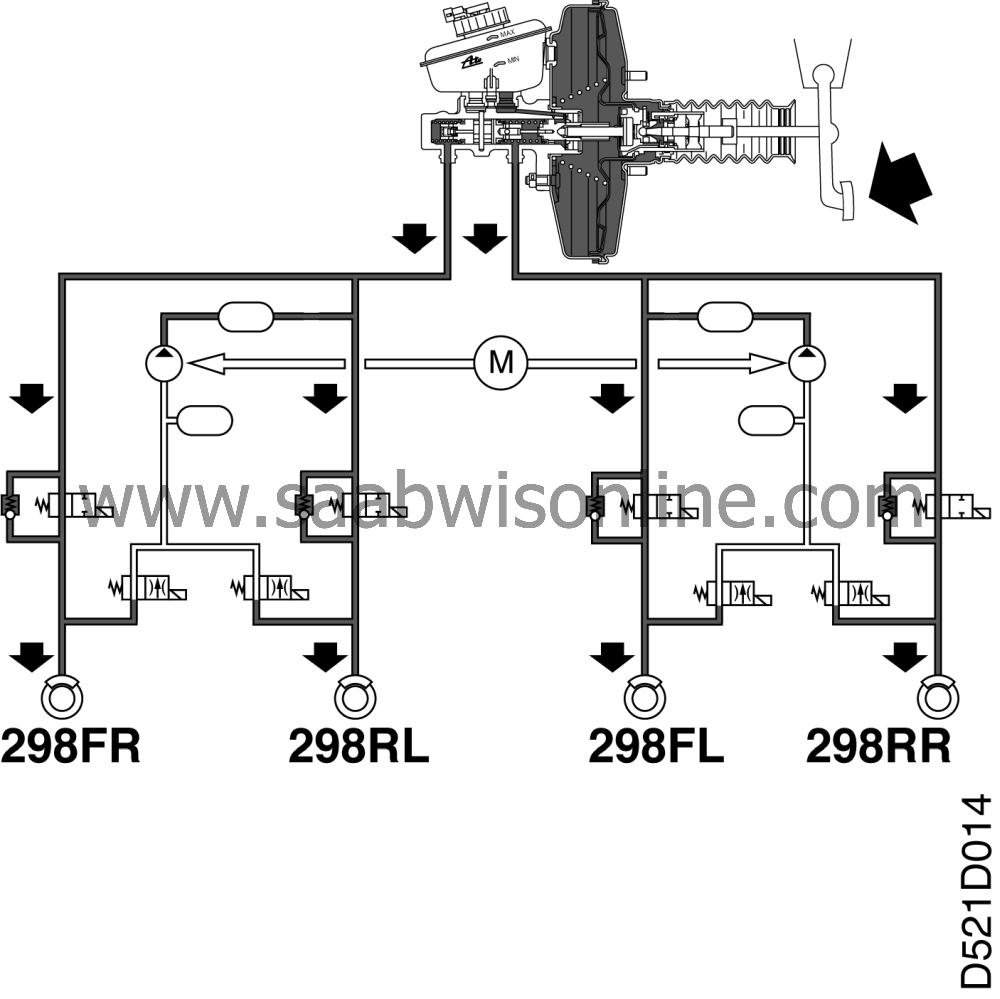
Brakes applied without ABS modulation
| Brakes applied without ABS modulation |
The primary piston closes the return passage to the brake fluid reservoir and pressure mounts in front of the primary piston. The pressure also effects the secondary piston that is pushed forwards causing the central valve of the secondary piston to close.
The hydraulic pressure in both circuits increases, and as the pistons have the same area, the pressure through the valve block is equal in both brake circuits.
The pressure is propagated through the brake system and acts on the brake piston in each brake housing. The brake pistons force the brake pads against the brake discs. When the brake pedal is released, the pistons in the master cylinder are returned and the central valves open. The pressure drops and the brake piston in each brake caliper stays in the brake off position aided by the piston sealing rings.