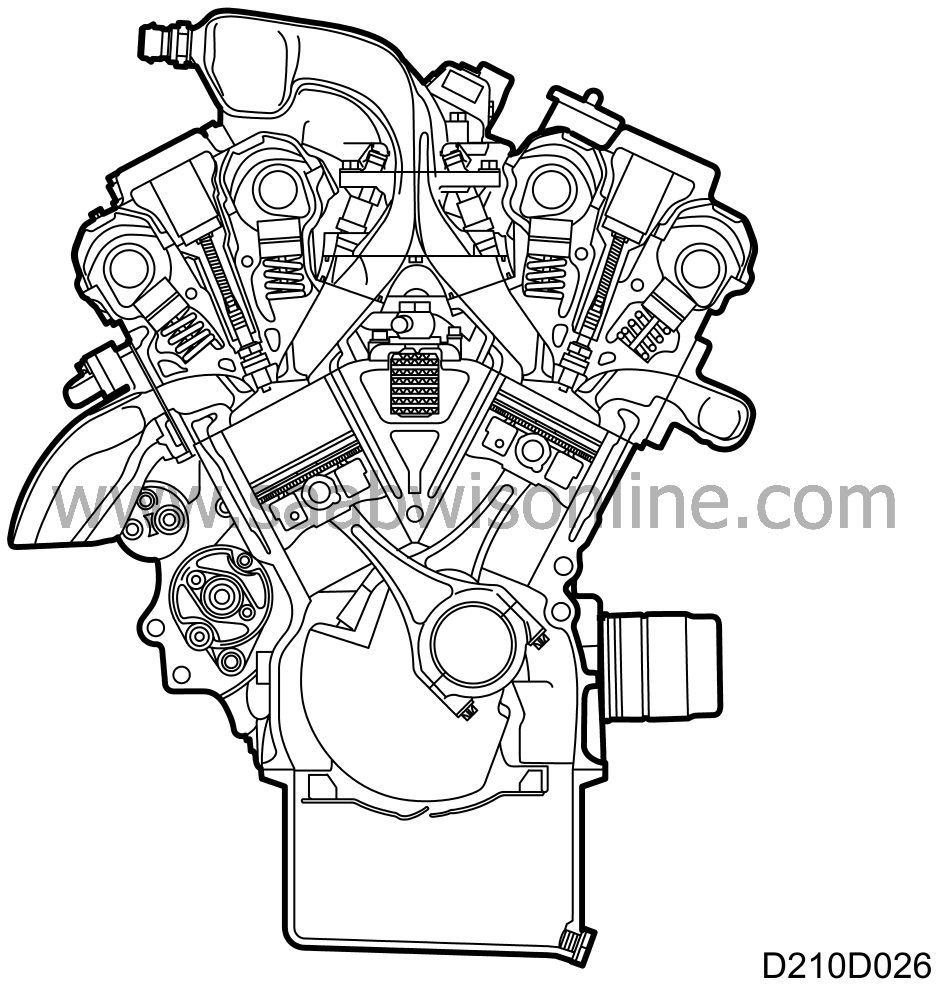
Engine block
| Engine block |
The engines are fuel injected and equipped with the Motronic engine management system.
The camshafts are driven by an internally-cogged belt. The engine has automatic purging of the air in the oilways supplying the oil to the tappets, an integral heat exchanger for the engine oil and a torque member which stabilizes the block round the main bearings.
The heat exchanger has a dual function. It heats the oil when starting from cold and cools the oil when the engine has reached working temperature.
| Cylinder block |

The block is a special one-piece casting with the cylinder bored in the block. Special oilways for the lubricating system are also drilled in the block.
| Pistons |
The pistons are made of light alloy and have grooves for two compression rings and one oil scraper ring.
The top compression ring is flat and coated with molybdenum, the lower compression ring, which is slightly wider than the top one, also has an oil-scraper function. The oil-scraper ring itself is in three parts.
The gudgeon pins are shrunk into the connecting rods and are consequently not of fully-floating type.
| Connecting rods |
All connecting rods are one-piece forgings with a fractural impression or nick at the big end where the connecting rod is "snapped" into two parts, one of which forms the bearing cap. The bearing caps are bolted to the connecting rods. Connecting rod and bearing cap are both marked with a "protuberance" to prevent them being assembled the wrong way round. The connecting rods are not numbered.
| Crankshaft assembly |
The crankshaft has ground journals which are hardened by an induction hardening process. This provides a surface finish with hard-wearing properties.
There are four main bearings. Lubrication is provided through drilled oilways in the crankshaft. All main bearings are replaceable. The No.2 and No.3 main bearings have no grooves in the bearing caps.
The perforated disc, which is part of the engine management system, is bolted to the crankshaft.
| Cylinder head |
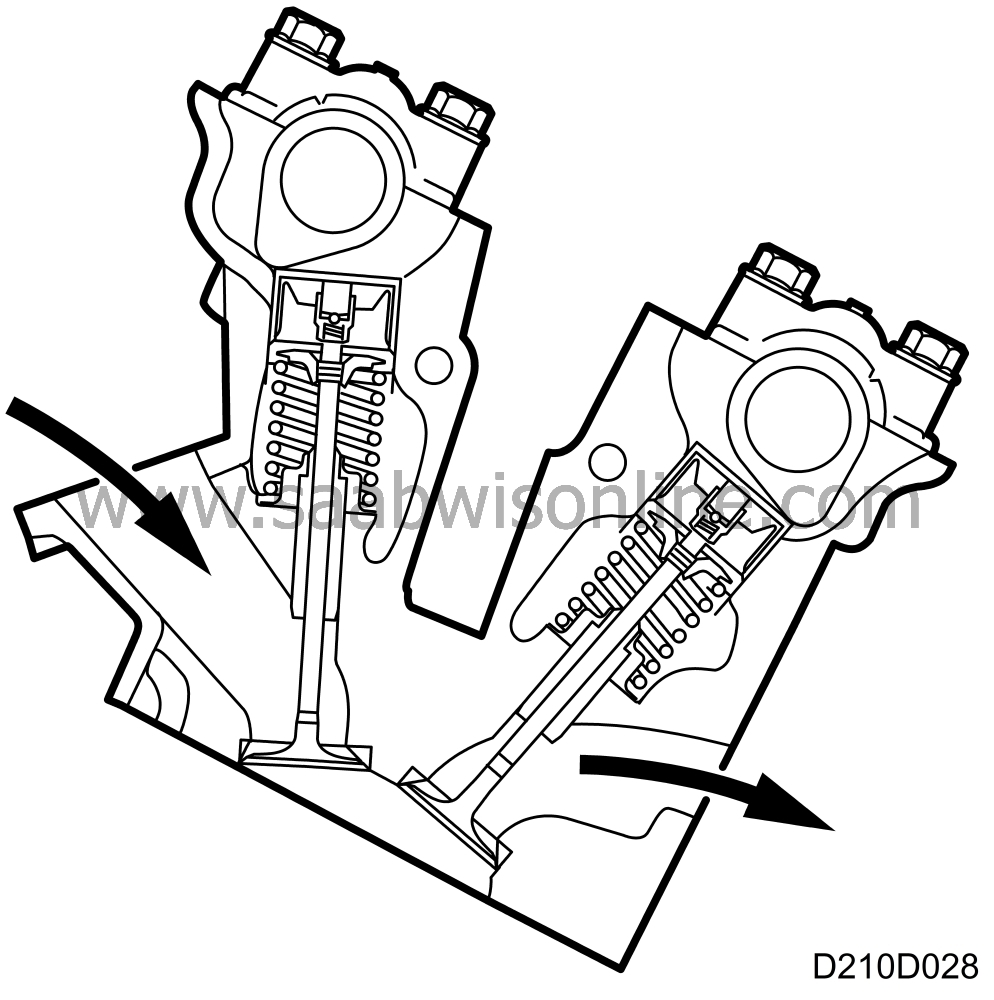
The engine has two cylinder heads, called the rear (cylinders 1,3,5) and the front (cylinders 2,4,6) cylinder heads.
The cylinder heads are light alloy precision castings bolted to the cylinder block. The combustion chambers are hemispherical with four valves per cylinder and the spark plug in the centre. This design improves the flow of gases in the cylinders and also ensures effective combustion of the fuel-air mixture the engine runs at high efficiency.