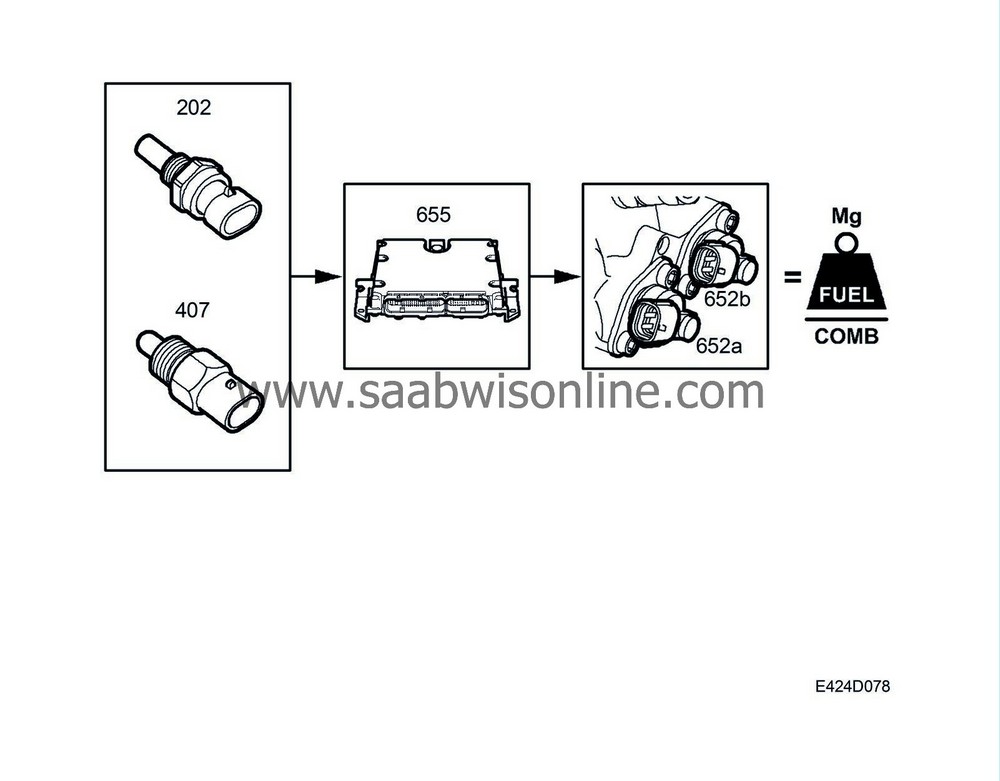
Idle speed control
| Idle speed control |
Idle speed control comprises two sub-functions:
| - |
desired value, idling speed
|
|
| - |
idle speed control
|
|
| Desired value, idling speed |
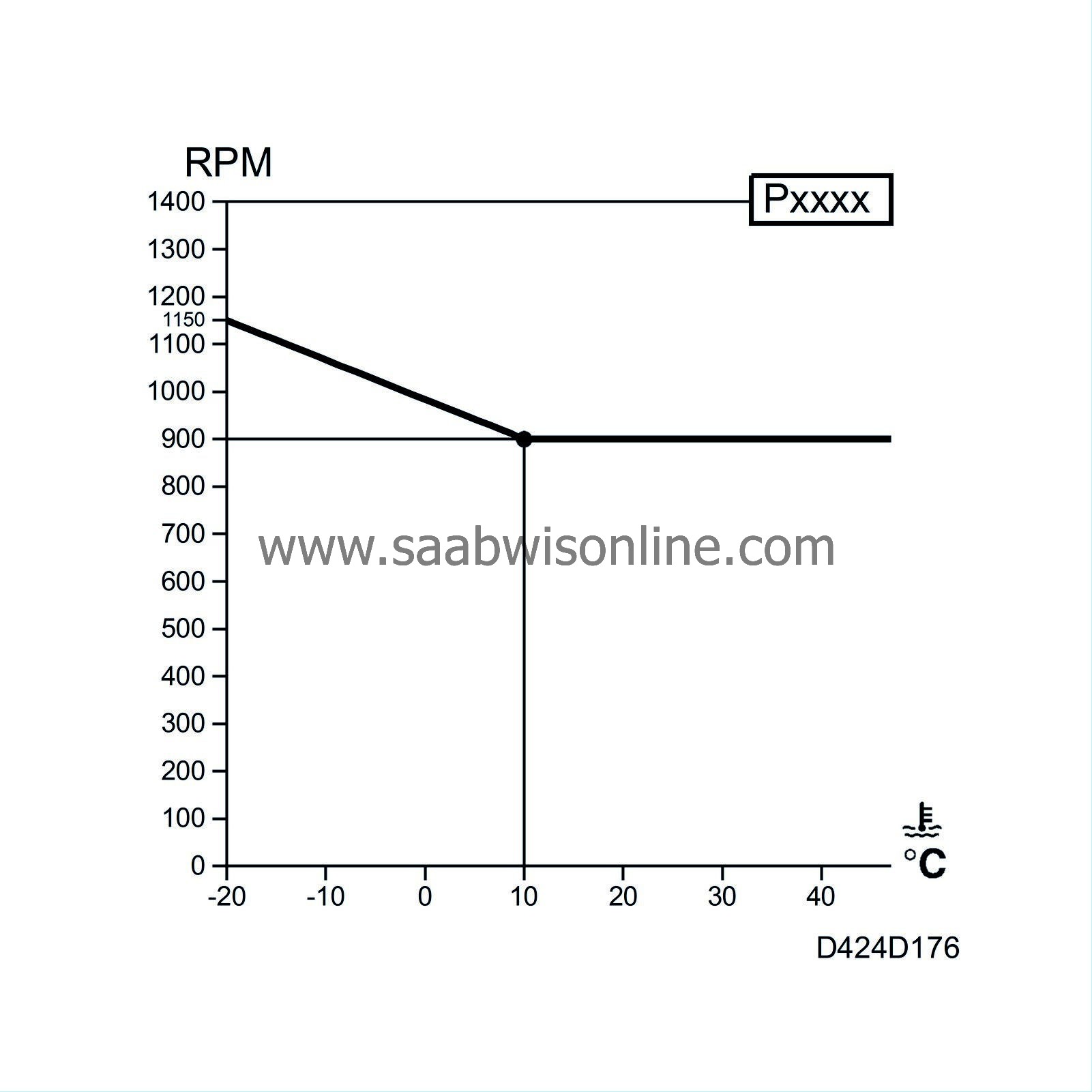
The idling speed to apply is chosen depending on coolant temperature, intake air temperature, whether the control module has diagnostic communication or whether there is a system fault (DTC).
Depending on the coolant temperature and intake air temperature, the idling speed can vary from approx. 1150 rpm for a cold engine to 750 rpm for a warm engine.
The ACTIVATE function in the diagnostic tool can be used to temporarily increase or decrease the idling speed. It can be increased to max 2000 rpm and decreased to min 700 rpm. After terminating the ACTIVATE function, the engine will return to the programmed value. If a system fault should occur, the idling speed will be set to 1400 rpm. The idling speed can be reprogrammed permanently with the diagnostic instrument. Changes can be made in steps of 50 rpm with the ADJUSTING function. If an adjustment of the desired idling speed has been carried out using the diagnostic tool, the calculated idling speed will be increased or decreased by a corresponding amount and the total idling speed will be sent to the idle speed control.
Desired value, idling speed is a synchronized calculation, i.e. the calculation takes place at certain time intervals.
| Idle speed control |
The idle speed control sub-function executes the order from "desired value, idling speed".
Idle speed control comprises a number of different internal calculations that are synchronized with the engine speed. This means that each new calculation of the fuel quantity is controlled by the engine speed. A new calculation takes place for each power stroke in order to determine an injection quantity that corresponds to the desired idling speed.
The fuel quantity from idle speed control is passed on to the decision chain in the engine control module.