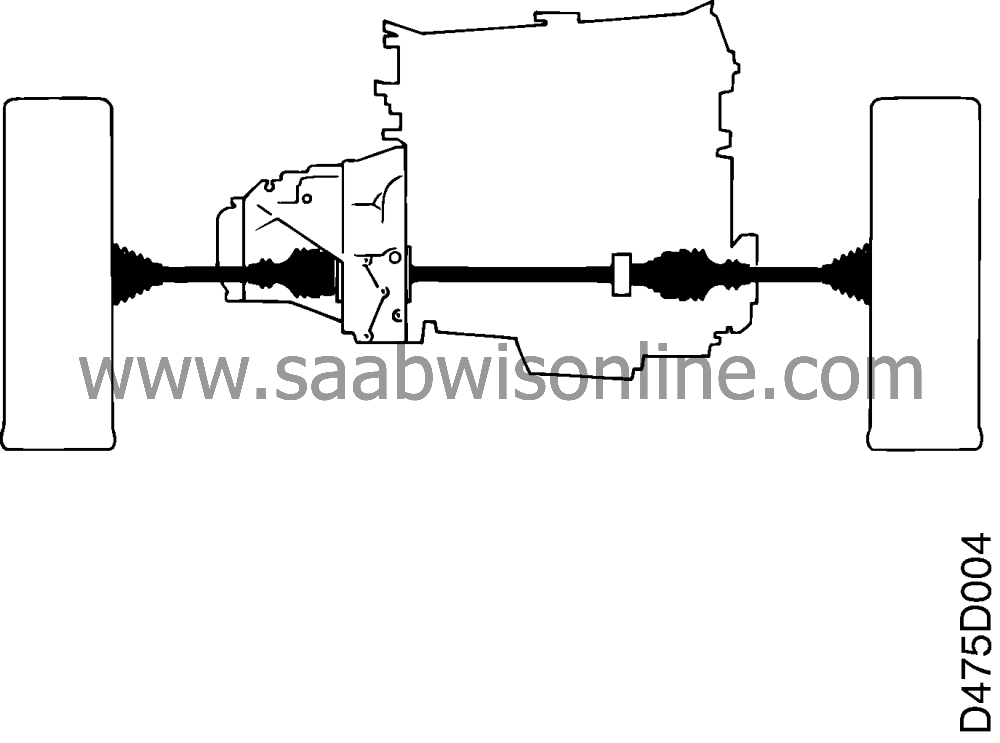
Drive shafts and universal joints
| Drive shafts and universal joints |
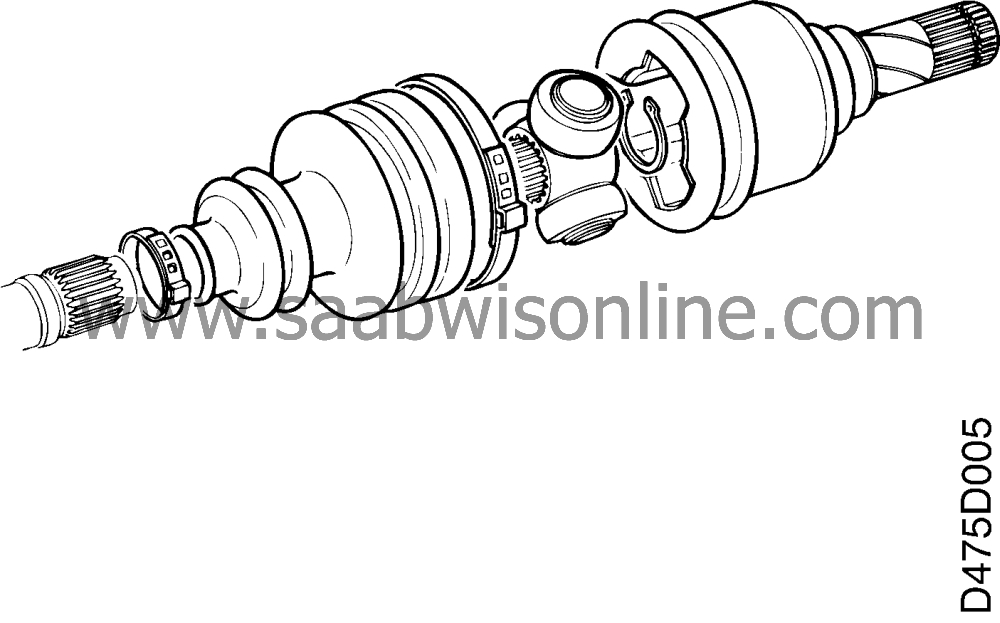
On the left-hand side the inner universal joint is connected to the differential by a quick coupling. In a corresponding way the right inner universal joint is connected to the intermediate shaft. The universal joints are filled with grease and protected from dirt and moisture by a rubber bellows.
There are two variations of the inner universal joint.
| 1. |
Tripode type
which consists of a tripod housing and a tripod. The tripod consists of three rollers in needle bearings and can move axially in the tripod housing. |
|
| 2. |
The Rzeppa type
in which the torque is transferred via six balls which run in axial grooves. In this variant of the Rzeppa universal joint the joint can move axially. 
|
|