P0300
Symptom: The CHECK ENGINE lamp (MIL) is on or flashing. Uneven running when
misfiring.
Misfiring, randomly in several cylinders.
Symptom of fault
The CHECK ENGINE lamp (MIL) is on or flashing. Uneven running when
misfiring.
Conditions
An engine load and speed dependent matrix in the electronic control module's
memory specifies how large a proportion of misfires is required for exhaust emissions to
reach prohibited limits or for the three way catalytic converter to be damaged. If the number of
misfires exceeds the matrix value, a diagnostic trouble code will be generated. Misfiring
occurs in several cylinders.
Diagnostic help
The cause of misfiring could be:
|
•
|
Low fuel level in the tank. If this is
the case it will be indicated by diagnostic trouble code P1416 also being
generated.
|
|
•
|
a fault in the fuel system
low fuel pressure
purge valve open continuously
incorrect voltage from front heated oxygen sensor
defective injectors
|
|
•
|
a fault in the ignition system
defective spark plugs
defective ignition discharge module
|
|
•
|
a fault in the basic engine
poor compression
|
|
•
|
faults in common components
- pressure sensor
- main relay
- coolant temperature sensor.
|
The cause of incorrectly detected misfiring, diagnostic trouble code P0300
without misfiring, could be:
control module pin 17 or 18 shorted to ground
Momentary misfiring can be ascertained using an ISAT scan tool.
|
-
|
Select
"READ FUNCTIONS".
|
|
-
|
Select
"MISFIRING CYLINDER 1".
|
Other cylinders can also be selected.
Checking the wiring. Intermittent faults may occur as a result of occasional short circuits
and breaks in the wiring. Jiggle the leads and in-line connectors at several places and in
different directions to reveal faults in the wiring harness. Observe the multimeter, ISAT scan
tool or test lamp while carrying out this check.
Diagnostic procedure
1. Check additional Trionic diagnostic trouble codes.

|
-
|
Obtain readouts of all diagnostic
trouble codes using the ISAT scan tool.
|
Are any of the above diagnostic trouble codes present?
Continue fault diagnosis for the relevant diagnostic trouble
code.
Continue with point 2.
|
Note
|
|
P1171 can be caused by persistent
misfiring.
|
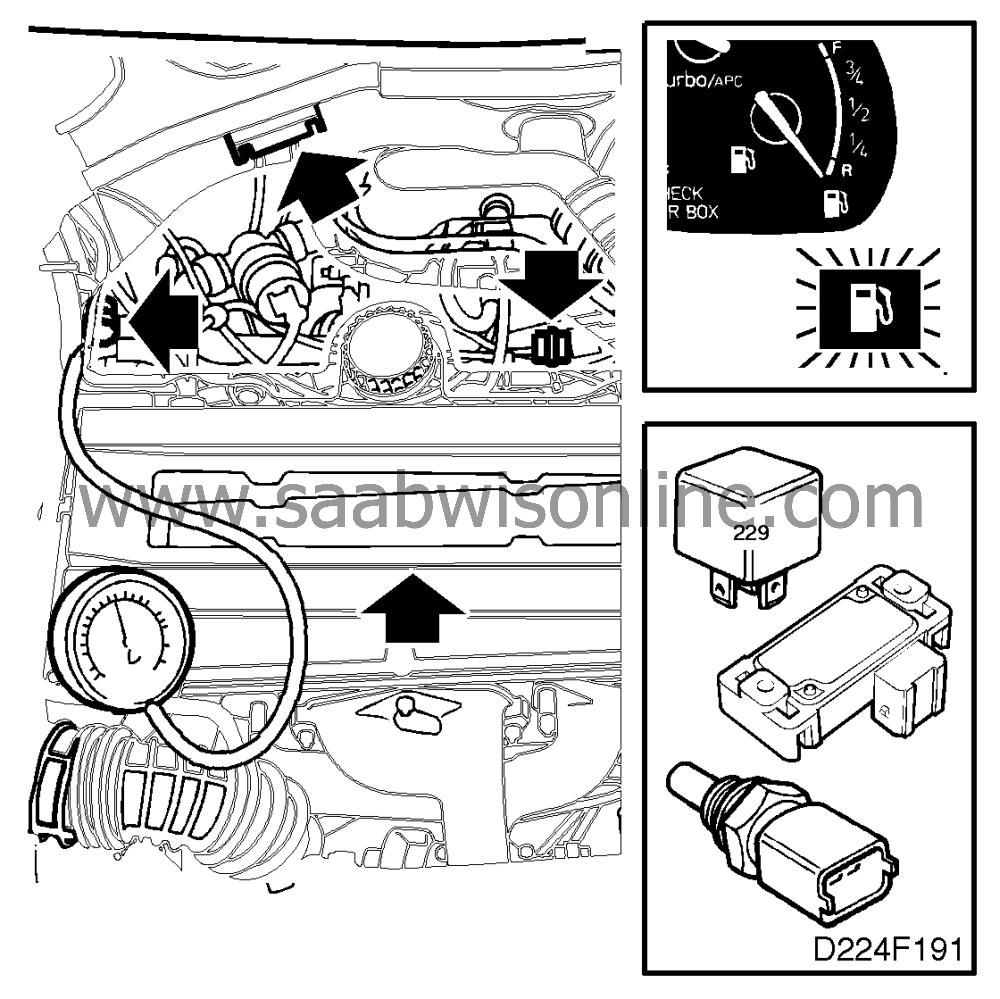
2. Check the basic causes of the
fault
|
-
|
Inspect the vacuum hose between
the pressure sensor and intake manifold.
|
|
-
|
Check the pressure sensor's
electrical connections for moisture and corrosion. Also check that the seal in the female
connector is present and undamaged.
|
|
-
|
Inspect the vacuum hose between
the fuel pressure regulator and intake manifold.
|
|
-
|
Using an ISAT scan tool, check
that the coolant temperature is plausible.
|
|
-
|
Using an ISAT scan tool, check
that the operation of the pressure sensor is plausible:
|
With the ignition switch in the ON position, the reading obtained on the ISAT
scan tool should be about 102 kPa (NOTE: the reading is dependent on air pressure).
With the engine idling, the reading obtained on the ISAT scan tool should be 40-60
kPa.
|
-
|
Check the wiring connected to the
front heated oxygen sensor for shorting, continuity and chafing of the
insulation.
|
|
-
|
Check the front heated oxygen
sensor's connector for moisture and corrosion.
|
Have any of the basic causes of the fault been found?
Rectify the fault and proceed to point 8.
Continue with point 3.
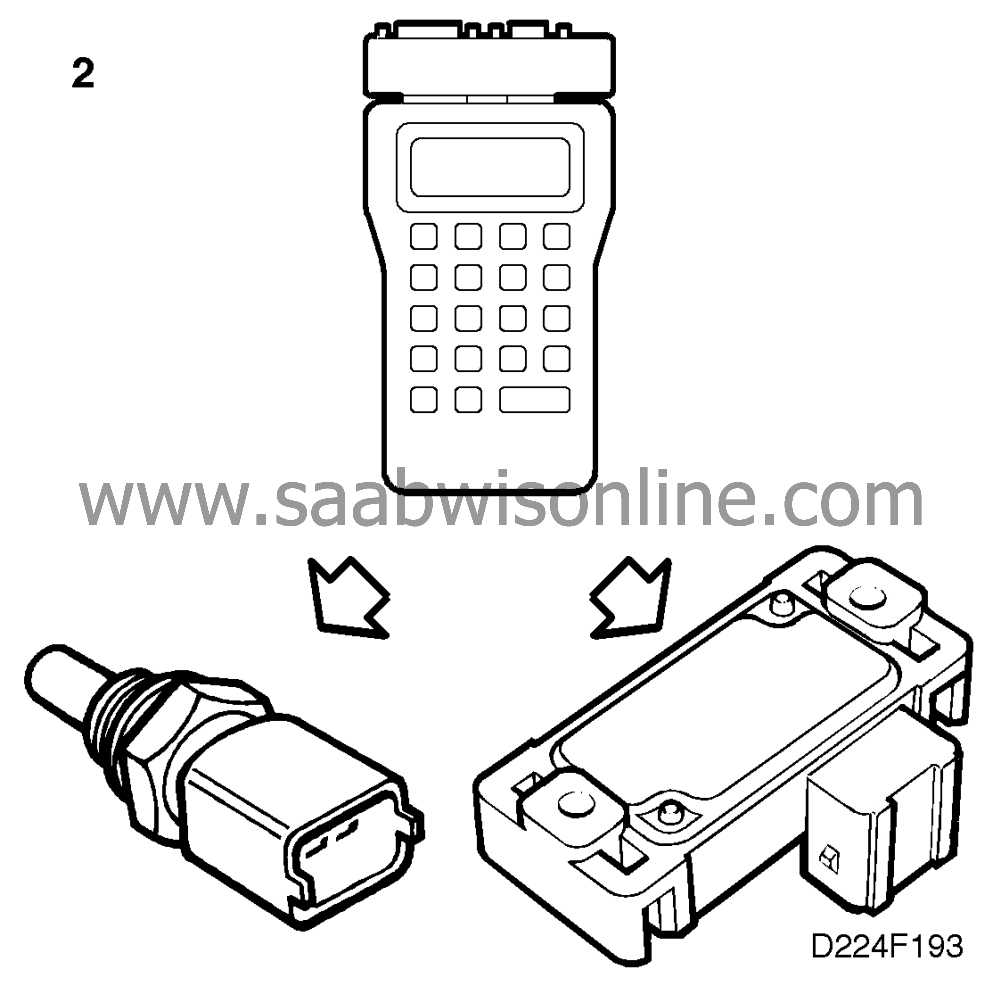
3. Check the condition of the ignition discharge
module
|
-
|
Remove the ignition discharge
module from the camshaft cover.
|
|
|
•
|
that the four rubber seals for the
spark plugs are in good condition.
|
|
|
•
|
that no contact spring for the spark plugs is missing or that spring travel is
inadequate.
|
|
|
•
|
the connector for moisture and corrosion
|
Is the ignition discharge module OK?
Continue with point 4.
Rectify the fault and proceed to point 4.
4. Check the spark plugs
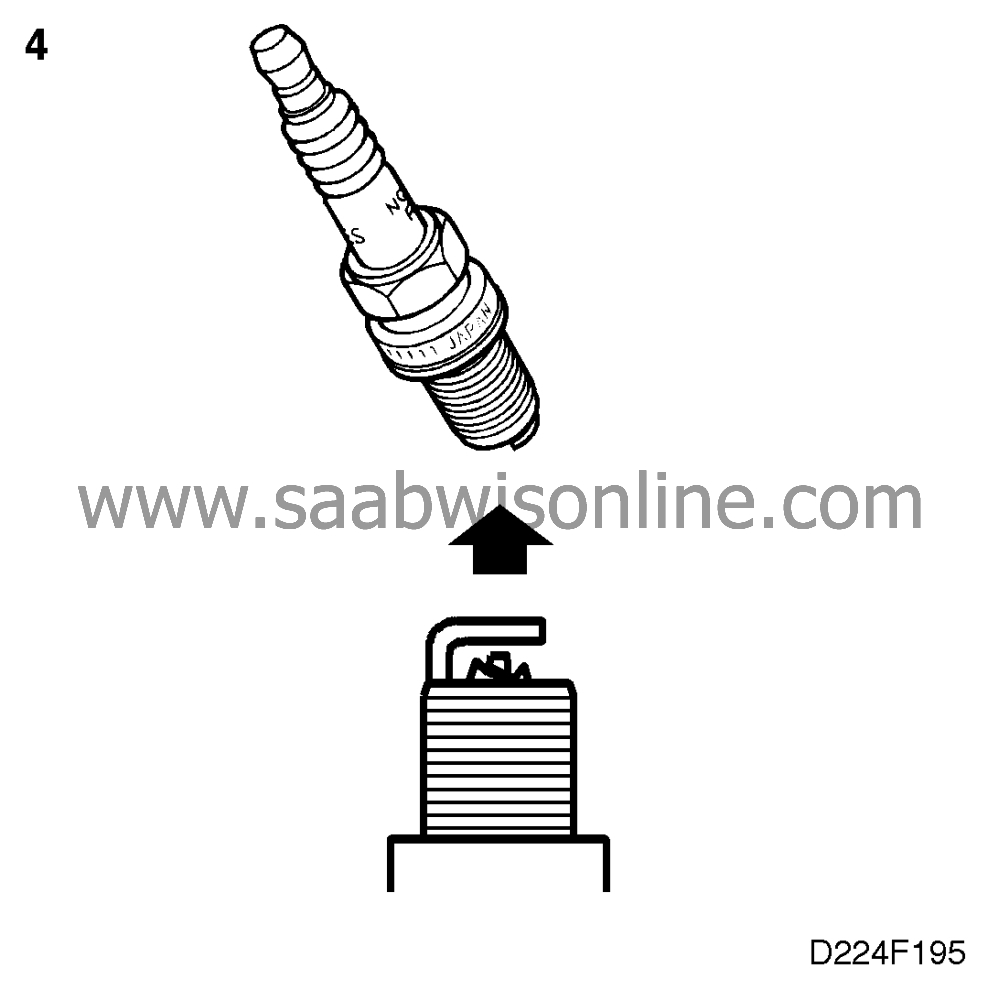
|
-
|
Remove the spark plugs and check
their condition visually.
|
Are the plugs OK?
Continue with point 5.
The electrode gap is wider than 1.4 mm or is otherwise obviously incorrect.
Change the spark plugs and proceed to point 8.
5. Check the operation of the ignition discharge
module
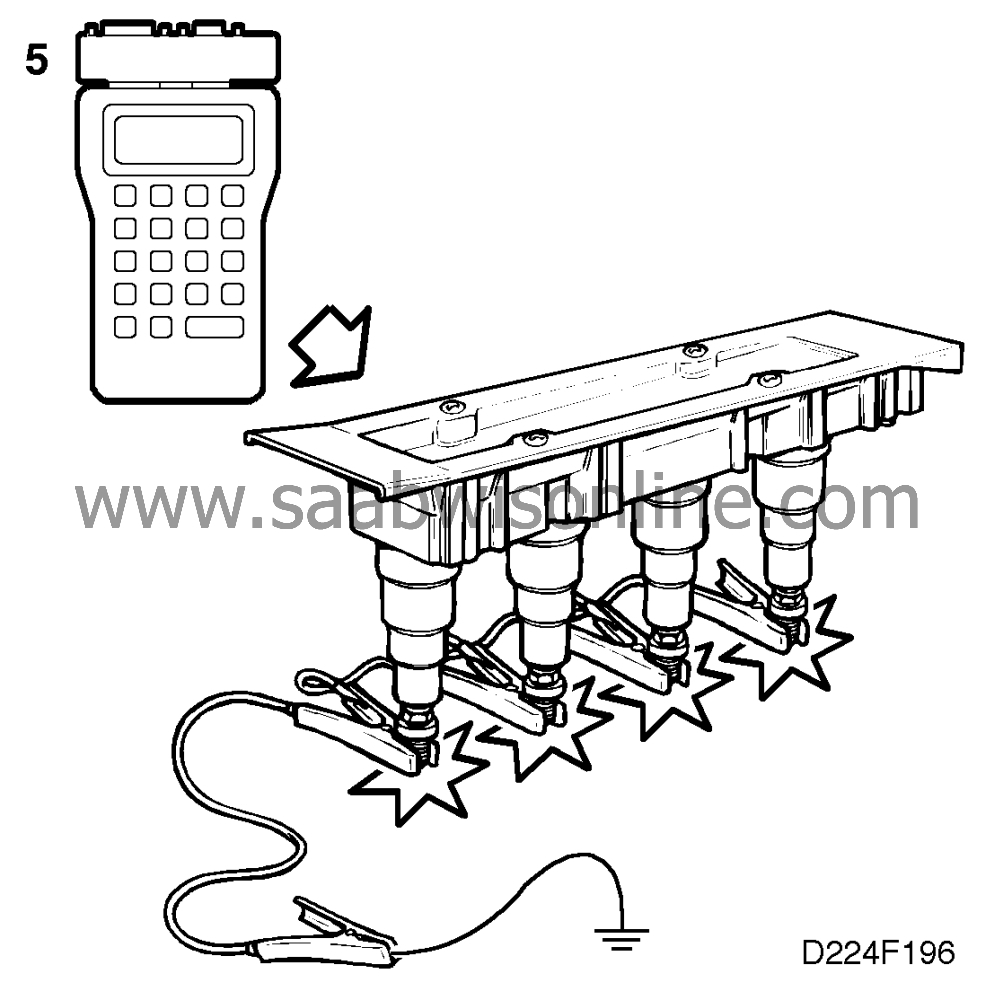
|
-
|
Fit test spark plugs (part No. 86 11
386) in the ignition discharge module.
|
|
-
|
Ground the spark plugs using test
cable 86 10 867.
|
|
-
|
Activate each separate ignition coil,
using the ISAT scan tool.
|
|
-
|
Ignition switch in ON
position.
|
|
-
|
Select
"IGNITION COILS"
|
|
-
|
Select
"IGNITION CYL 1", "CYL 2", "CYL 3" and "CYL 4".
|
Activation of an ignition coil takes place for 10 seconds at 200 Hz. If a longer
activation time is required, the command must be repeated.
|
-
|
Check that each activated spark
plug produces a spark.
|
Is a spark produced?
Continue with point 6.
Change the ignition discharge module and proceed to point
8.
 Warning
Warning
|
|
The electronic ignition system generates up to 40,000 Volts. Such voltages can prove
fatal to people with weak hearts or those who are fitted with a pacemaker. All due caution
should therefore be observed when carrying out any work involving the ignition system.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Important
|
|
The ignition discharge module must be positioned with the ignition coils facing down
during the test so that the transformer oil will provide good insulation in the high-voltage part of
the ignition coils.
|
|
|
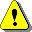
6. Check the compression
|
-
|
Check the compression of each
cylinder.
|
Is compression OK?
Change all spark plugs and continue with point 7.
Continue fault diagnosis as described in Service Manual 2:1 "Basic
engine".
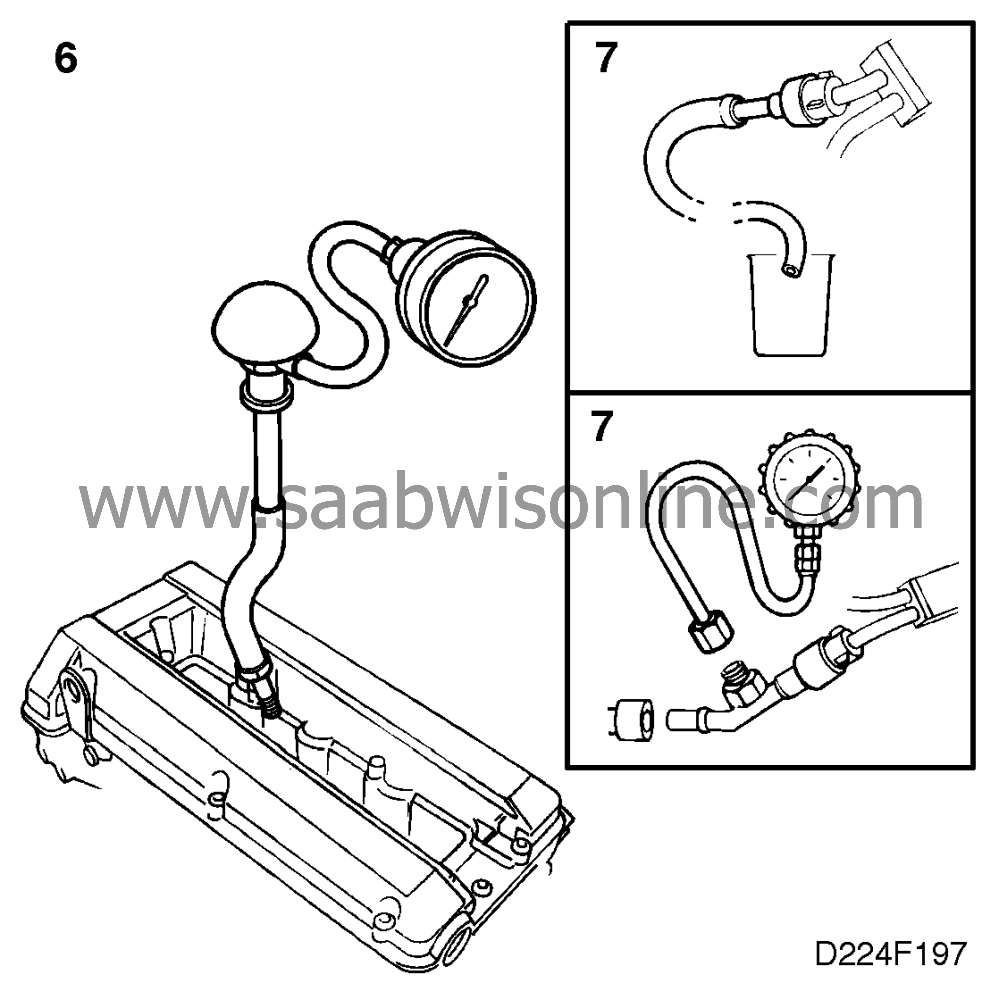
7. Check the fuel system
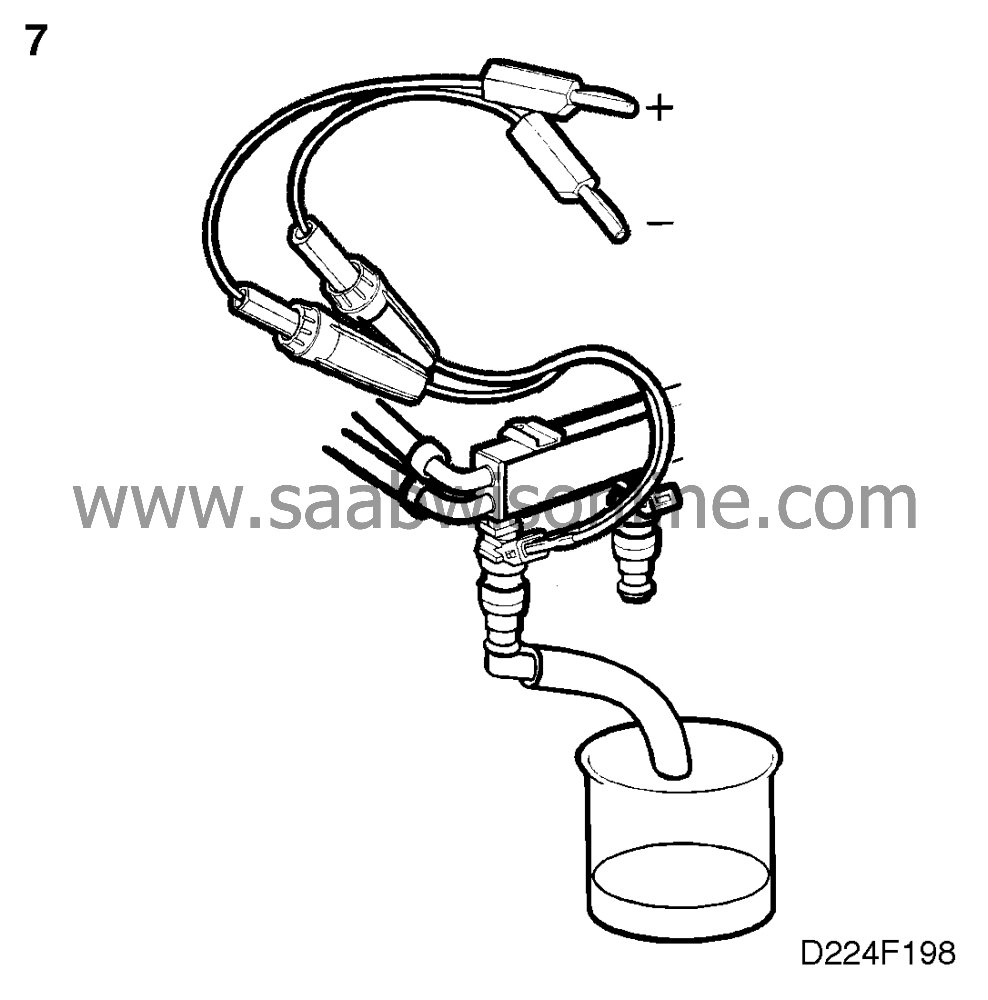
|
-
|
Carry out fuel pressure and fuel
flow measurement on the fuel pump and all the injectors.
|
Is the fuel system OK?
Continue with point 8.
Rectify the fault and proceed to point 8.
8. Final check:
|
-
|
Clear the diagnostic trouble
code
|
|
-
|
Implementation of driving cycle:
Drive the car at different engine rpm and varying loads, especially at high revs, while the
engine is warming up.
|
|
-
|
Evaluation of driving cycle: Check
whether the diagnostic trouble code has recurred.
|
Has the diagnostic trouble code recurred?
Proceed to
 .
.
The remedial measure taken was correct.










 Warning
Warning


