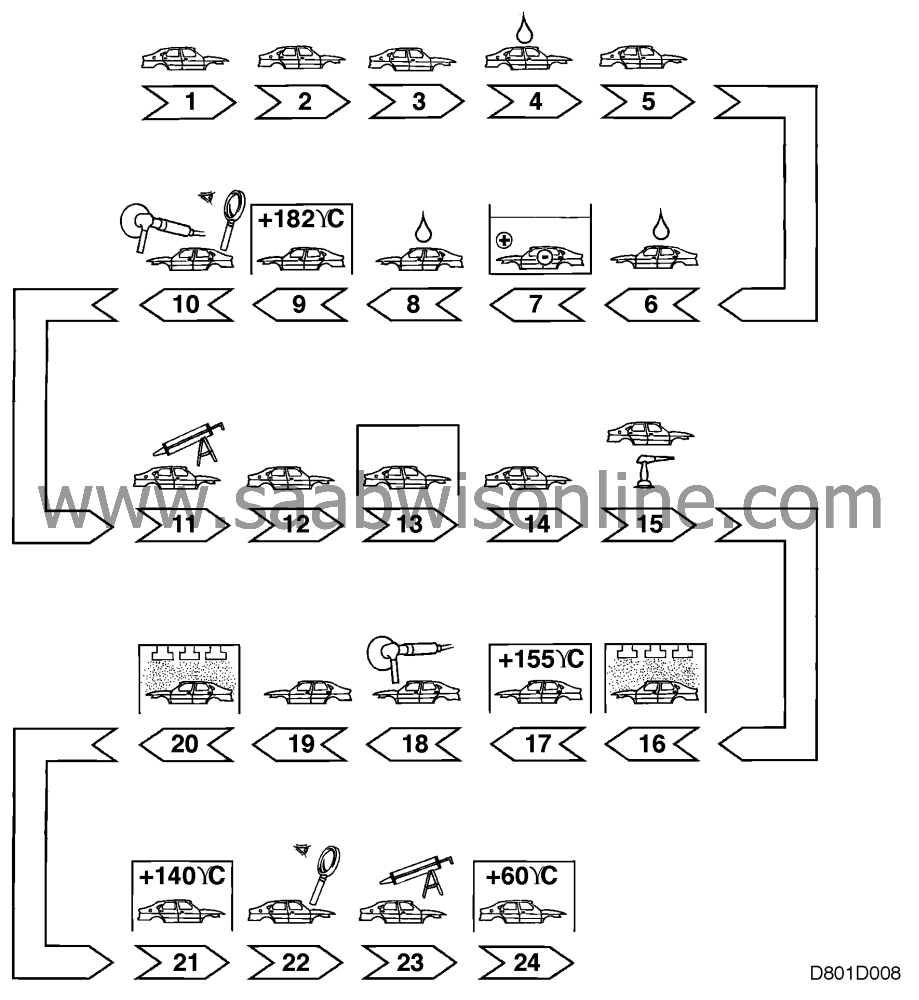
The surface treatment process
|
|
The surface treatment process
|
Corrosion protection measures are begun as early as in the
body shop. Galvanized sheet metal is used for those parts of the car
body that are most exposed to corrosive attacks. See also page
800Ä15.
|
1.
|
Cleaning
the body shell from the body shop.
When the
body shell arrives at the paint shop it goes through an initial coarse
cleaning process. Here all the filings, etc. left over from the
mechanical machining processes are removed as well as most of the oil
and grease that the body has picked up in the body assembly shop.
|
|
2.
|
Degreasing
To obtain as good a foundation as
possible for the subsequent surface treatment, the remaining oil and
grease is removed from the body by means of an alkali degreasant.
|
|
3.
|
Phosphatizing
Phosphatizing gives basic
corrosion
protection as well as a good foundation for the primer.
|
|
4.
|
Rinsing
The body is rinsed to flush away the
remnants
of the phosphatizing process.
|
|
5.
|
Passivation
A chromiferous solution is sprayed
over the
body. This densifies the phosphate layer and so further increases
corrosion protection efficiency.
|
|
6.
|
Rinsing
The body is rinsed with desalinized
water.
|
|
7.
|
Cathodic electrodip (ED)
The body is submersed
in a
bath of anti-corrosion paint and a negative electric charge is applied to the body. The
positively charged paint particles are then attracted to the body in the same way as iron filings
are attracted to a magnet. A layer of
anti-corrosion paint is thus deposited on the entire body surface,
including almost inaccessible places in cavities, joints and the like.
|
|
8.
|
Rinsing
After the ED bath, the body is dipped
and
rinsed clean of surplus paint particles.
|
|
9.
|
Oven drying
The paint from the ED bath dries in
17
minutes at a temperature of +182°C.
|
|
10.
|
Inspection and grinding
Any specks of dust and
paint runs are removed.
|
|
11.
|
Sealing
Seams, folds, joints, etc. are sealed with
PVC
sealing compound throughout the body. The purpose of this is chiefly to
prevent moisture from getting in but the sealant also has a sound- absorbing effect.
|
|
12.
|
Sound absorbing material
Sound absorbing
material is
affixed at strategic points in the body to reduce resonant noise.
|
|
13.
|
Oven drying
The body passes through an IR
oven to
harden the sealant. The sound absorbing material also softens and
shapes itself to the contours of the bodywork.
|
|
14.
|
Cleaning
Dust is removed from the body.
|
|
15.
|
Undersealing
Stone damage protection
compound and
underseal are applied to all bottom pan and wheel arch surfaces.
|
|
16.
|
Undercoat
The undercoat constitutes a good
foundation
for the finish paint as regards both adhesion and appearance. In
addition, it provides additional corrosion protection in that it
affords good protection against stone damage. The paint is applied by means of industrial
robots equipped with rotary spray nozzles. When they rotate, a fine mist of paint is formed
which migrates to the body and settles on it as an extremely even layer of paint. Inside
surfaces which are hard to reach are painted manually.
|
|
17.
|
Oven drying
The undercoat is oven-dried for 32
minutes
at a temperature of +155°C.
|
|
18.
|
Grinding
Any specks of dust and paint runs
rubbed down.
|
|
19.
|
Cleaning
Grinding dust and other foreign
particles are
removed from the body so that it is absolutely clean before the finish
paint is applied.
|
|
20.
|
Finish paint
Just like the undercoat, the finish
paint
is applied by means of industrial robots equipped with rotary spray
nozzles. Metallic paint is applied in two layers. First a thin layer with a high pigment content
and then a thick layer of clear transparent enamel
which protects the pigment and lends a high gloss to the finish
paint.
|
|
21.
|
Oven drying
The finish paint is oven-dried at a
temperature of +140°C.
|
|
22.
|
Final inspection
After painting the body is
carefully
inspected. If any paint runs, scratches, specks of dust or other
imperfections are found, the body is sent to be touched up before
proceeding to the next station.
|
|
23.
|
Anti-corrosion treatment
Penetrating cavity wax
is
sprayed into the cavities in sills, reinforcement members, etc.
|
|
24.
|
Oven
The body is heated up to +60°C for 15
minutes so
that the cavity wax will spread out as much as possible in the cavities.
|