Dipped beam, halogen
| Dipped beam, halogen |
To enable DICE to determine what position (0-1-2) the light switch (10) is set to, the control module uses bus information from TWICE and its own pins 39 and 15.
TWICE monitors the parking lights and sends information on the bus (Rear light Left ON/OFF and Rear light Right ON/OFF). The ON message corresponds to switch position 1 and the OFF message corresponds to position 0 or 2.
To enable DICE to determine the position setting, it uses pins 39 and 15. DICE pin 39 is connected to light switch pin 10, which corresponds to position 0. DICE pin 15 is connected to light switch pin 11, which corresponds to position 2.
From pin 11 on the dipswitch (10), a voltage of +X is fed from the ignition switch to pin 15 on the control module, thus grounding the main light relay through pin 4 on the control module and causing the relay to close. A voltage of +30 is fed through the relay by way of the filament monitor and on to the fuses (11 and 13).
Limp-home

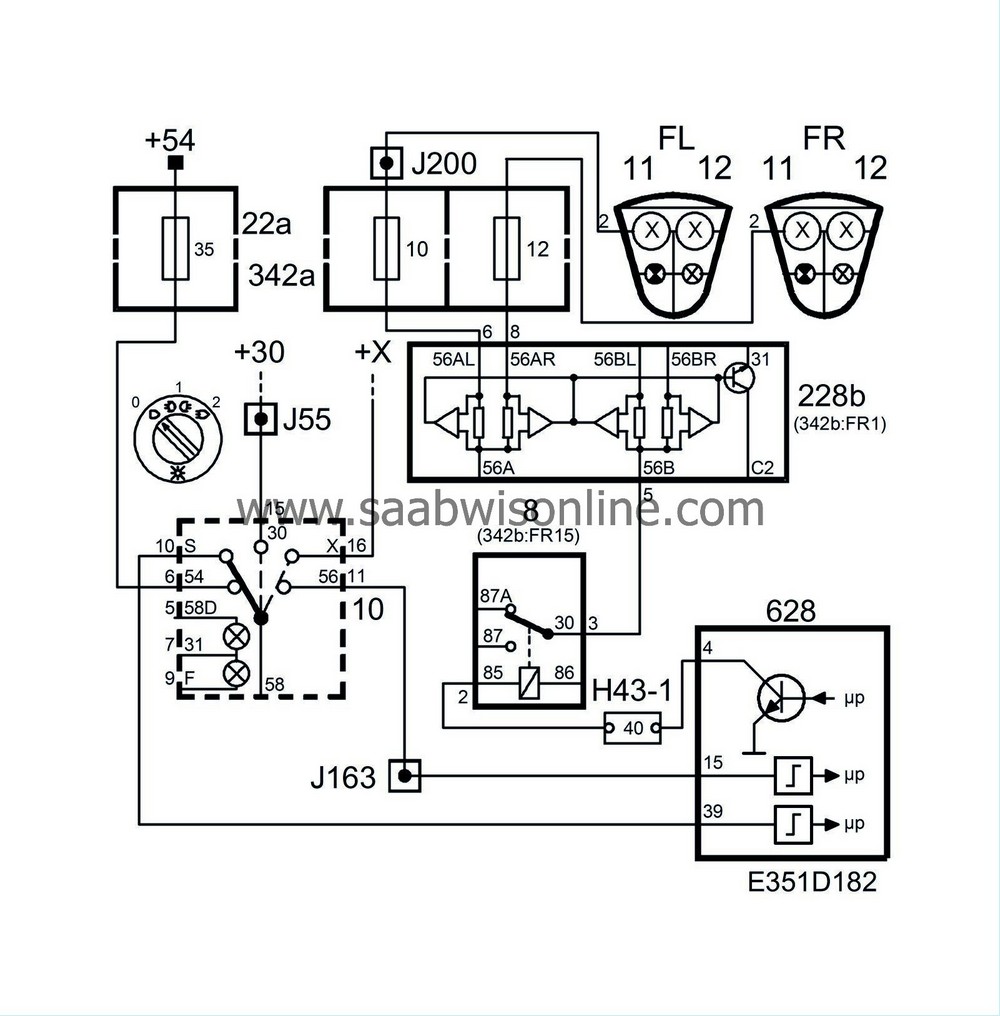
The limp-home function is a safety circuit in the lighting system which ensures that dipped beam can always be switched on even if DICE should be put out of action.
When the light switch is in position 2, voltage +X can also be utilized to supply the dipped-beam lamps with power. Voltage +X is fed to the dipped-beam relay, which will then be in the closed position, and the power is passed straight through the relay via the filament monitor (228b) and fuses (11 and 13) to the dipped-beam lamps. The dipped beam is somewhat dimmer, however, because the voltage drop in the system is larger than normal.
| Important | ||
|
When changing a bulb, use a replacement bulb of the correct wattage, since there could otherwise be damage to components. |
||
| Diagnosis |
Diagnostic trouble code 1160 is generated in the event of an open circuit or a short circuit to ground or a short circuit to B+.
DTCs are not generated if the voltage is below 11 V or during diagnostic communication.
| Follow me home |
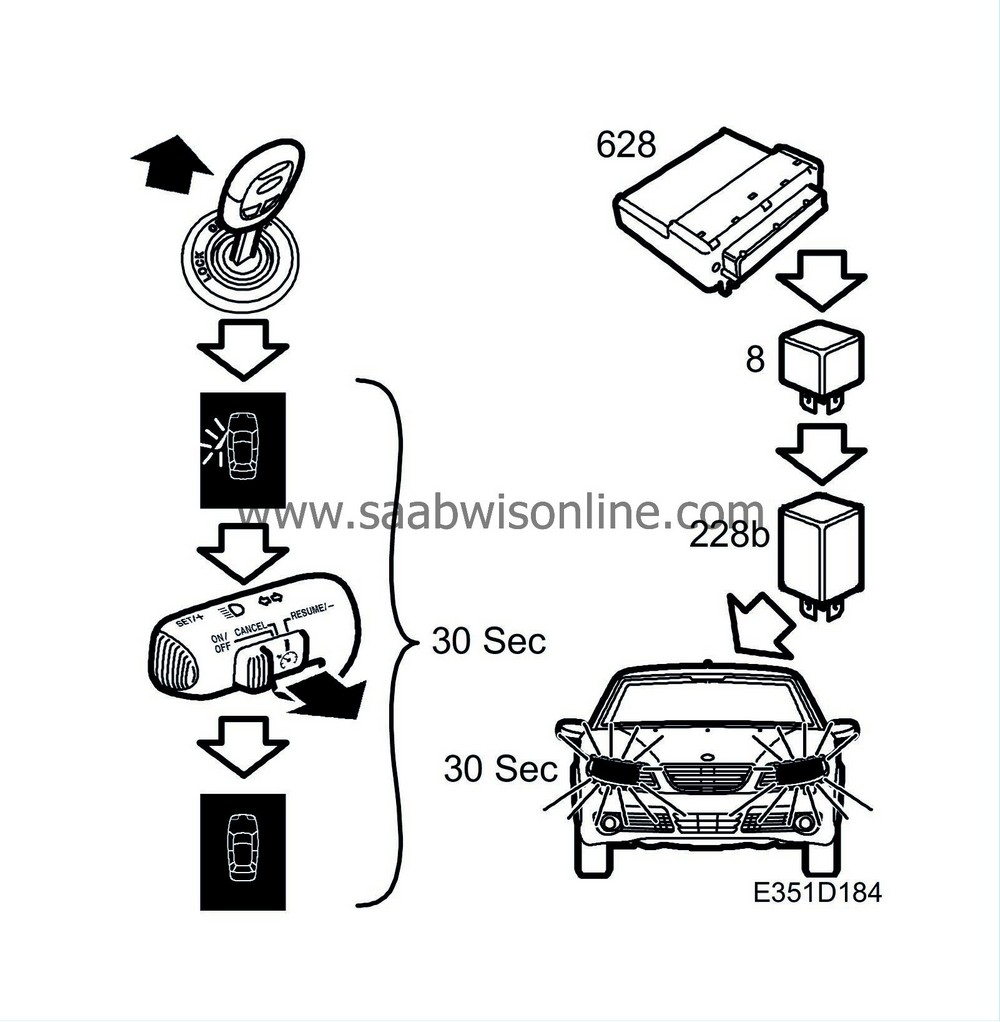

This function activates the dipped beam when the car key is taken out of the ignition switch, the driver's door is opened and the dipswitch is moved to its rearmost position “flash”. If the driver's door is closed at any time within the next 30 seconds the dipped beam comes on for a preprogrammed duration.
The point of “Follow me home” is that the car's dipped beam is used when no light sources are available other than those on the car. The car's dipped-beam function remains active for a certain time after the car key is withdrawn from the ignition switch and the driver's door is closed. The duration is programmable in DICE (20-50 seconds).
A number of conditions must be fulfilled before DICE will activate this function.
DICE uses pin 7 to detect that the key has been withdrawn from the ignition switch. DICE then needs to get a message from TWICE concerning the status of the driver's door (OPEN). When the dipswitch (215) is activated, power is supplied to pin 41 on DICE.
The last precondition is fulfilled when TWICE puts a message on the bus concerning the status of the driver's door (CLOSED). The dipped-beam relay is thereupon grounded via pin 4 on DICE for a pre-set time (20-50 seconds), causing the dipped-beam lamps to light up.
| Important | ||
|
When changing a bulb, use a replacement bulb of the correct wattage, since there could otherwise be damage to components. |
||
| Diagnosis |
Diagnostic trouble code 1160 is generated in the event of an open circuit or a short circuit to ground or a short circuit to B+.
DTCs are not generated if the voltage is below 11 V or during diagnostic communication.



