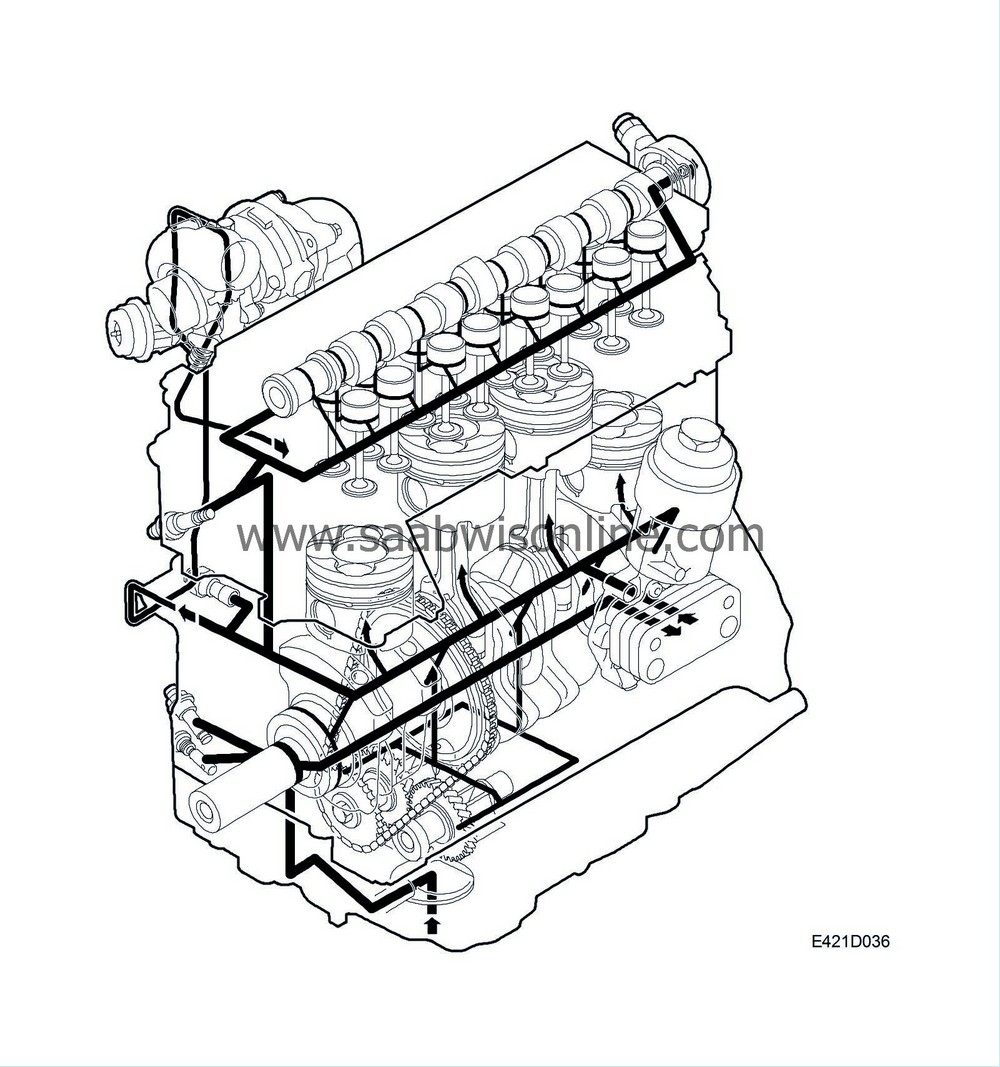
Lubricating system
| Lubricating system |
| 1. |
Check valve
|
|
| 2. |
Piston cooling nozzle
|
|
| 3. |
Oil pump
|
|
| 4. |
Chain tensioner
|
|
| 5. |
Heat exchanger
|
|
| 6. |
Oil filter
|
|
Engine lubrication is through a forced-feed lubricating system, in which the oil pressure is generated by a gear pump comprising a gear wheel and an off-centre ring wheel. The pump is located in the timing cover and is driven by the crankshaft.
The oil is drawn up from the sump via a strainer and suction pipe to the oil pump. A reduction valve in the timing cover limits the oil pressure at the same time as excess oil is led back to the suction side of the pump. The oil then passes via an oilway into the cylinder block and on to the oil filter.
The engine is equipped with a heat exchanger, in which the coolant and oil temperatures act on each other, which offers a more even engine temperature.
After filtering and cooling/heating, the oil is led out of the main passageway in the cylinder block, where the engine oil pressure sensor is situated. If the oil pressure is too low, the sensor will ground the electric circuit to the warning lamp located in the main instrument unit.
The crankshaft main and big-end bearings are lubricated via oilways in the block and crankshaft, while the pistons and cylinder walls are lubricated with oil mist and splash from the crankcase. In addition, each cylinder has a piston cooling nozzle, which sprays a fine jet of oil on the bottom of the piston.
The engine pistons have cooling passages for piston cooling. The nozzles that spray oil into the pistons are also specially designed for efficient cooling. A check valve retains the oil in the cylinder block.
The balancer shafts are supplied with oil through holes in the main bearings, which transport the oil down to the main bearing bridge. This is also used to mount the balancer shafts.
An oilway leads from the main passage in the cylinder block via a check valve to the cylinder head to lubricate the camshafts, valve gear and vacuum pump. Via a hole for one of the cylinder head bolts, the oil is led through drilled passages to all the camshaft bearings and valve tappets.
| Oil sump |
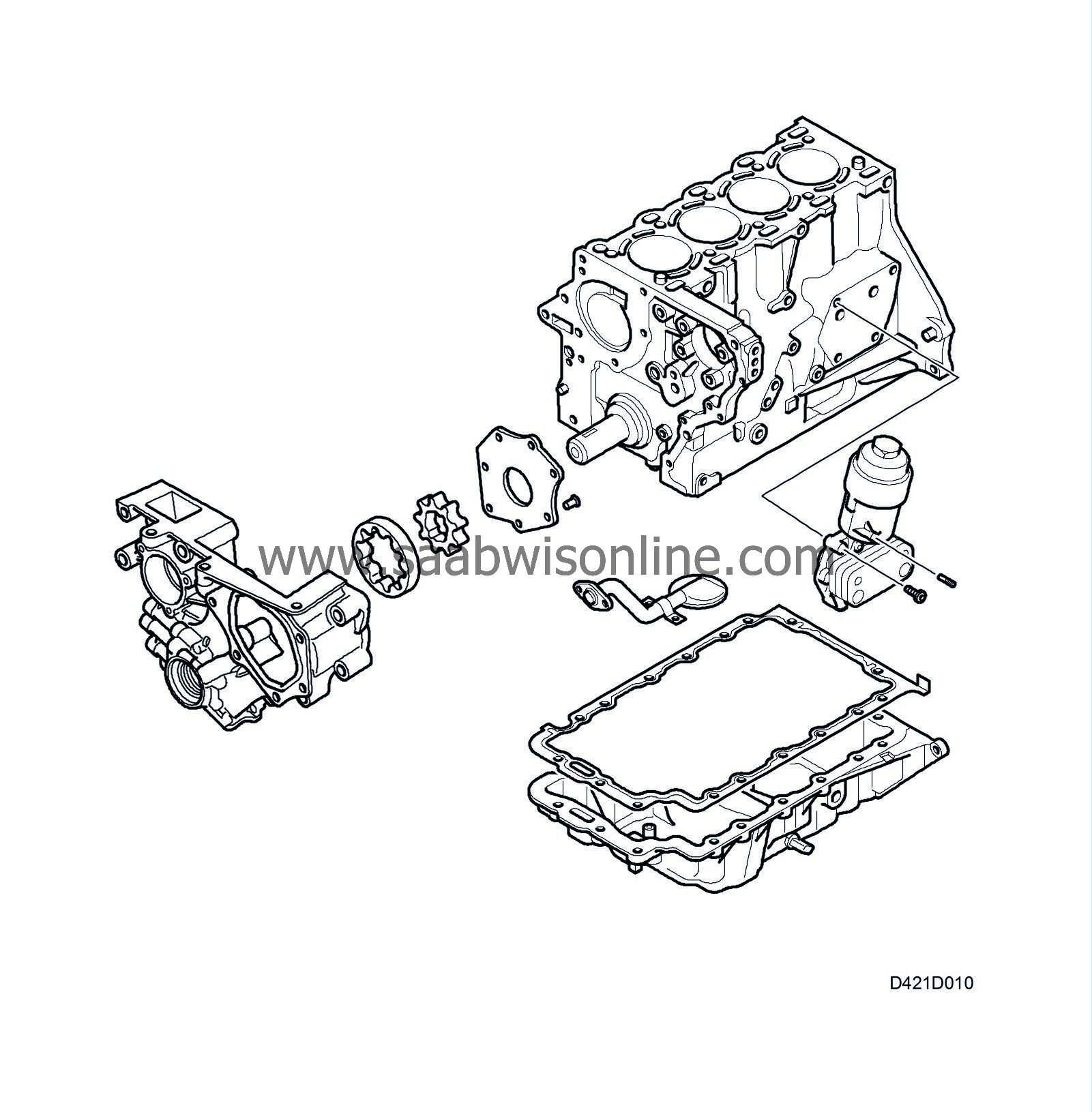
The oil sump is adapted to the cylinder block and is sealed with a metal gasket with vulcanized rubber elements.
| Oil filter |
The cartridge type oil filter is located in a filter housing, which is integrated with the heat exchanger on the cylinder block facing forwards in the car.