EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)
|
|
EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)
|
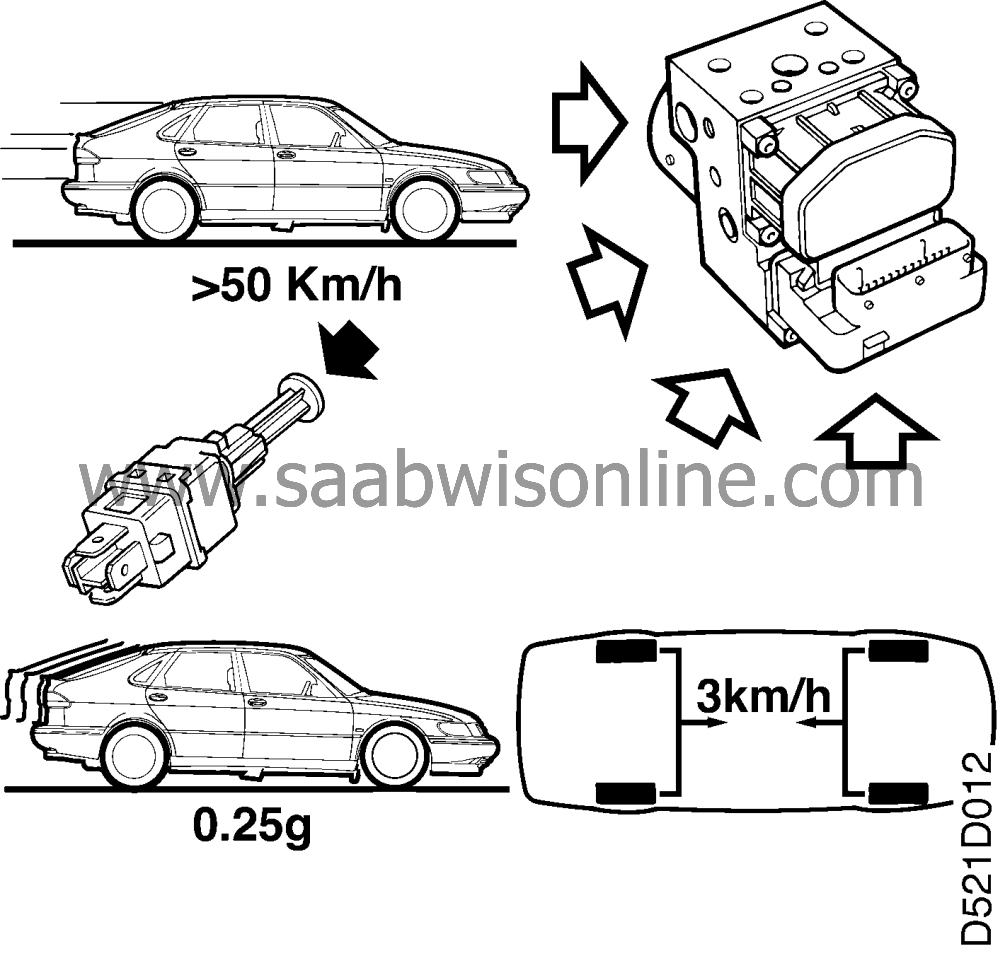
EBD is a function built into the electronic control module that can be compared to a load sensing valve for the rear wheel brakes. To get the best possible braking performance it is important that both the front and rear wheels get the optimum braking action under all conditions and loads.
It is important for good course stability that the rear wheels do not lock first when braking. To achieve this under varying load conditions (i.e. a heavily loaded vehicle demands stronger braking action before the wheels lock) the electronic control module uses the wheel velocity and controls the rear wheel braking operation with the solenoid valves so that the permitted slip between the front and rear wheels does not exceed 3 km/h.
The EBD should come into operation when the following criteria are met:
|
•
|
The vehicle speed should be higher than 50 km/h.
|
|
•
|
The brake light switch signals to the electronic control module that the brakes are activated.
|
|
•
|
The retardation is greater than 0.25 G.
|
|
•
|
The slip on the rear wheel compared to the slip on the front wheel is greater than 3 km/h.
When the above criteria are met the intake valve closes for both the rear wheels and the EBD operation is activated to control slippage between the front and rear wheels until it is lower than 3 km/h. If the rear wheels lock, normal ABS-control operates on those wheels.
|