
Brake servo unit
The brake servo unit reinforces the driver pedal effort when the brakes are
applied. The reinforcement of the applied force achieved through the servo unit is obtained
from the vacuum in the engine intake manifold and amounts to around 3.9:1.
The servo unit is connected to the intake manifold by a hose.
The servo unit consists of a metal reservoir fitted between the brake pedal and the
master cylinder and connected to these by push rods. In the event of a leak in the servo unit,
the two pushrods act as a single pushrod. The brakes then operate without servo assistance,
with the result that a considerably greater pedal effort is required.
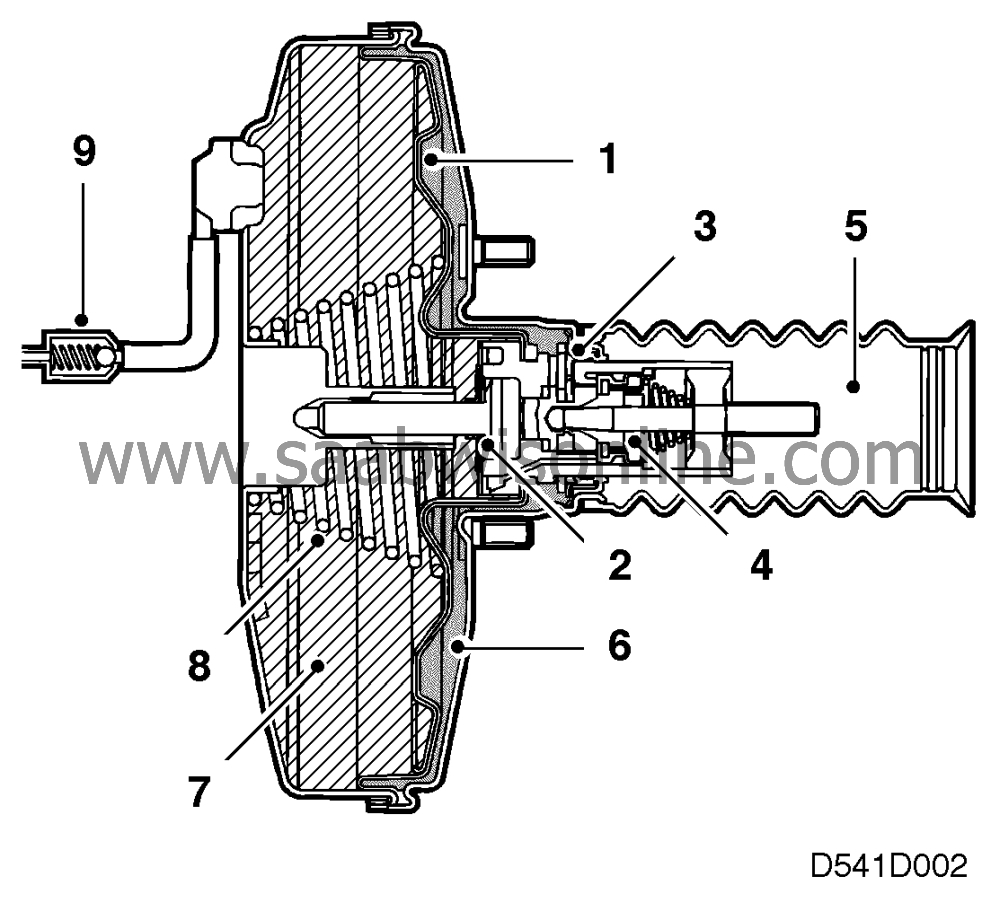
In the brakes off position the air duct (4) is closed and the vacuum chamber (7) is
connected to the working chamber (6) via the open cross over valve (3). Equal vacuum exists
on both sides of the diaphragm (1) in the brake off position.
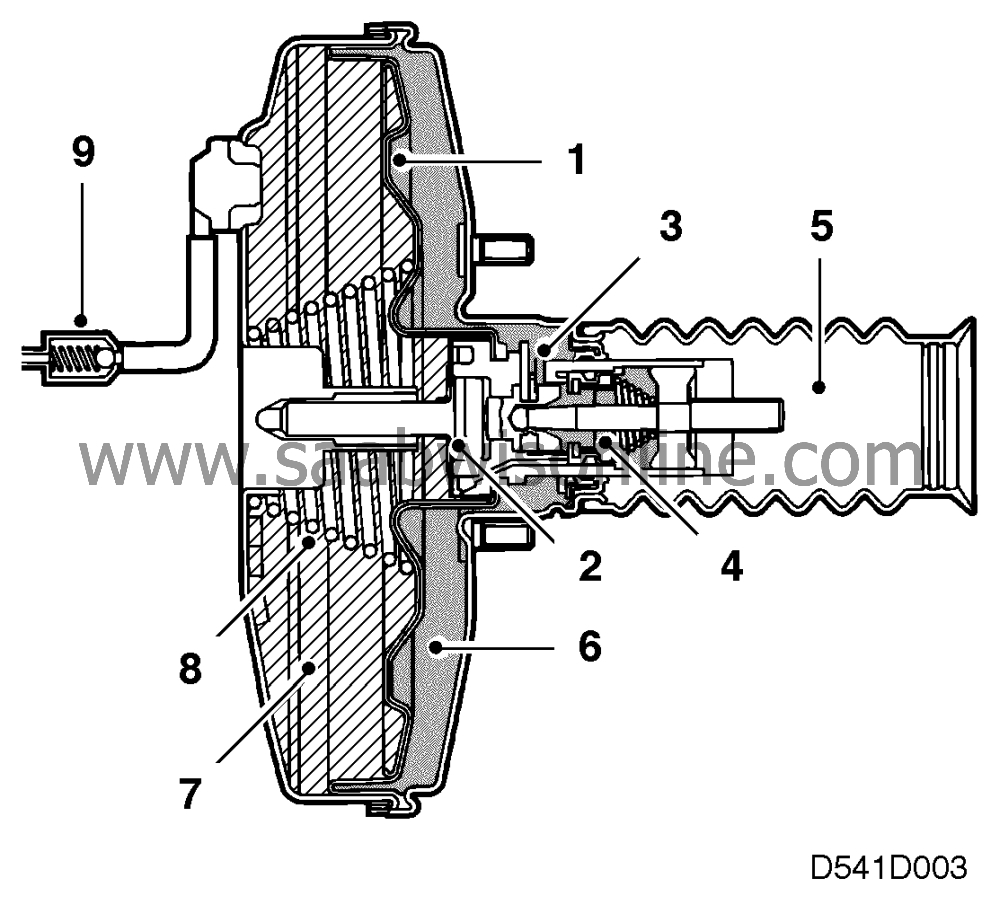
As the brake pedal is depressed the pushrod forces the valve piston and the diaphram
(1) forwards, causing the vacuum passage to close. When the push rod is pressed further, the
valve piston opens a passage (4), which makes it possible for air at atmospheric pressure (5)
to flow through the filter and in behind the diaphragm.
As vacuum from the intake manifold acts in front of the diaphragm, the pressure
difference causes the diaphragm (1) and the pushrod to the master cylinder to be moved
forwards, resulting in reinforcement of the pedal force.
When the pedal force ceases, the vacuum valve opens and air at atmospheric pressure
on the back of the diaphragm flows across to the front and from there through the non-return
valve (9) to the intake manifold. The opening for atmospheric air is closed and the return
spring presses the diaphragm, valve piston and pushrod from the brake pedal back to the
brake off position. The non-return valve prevents air at atmospheric pressure from flowing
back from the intake manifold to the servo unit. The non-return valves only opens when the
vacuum in the intake manifold is greater than in the servo
unit.





