Brief description
| Brief description |
| Description |
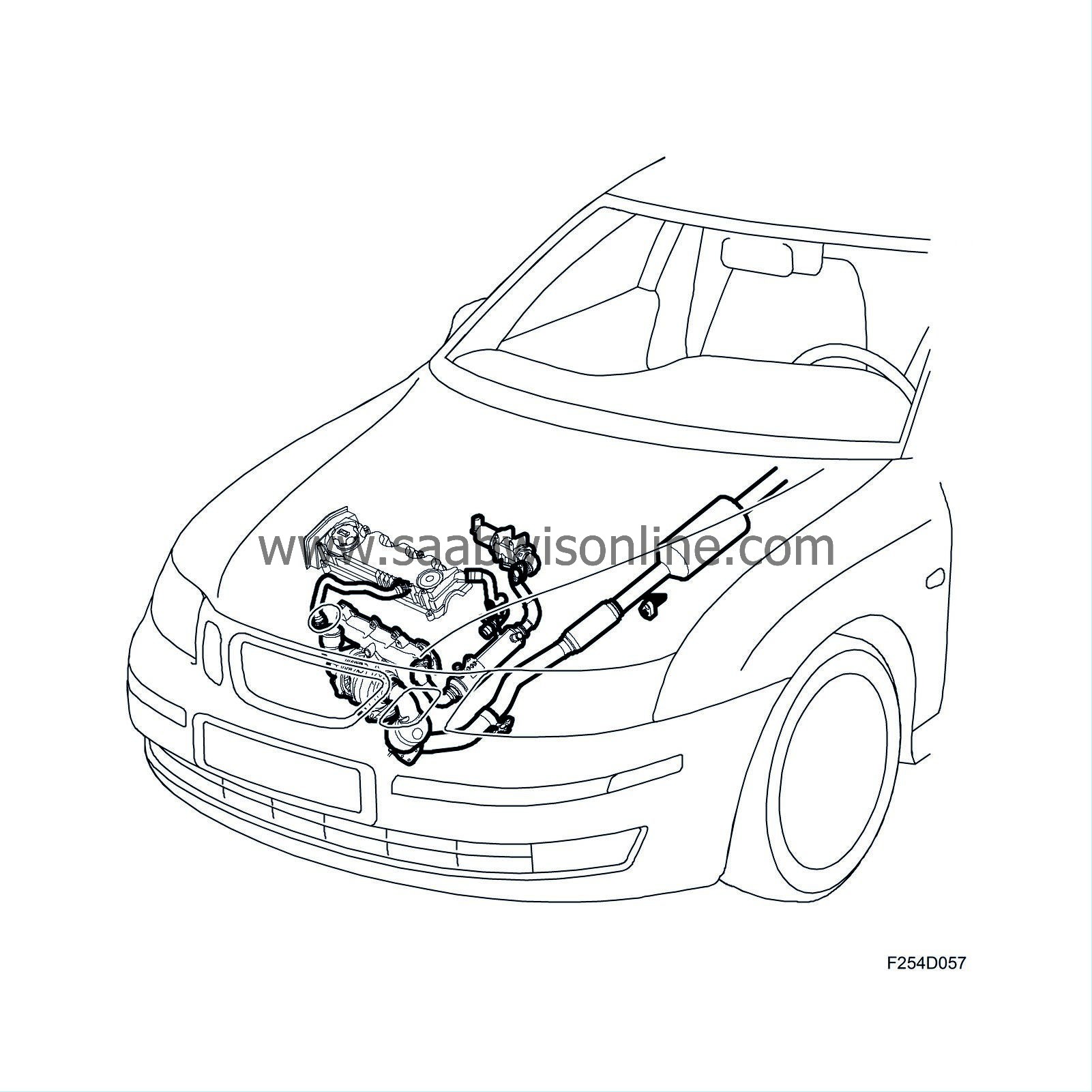
The exhaust emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
| • |
Catalytic converters
|
|
| • |
Particle trap (cars with particle trap)
|
|
| • |
Crankcase ventilation
|
|
| • |
EGR system
|
|
| • |
Oxygen sensor (cars without particle trap)
|
|
Catalytic converters
A catalytic converter is mounted just after the turbine outlet. Because of its proximity to the turbocharger, the catalytic converter warms up quickly after start. On cars with particle trap, a second catalytic converter is housed in the particle trap. On cars without particle trap, a catalytic converter is mounted on the exhaust system a little farther back. Catalytic converters reduce HC and CO emissions.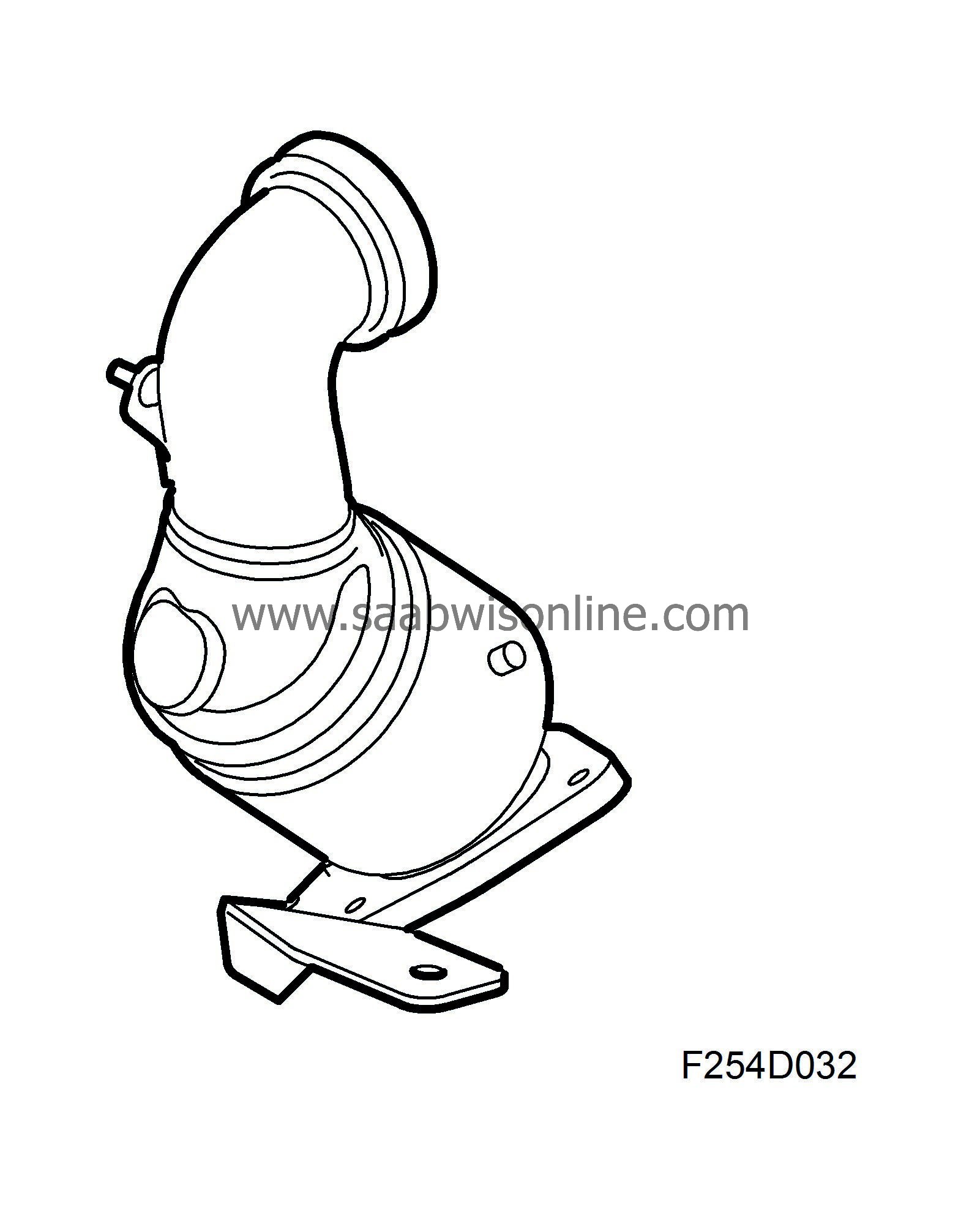
Particle trap (cars with particle trap)
Cars with engine option Z19 can be equipped with a particle trap, which catches soot particles in the exhaust gases. Once the particle trap is full of particles, they are combusted. This is called regeneration.The particle trap consists of a ceramic body, similar to a catalytic converter, with many small channels. Soot particles fasten in these channels. A differential pressure sensor measures the pressure drop across the particle trap. When the pressure drop exceeds a limit value, the particle trap is considered full and regeneration is initiated. This normally occurs automatically without the driver noticing anything. During regeneration, a small, extra dose of fuel is injected during the exhaust stroke, which dramatically increases exhaust temperature in the particle trap. This high exhaust temperature combusts the soot and thereby "cleans" the particle trap. The process takes about 15 minutes. Regeneration can also be activated with the diagnostic tool.

Oxygen sensor (cars without particle trap)
Cars without particle trap are equipped with an oxygen sensor mounted in the catalytic converter inlet. The oxygen sensor is a broadband sensor.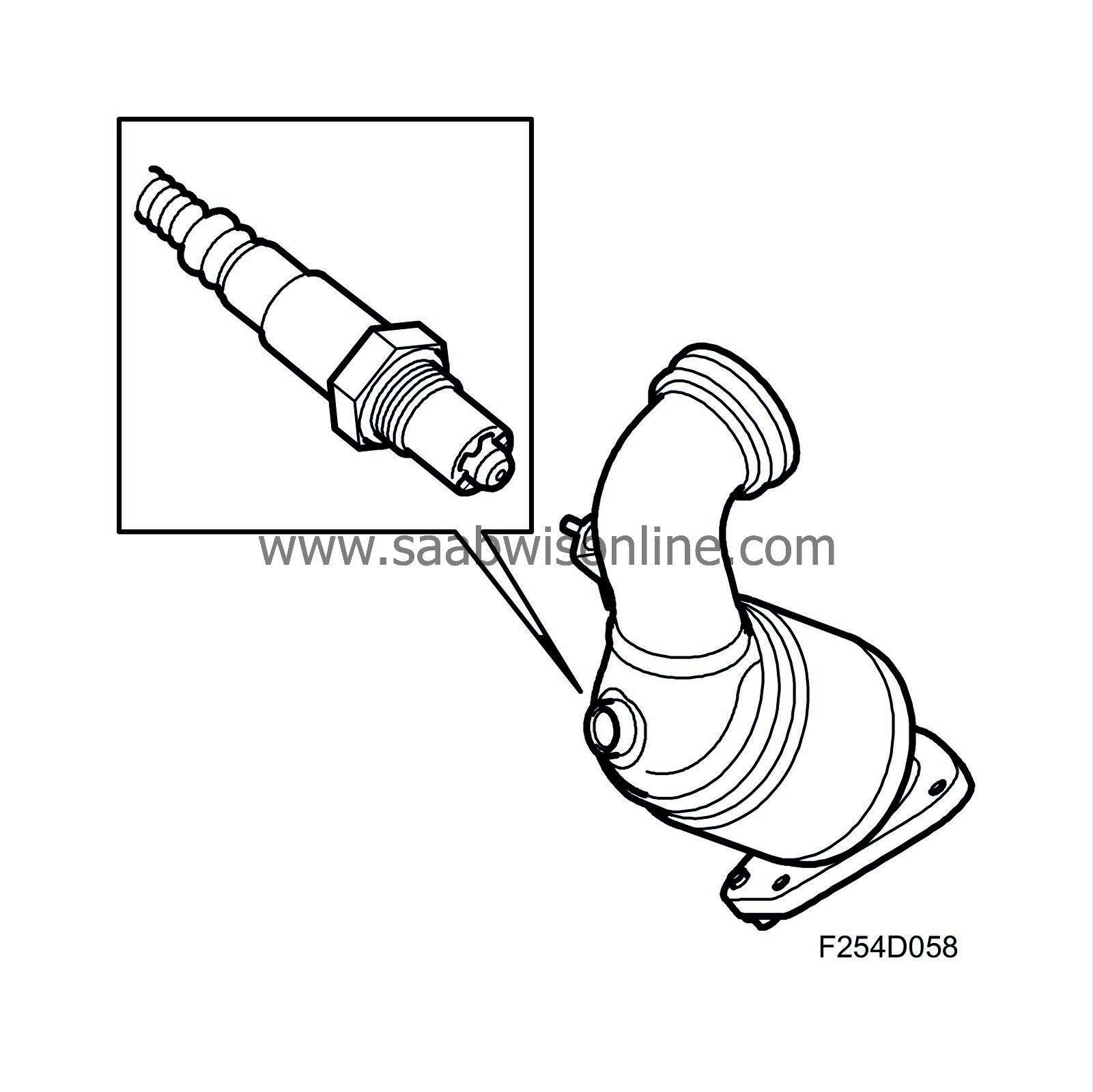
Crankcase ventilation, general
The combustion gases that pass the piston rings gather in the crankcase and must be lead out of the engine via crankcase ventilation. This prevents excessively high pressure in the crankcase and removes the water vapour and hydrocarbons from combustion. Since crankcase gases contain hydrocarbons, they must not be released into the air. They must be led back into the cylinders for combustioner. Engine crankcase ventilation is thus a closed system.Crankcase ventilation
Z19DTH has an external oil trap which catches most of the oil mist from the crankcase gases. The oil is led back into the crankcase. The air is led into the engine induction system and combusted in order to render it harmless.
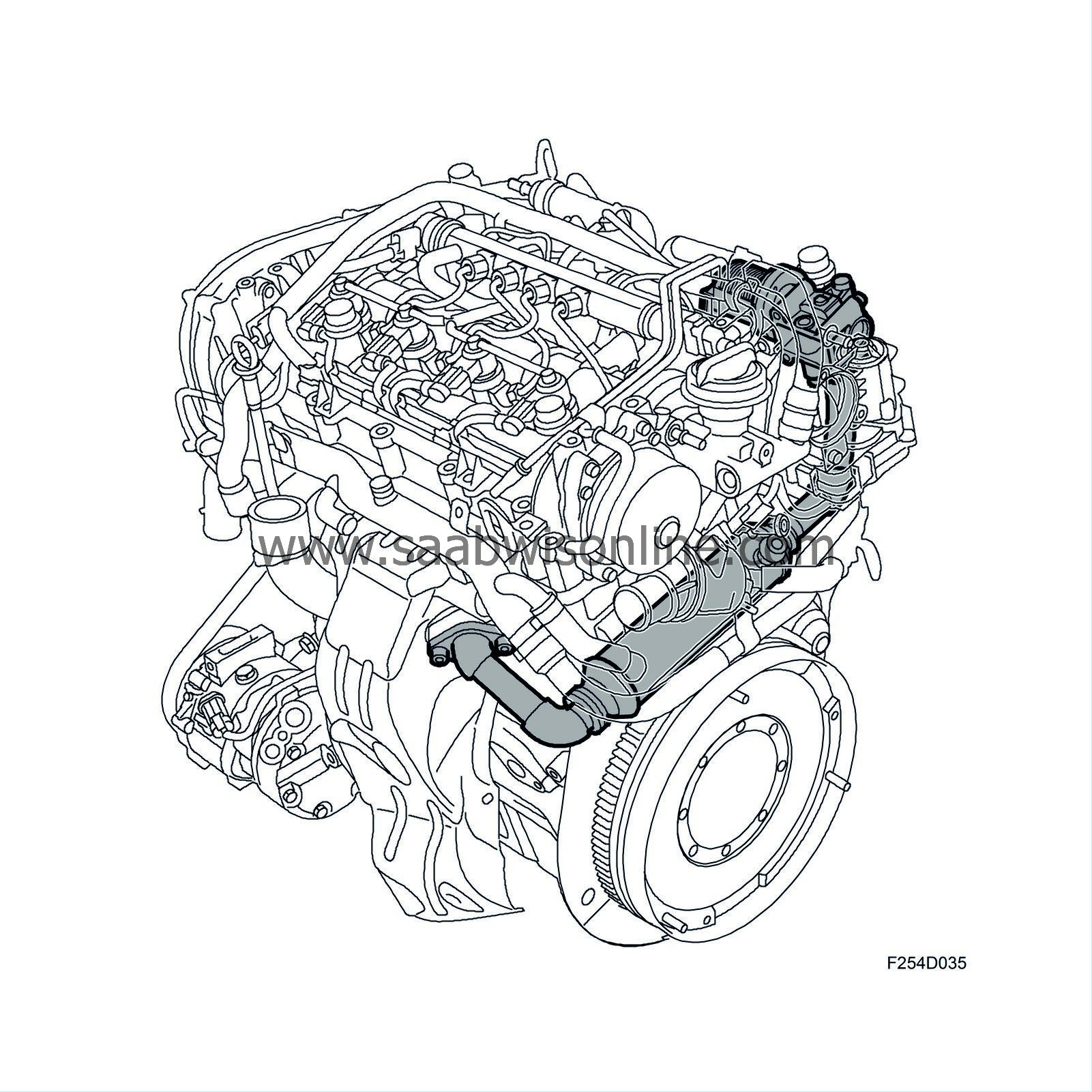
EGR system
To reduce NO x (nitrous oxides), you must simply prevent them from forming. This is done by reducing temperature during combustion. By allowing recirculated, cooled exhaust gases into the intake air, the combustion temperature and thereby NO x emissions are reduced.The following components are part of the EGR system:
| • |
EGR valve to control the amount of exhaust gases to be recirculated
|
|
| • |
EGR cooler to cool the exhaust gases
|
|



