Mass air flow sensor
| Mass air flow sensor |
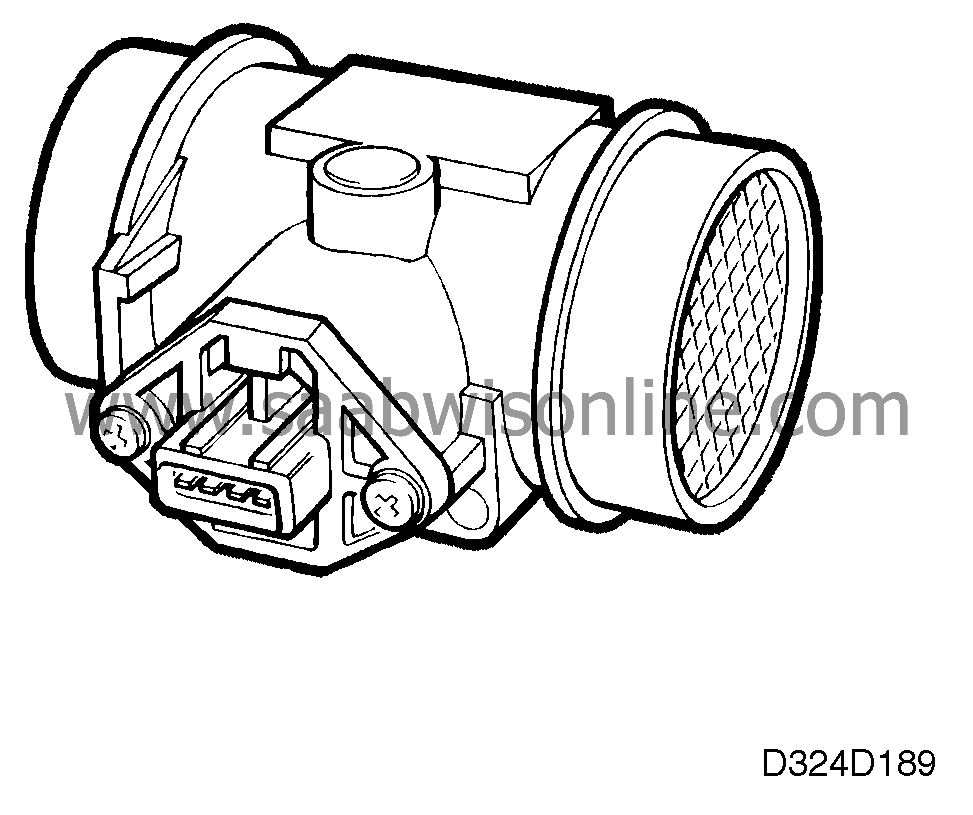
The mass air flow sensor contains a ceramic plate which is positioned in the air flow and heated electrically to 165°C (329°F). When the air flow increases, the heating element requires a higher voltage to maintain the temperature at 165°C (329°F).
The voltage level is used by the control module as a measure of the inflowing air mass and constitutes the principal measured quantity for fuel injection.
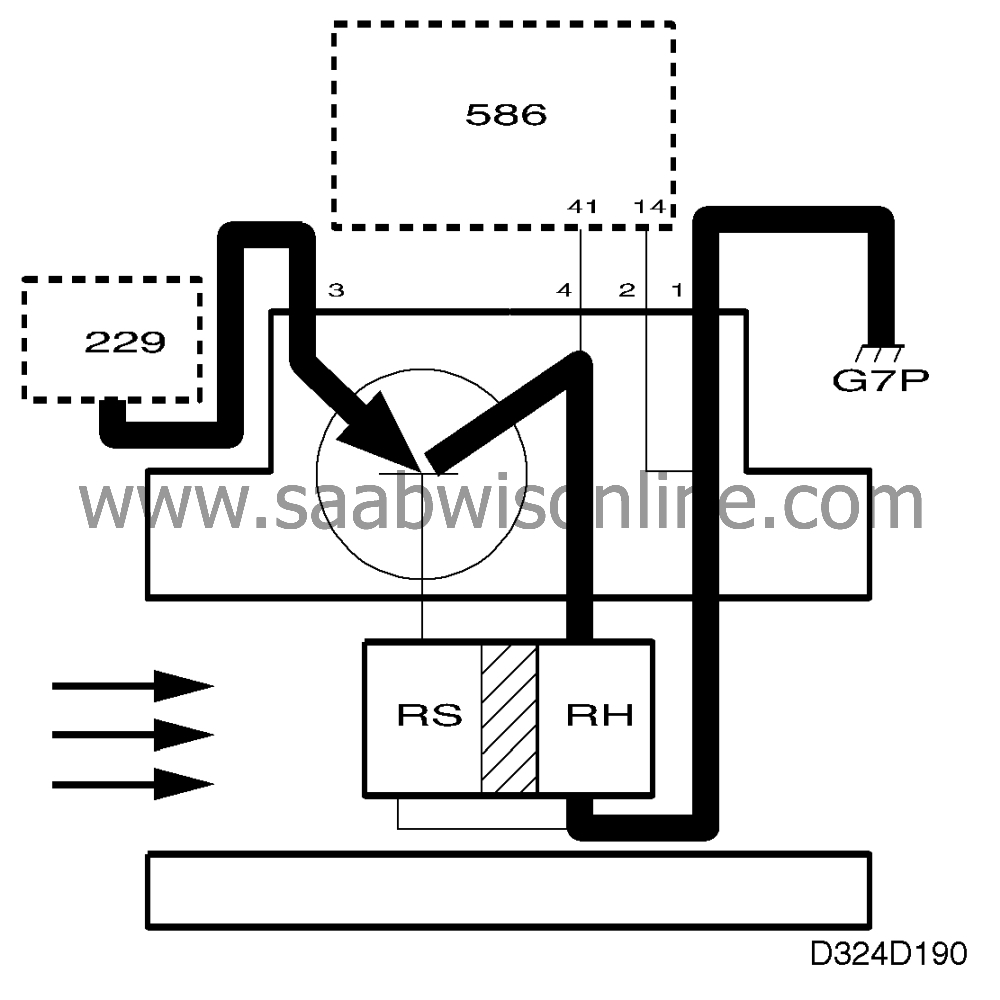
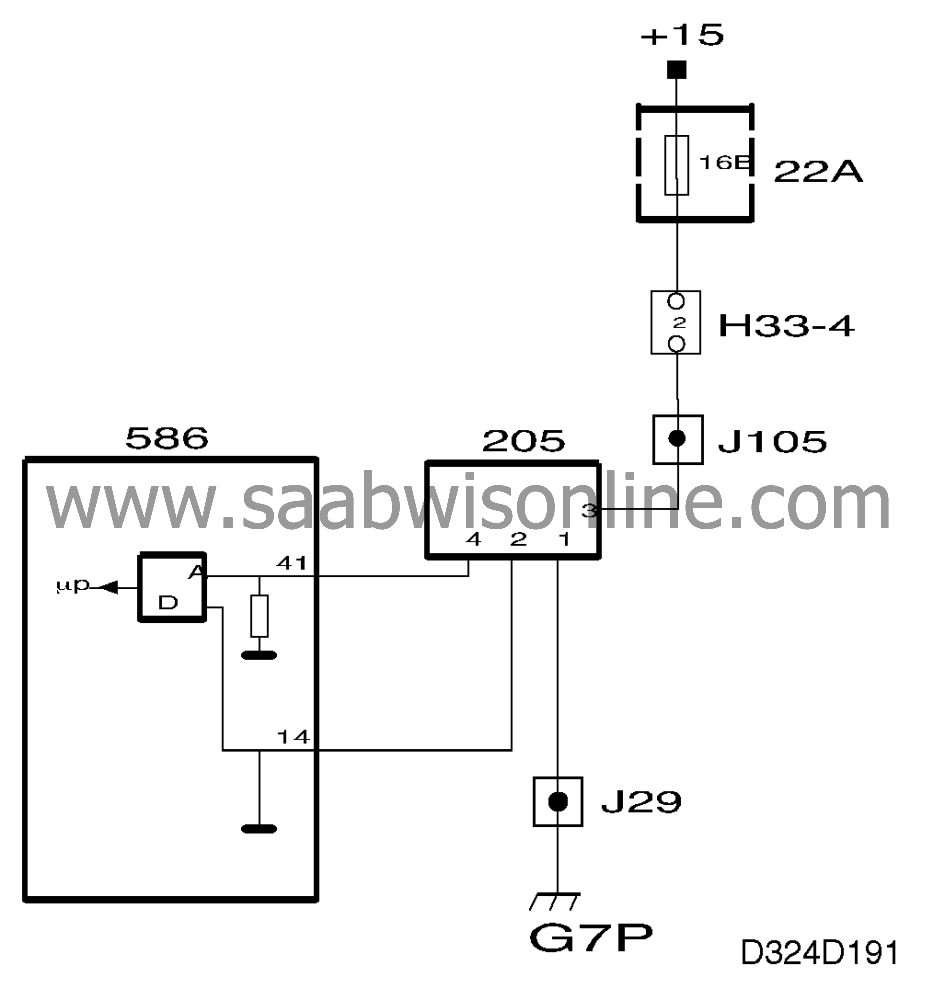
When the ignition switch is turned to the ON position, the main relay supplies battery positive voltage (B+) through the transistor and PTC resistor RS to grounding point G7P. Since RS is cold, the transistor's base current will be high. The transistor will then conduct a heavy current through heating element RH which is baked together thermally with RS in the ceramic plate.
The ceramic plate heats up and the PTC resistor R S reduces the base current through the transistor and thereby also the current through the heating element. The temperature stabilizes at 165°C (329°F).
The ceramic plate is cooled down when air flows past it. The resistance of the PTC resistor drops and the transistor increases the voltage across R H so that the temperature returns to 165°C (329°F).
The voltage across R H goes to pin 41 of the control module.
To measure the voltage with a high degree of accuracy, pin 41 of the control module is connected directly to the mass air flow sensor. The voltage across pins 14 and 41 is a measure of the inflowing air mass.
In the event of a fault in the mass air flow sensor or a break in the circuit (no continuity), the control module uses the input from the throttle position sensor as a substitute value.