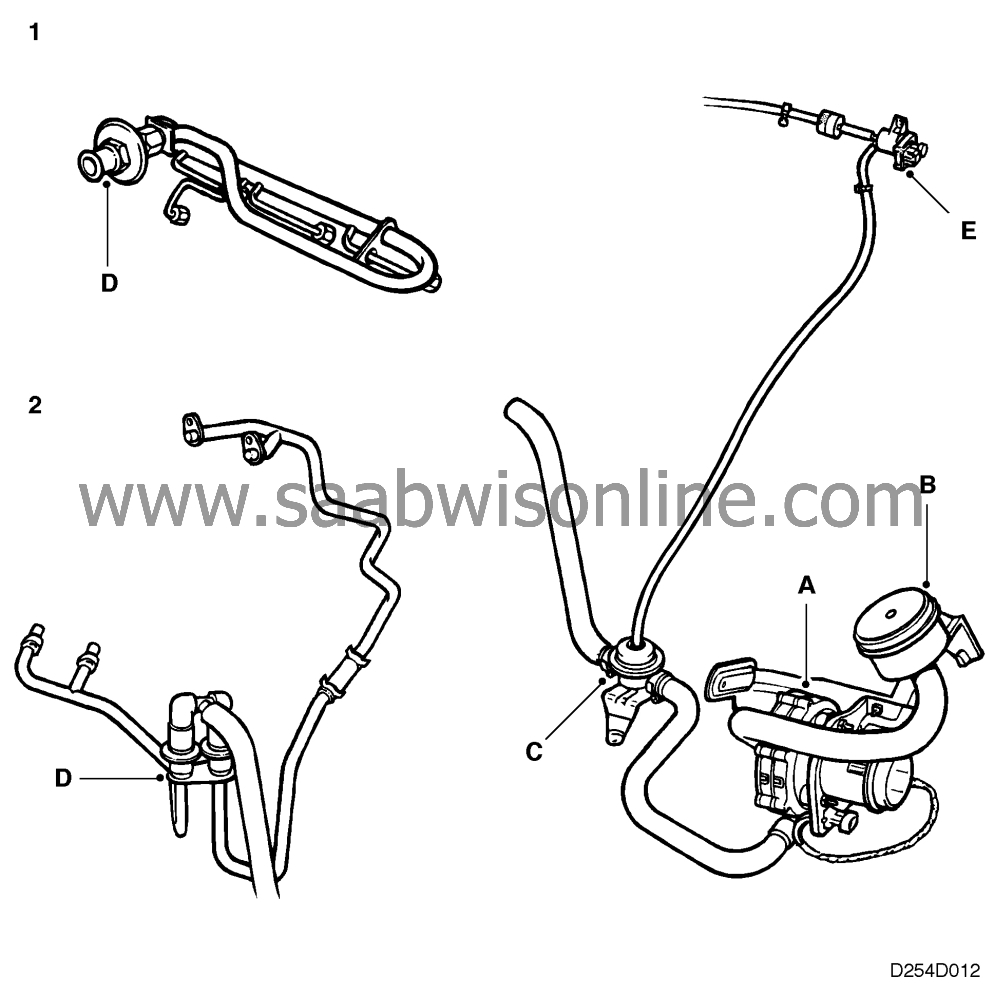
Secondary air injection
Before the oxygen sensor and the catalytic converter have reached their operating temperature, air is blown into the exhaust manifold to help with the secondary combustion of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. This means that the catalytic converter reaches its operational temperature more quickly as well.
This function is activated by the engine control module when the engine is started and has a running time which depends on the engine temperature and the point in time at which the oxygen sensor starts to operate.
The injection pump for secondary air (A), which is located in front of the left-hand side wheel housing, sucks in air via an air filter (B) and then blows the air through a secondary air switching valve (C) and check valve(s) (D) on to the exhaust manifold. The switching valve is operated by the engine's under- pressure by means of the engine control system opening the secondary air system's control valve (E). The function of the check valve is to ensure that the exhaust gases do not flow in the reverse direction and cause damage to the switching valve or the injection pump.