Checking and charging thebattery
|
|
Checking and charging the
battery
|
|
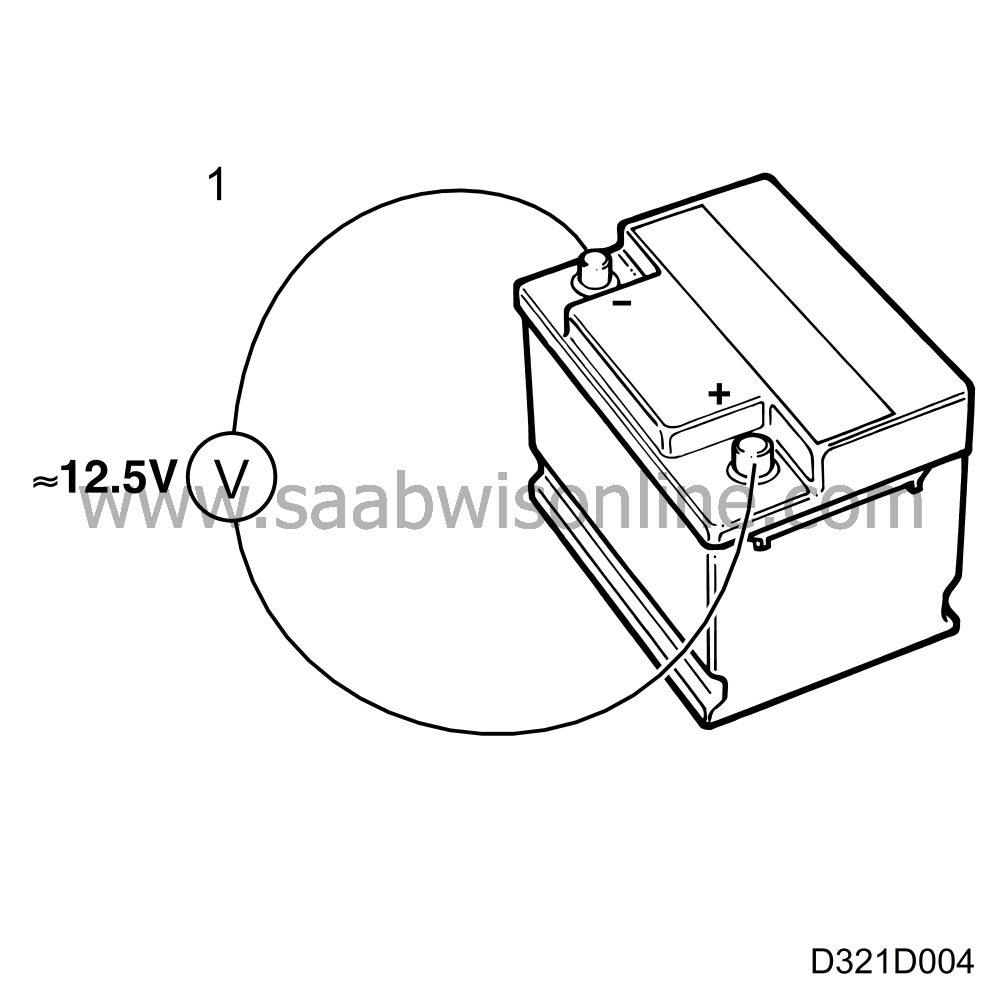
1.
|
Use a voltmeter to check that a
reading of at least 12.4 V is
obtained across the battery terminals.
If the voltage is too low it indicates that the battery is either
poorly charged or has insufficient capacity.
The state of charge in the battery should be checked. The most suitable
way of doing this is to use a hydrometer. The specific gravity of the
electrolyte in a fully-charged battery should be 1.28. A specific
gravity of 1.18 corresponds to about 50%%of a full charge.
The battery can normally be recharged by means of a conventional
battery charger.
|
|
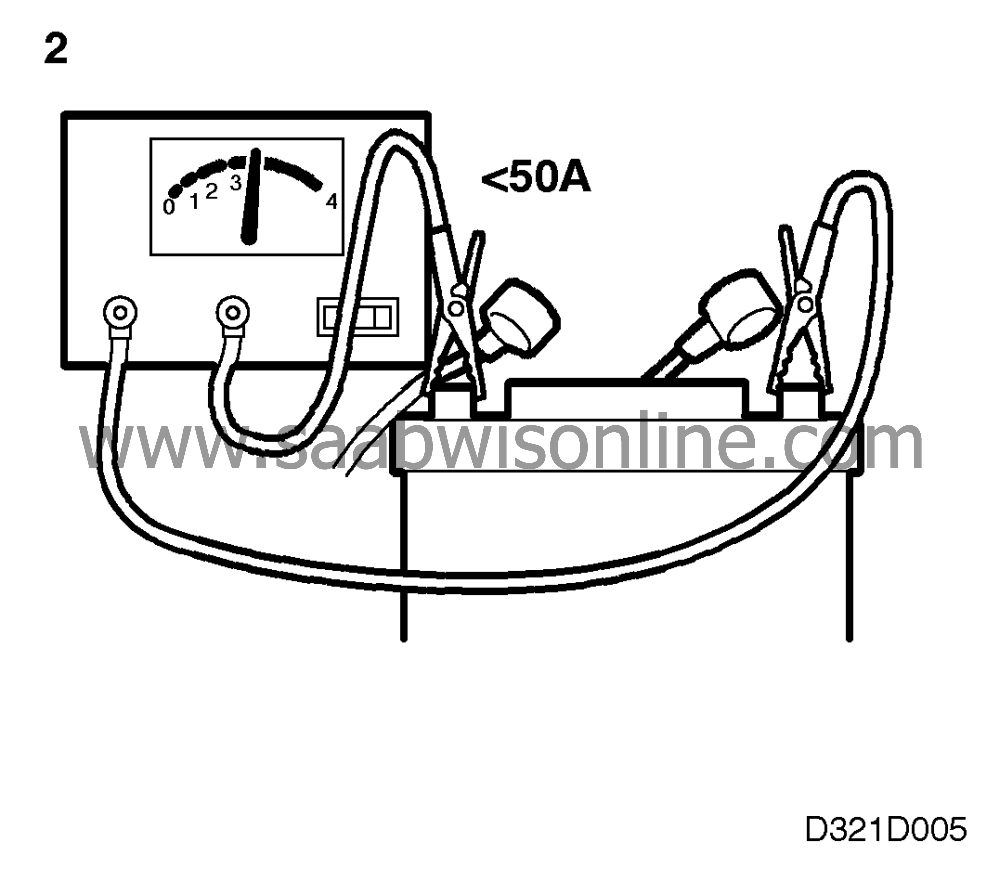
2.
|
If boost-charging is used, the charging current should not exceed
50 A.
|
Important
|
|
Do not boost-charge the battery if its voltage is less than 12 V or if
it is more than two years old.
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
If the battery is almost fully discharged, because a lamp or other
item of electrical equipment has been left on for a relatively long
time, a low initial charge is required to start the chemical process in
the battery.
In such cases, start charging the battery at 3 A (never more than 5 A)
for 24 hours or until the charging current has dropped to its lowest
stable value.
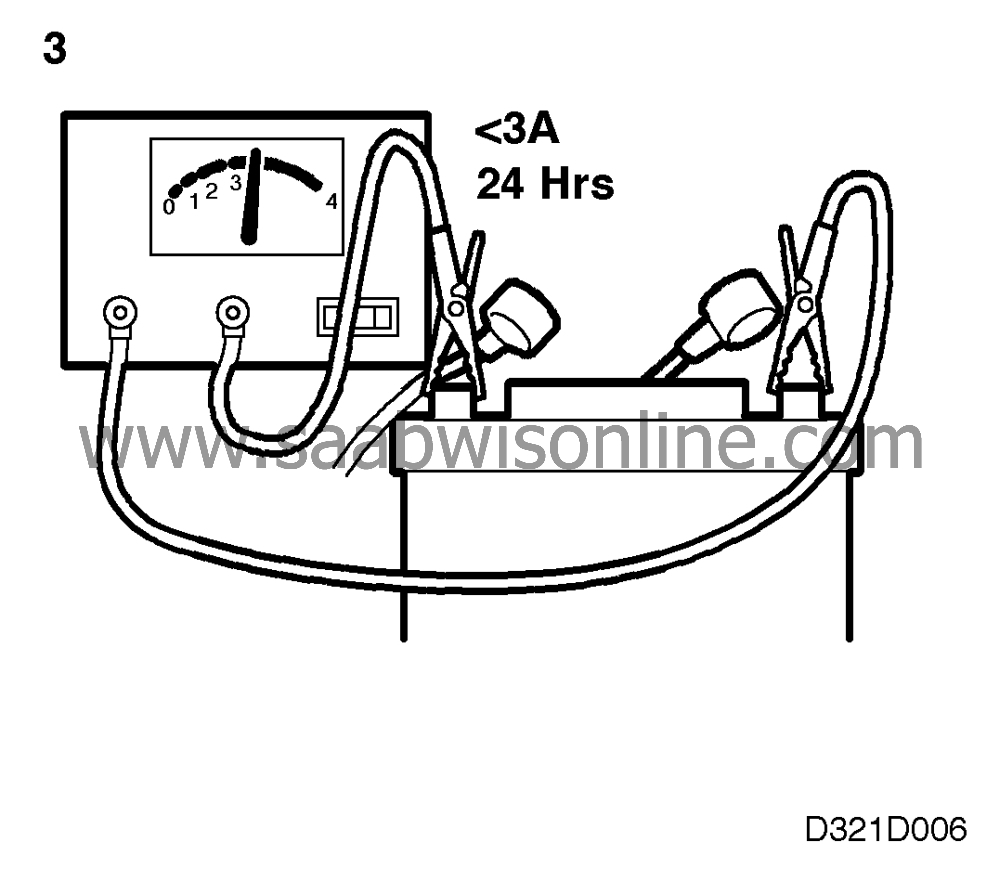
The battery will start to generate gas at 14.4 V. If
the battery is to be charged with a higher voltage it must be cooled
down.
|
A battery charger delivering a pulsating charging current should
preferably be used in the above case.