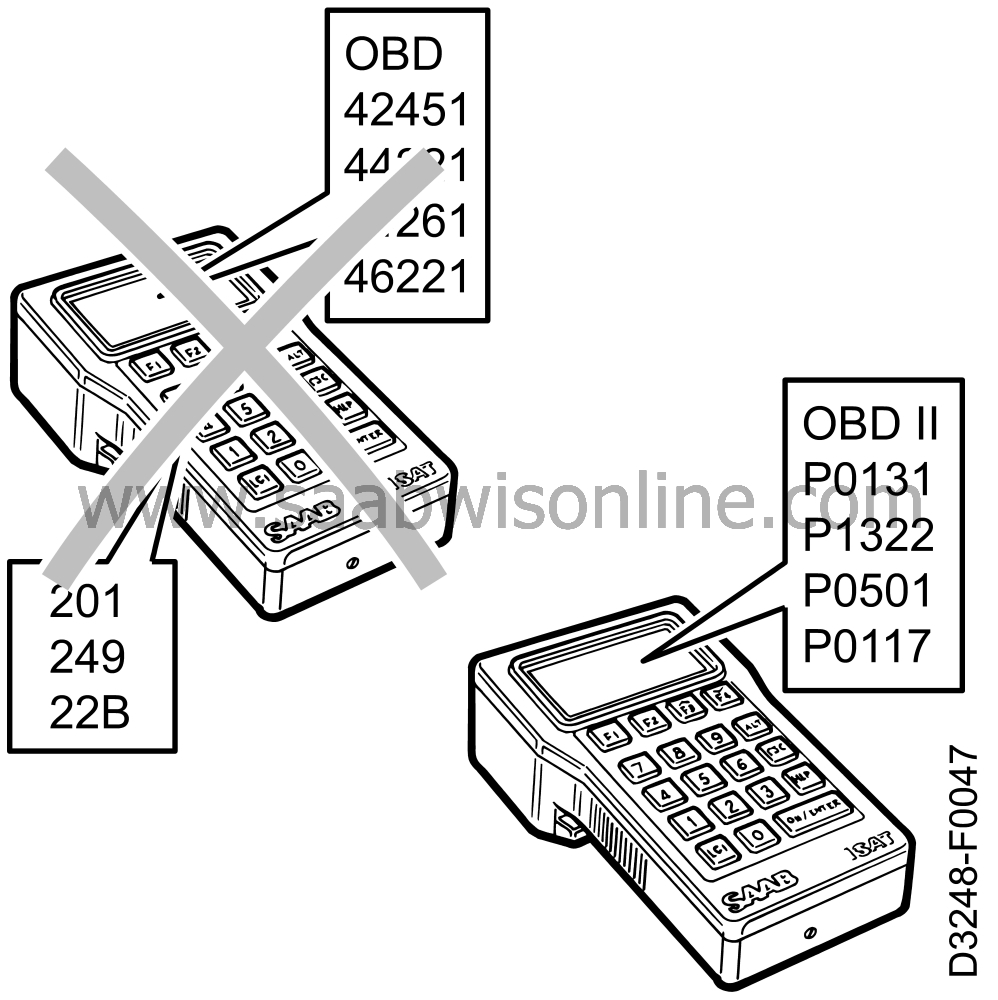
Diagnostic fault codes adapted to newlegal requirements
|
|
Diagnostic fault codes adapted to new
legal requirements
|
Since 1988, motor manufacturers have been required by the
authorities in California (later followed by other countries
around the world) to incorporate "smart" control systems in
the car for the purpose of detecting and localizing emission-
related faults with the aid of OBD (OBard Diagnostics).
From model year 1993 and later cars, the Californian
requirements were further sharpened through the introduction
of OBD II. In part, the new requirements entailed a
standardization of the structure of fault diagnosis and
command codes. This was done in order to achieve a degree of
uniformity between different motor manufacturers and so make
things easier for mechanics and other garage personnel who
work on several different systems and makes of car.
Recommendations for this standardization are to be found in
documents SAE J-2012 (fault codes and documents) and SAE J-
1979 (commands).
In view of the above, the diagnostic trouble codes for the
M1994 MOTRONIC system are different to those we had become
accustomed to earlier when using an ISAT for obtaining
readouts of diagnostic trouble codes.
With the advent of the new diagnostic trouble codes, the previous unique code
for an intermittent fault has been discontinued. This does not mean that it will no longer be
possible to detect an intermittent fault, but the new method of obtaining an intermittent fault
readout is different to the previous method. Basically, the following applies:
|
•
|
CHECK ENGINE lamp on and
diagnostic trouble code = permanent fault
|
|
•
|
CHECK ENGINE lamp out and diagnostic trouble code = intermittent fault
|
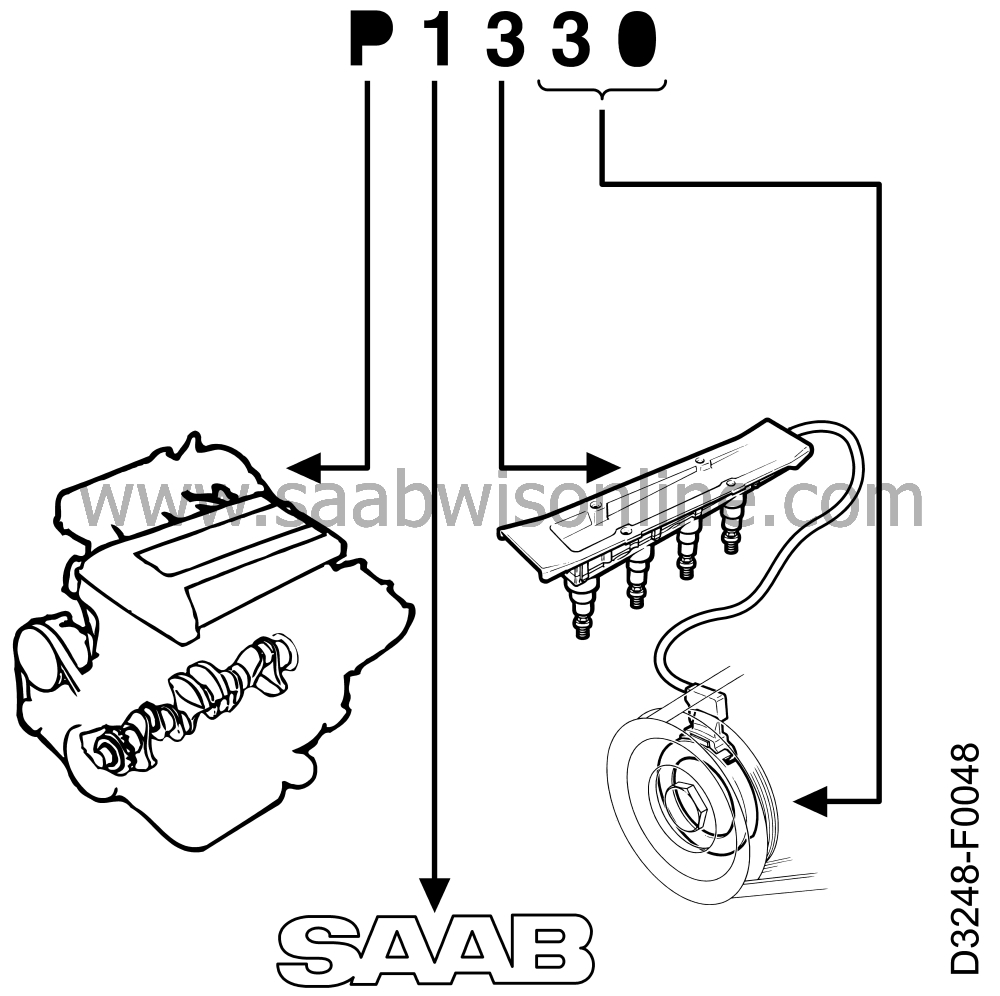 The new diagnostic trouble codes consist of five characters. The first
character is a letter and the other four are figures (e.g. P0111). The letter denotes system
affilation, as follows:
The new diagnostic trouble codes consist of five characters. The first
character is a letter and the other four are figures (e.g. P0111). The letter denotes system
affilation, as follows:
Also used in addition to the above is the letter U
(Undefined), which is in reserve.
The figure after the letter indicates whether the code is
associated with a legal requirement according to SAE (0) or
whether it is a unique manufacturer's code (1 or 2).
The second figure after the letter shows the subsystem in the
relevant main group to which the diagnostic trouble code
refers.
For Power train diagnostic trouble codes, the second figure
signifies the following:
|
•
|
P04xx Exhaust emission control system
|
|
•
|
P05xx Speed/idling control
|
|
•
|
P06xx Control module and control module output signals
|
Finally, the last two figures in the diagnostic trouble code
comprise a serial number which gives each diagnostic trouble
code a unique number in the respective group.