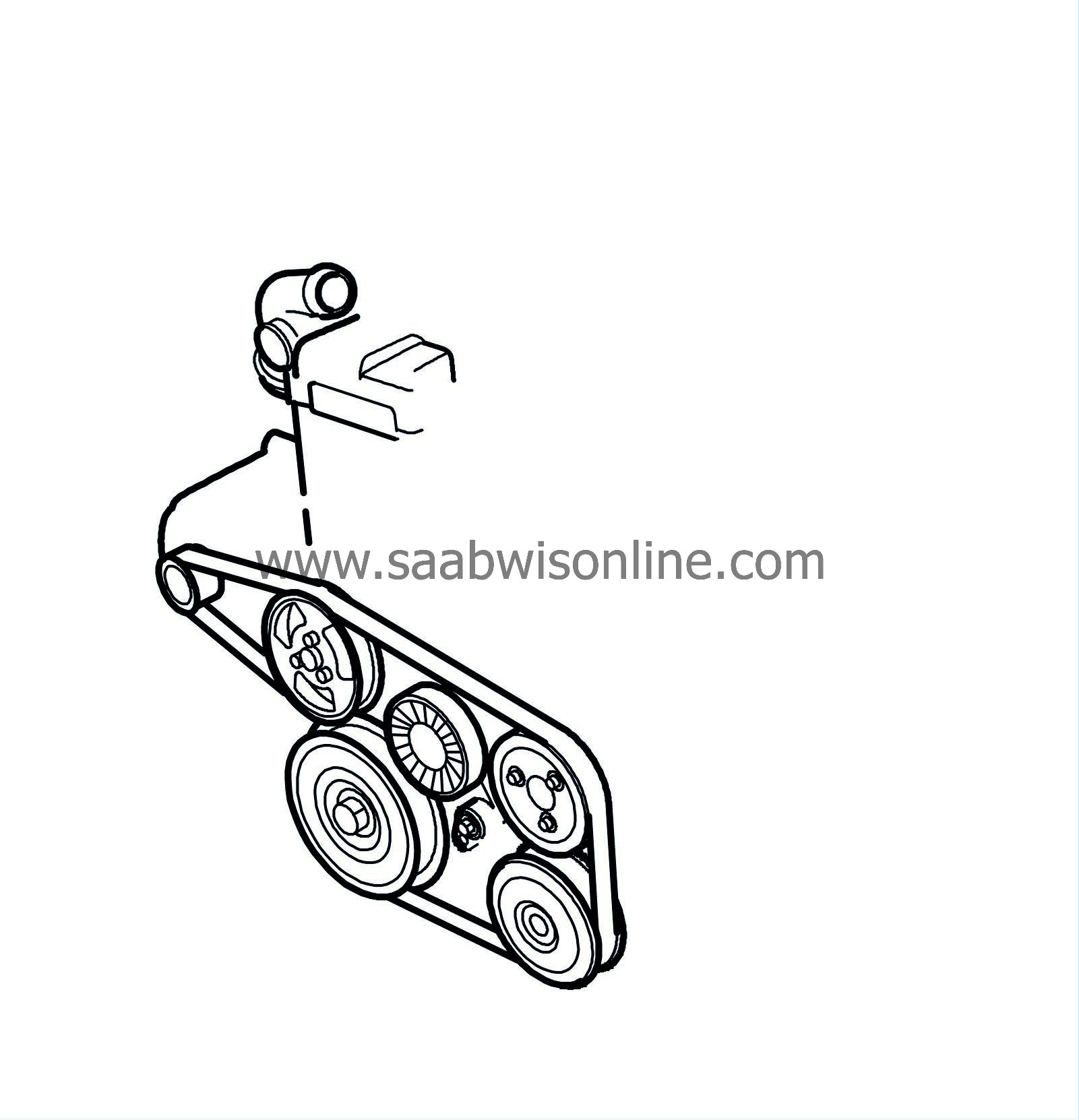
| Timing cover |
The timing cover is designed to fit the shape of the cylinder block. The oil pump and coolant pump are mounted in the timing cover, which is sealed with a metal gasket with vulcanized rubber elements.
| Crankshaft assembly |

The crankshaft is forged with ground bearing journals, which have been induction hardened. This provides a hard surface that protects against wear. The crankshaft is mounted on 5 main bearings, where the middle bearing acts as a thrust bearing. Oilways are drilled in the shaft for the lubricant. All main bearing caps are exchangeable.
| Connecting rods |
The connecting rods are forged and equipped with a bush for the gudgeon pin.
The gudgeon pins are of fully-floating type, being free to turn in both piston and connecting rod. Axial movement of the gudgeon pin is limited by circlips in the gudgeon pin holes.
| Pistons |
The pistons are made of light alloy and have grooves for two compression rings and one oil scraper ring. The combustion chamber is located on top of the piston.
The upper compression ring is flat and the lower compression ring has oil scraper properties, while being thicker than the upper ring. The oil scraper ring proper is in three pieces.
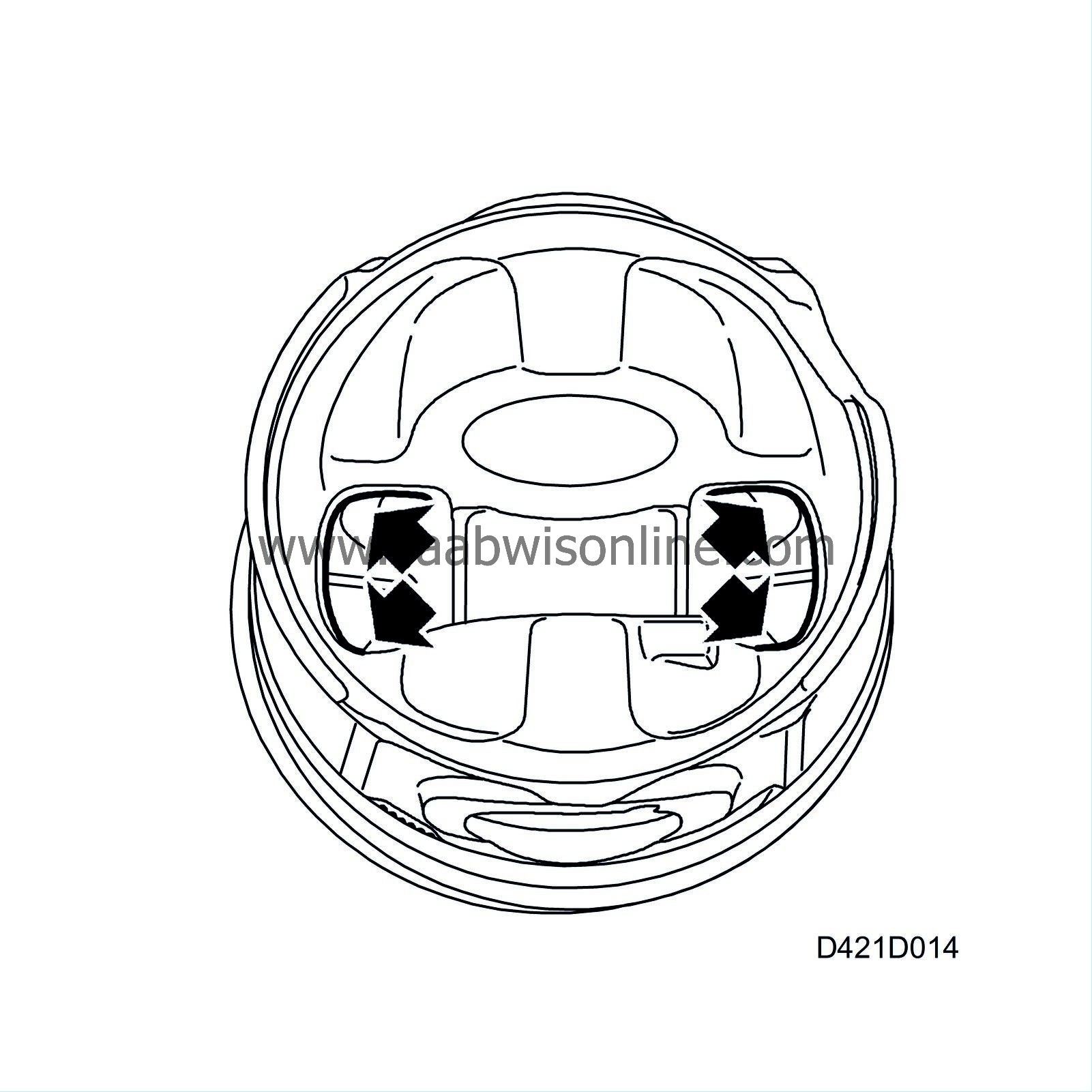
The engine pistons have cooling passages for better piston cooling. The nozzles that spray oil into the pistons are also specially designed for efficient cooling.