Ignition system, knock regulation
|
|
Ignition system, knock regulation
|
The Saab Trionic ignition system is a capacitive ignition system and consists of
four ignition coils and electronics built into the ignition discharge module. The ignition coils are
controlled by the electronics in the ignition discharge module, which in turn are regulated via
low-level outputs from the ECM.
When the engine is cranked, the ignition system produces a spark on two spark plugs
simultaneously, 1 and 4 or 2 and 3, for a number of consecutive complete combustion
processes. Following this, on the basis of the ionization current flowing through the spark
plugs and signals from the crankshaft position sensor, the system has sufficiently reliable
information to synchronize spark generation and fuel injection to the correct cylinder.
To improve starting performance when the engine temperature is below 0°C, the
ignition system generates a large number of sparks in quick succession (multispark function),
while the starter motor is engaged (10°BTDC - 20°ATDC).
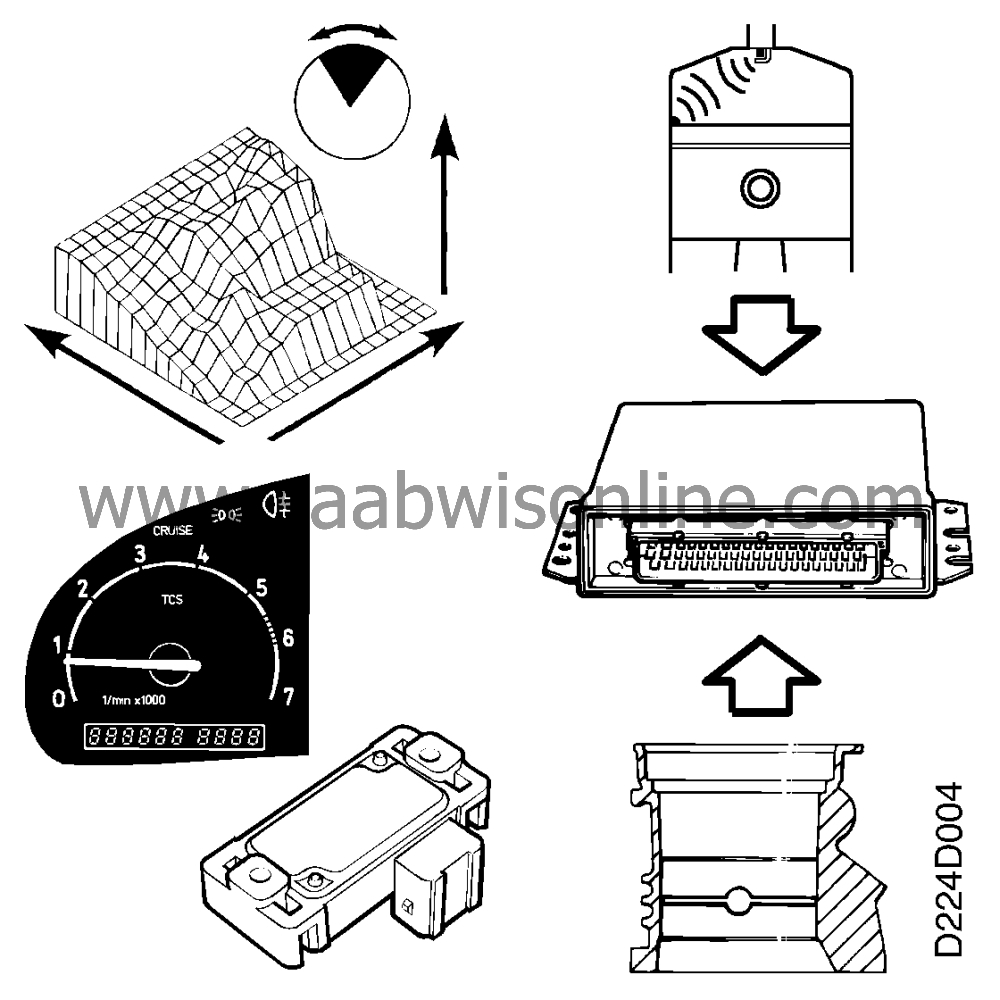
The crankshaft position sensor consists of an inductive sensor mounted in the
crankcase wall of the engine. The rotor is a perforated disc with 58 ribs, which is mounted on
the rear counterweight of the crankshaft.
Ignition timing
The ignition timing is calculated by the control module chiefly on the basis of the
following information:
|
•
|
throttle position (idling only)
|
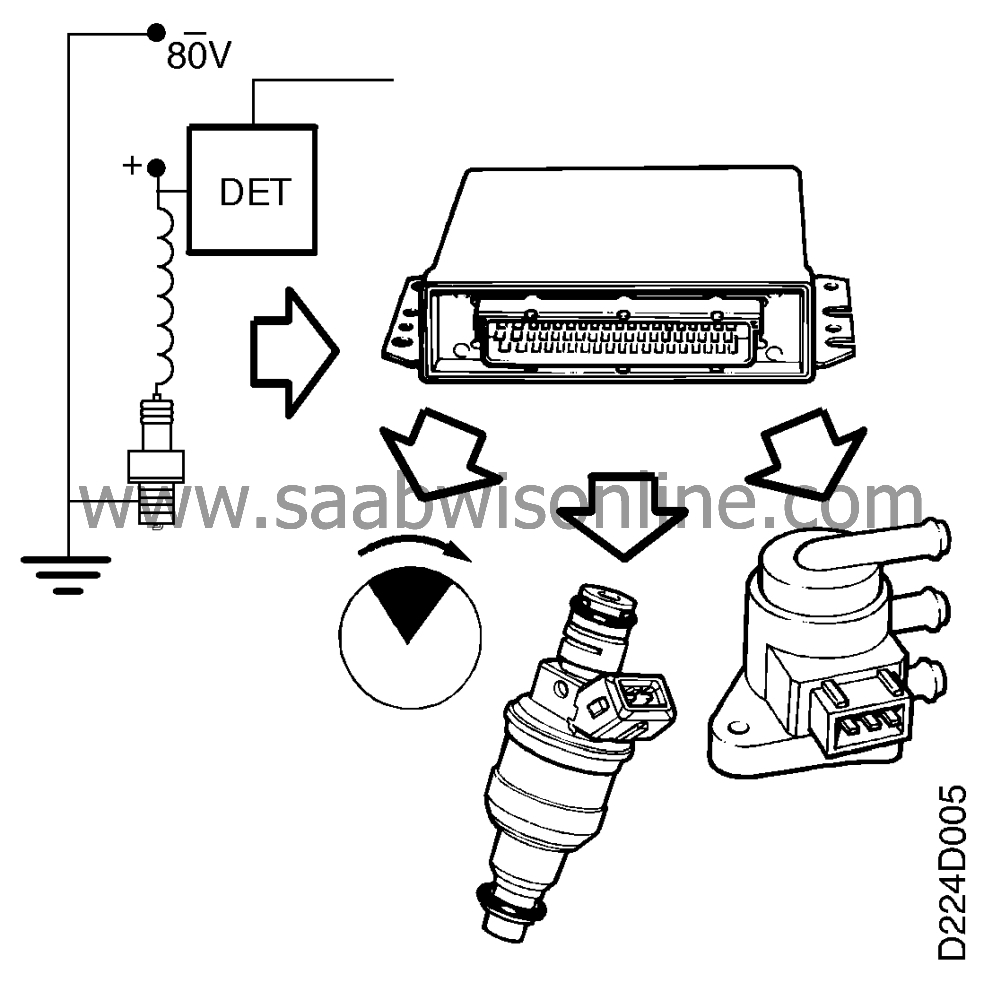 The control module determines whether knocking is occurring in any of the
cylinders by analyzing the ionization currents passing through the spark plugs. If knocking
occurs, ignition is retarded. In the event of major ignition regtardation or high boost pressure,
a richer fuel/air mixture is also produced. The boost pressure is reduced as a final step.
The control module determines whether knocking is occurring in any of the
cylinders by analyzing the ionization currents passing through the spark plugs. If knocking
occurs, ignition is retarded. In the event of major ignition regtardation or high boost pressure,
a richer fuel/air mixture is also produced. The boost pressure is reduced as a final step.