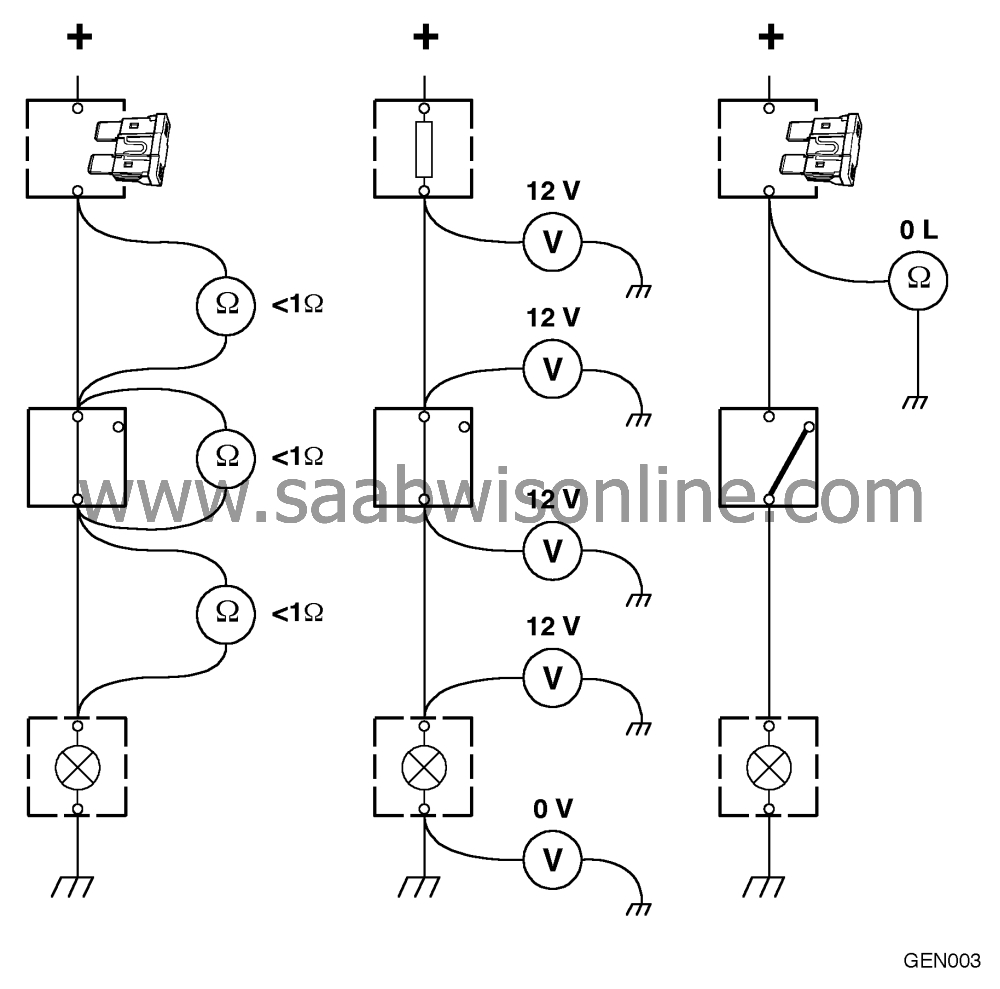
Testing forcontinuity/shorting
|
|
Testing for
continuity/shorting
|
|
Testing for continuity (Resistance measurement)
|
|
1.
|
Make sure that the component
or cable to be checked is not live.
|
|
2.
|
With the instrument set to measure resistance, connect the test leads to each
end of the component or cable to be checked. In the wiring, the resistance should normally be
less than 1 ohm.
|
|
Testing for continuity (Voltage measurement)
|
|
1.
|
Connect up the load, if any.
|
|
2.
|
With the instrument set to measure voltage, connect the black test lead to a
good ground and the red test lead to the wiring side (positive).
|
|
3.
|
At the output of a control module or switch: take readings in the direction away
from the component and proceed successively out towards the load. When the voltage
reading drops to zero you have just passed the break in continuity.
|
|
4.
|
At the input of a control module or load: take readings from the power source
and proceed successively in towards the control module or load. When the voltage reading
drops to zero you have just passed the break in continuity.
|
|
Shorting to ground (Resistance measurement)
|
|
1.
|
Make sure that the cable to be
checked is not live and that the load, if any, is disconnected.
|
|
2.
|
With the instrument set to measure resistance, connect one of the test leads to
the load side of the cable and the other test lead to a good ground.
|
|
3.
|
Carefully move the wiring about while checking the instrument to see whether it
shows infinite resistance (OL) the whole time.
|