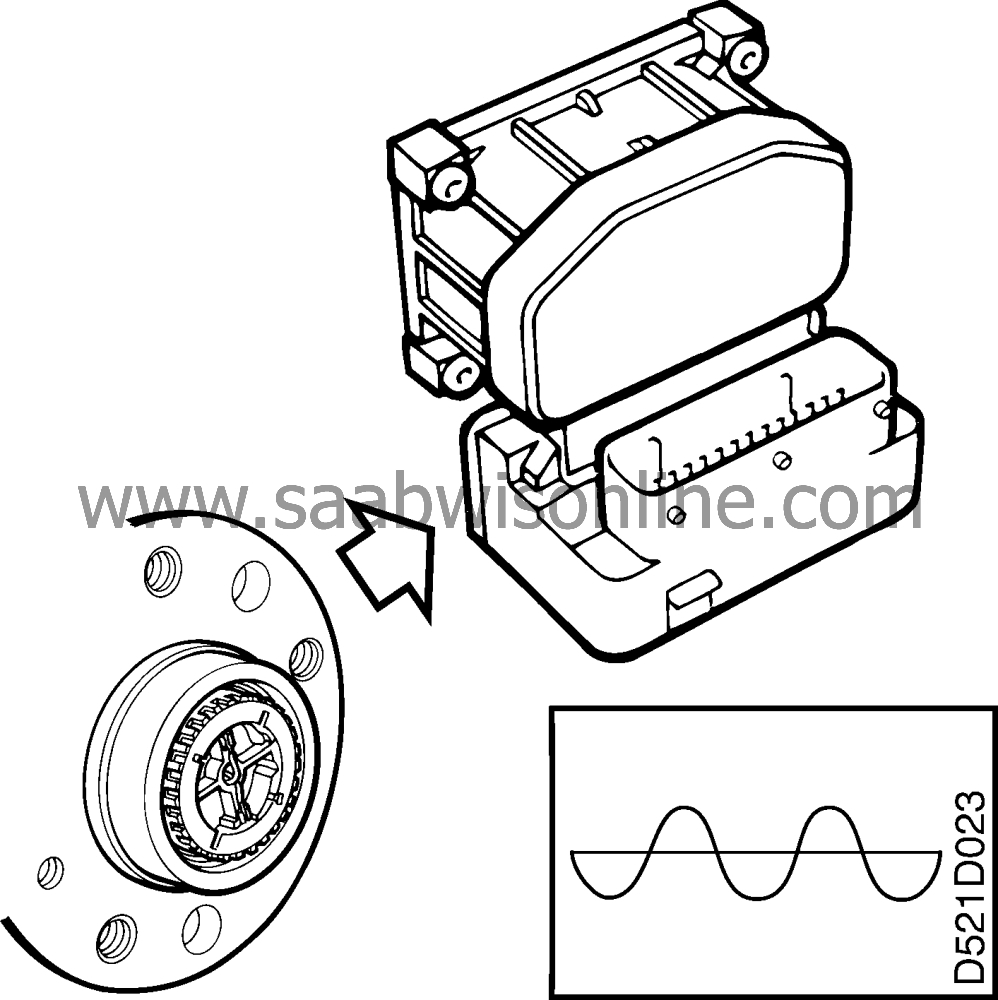
Wheel sensors, rear
| Wheel sensors, rear |
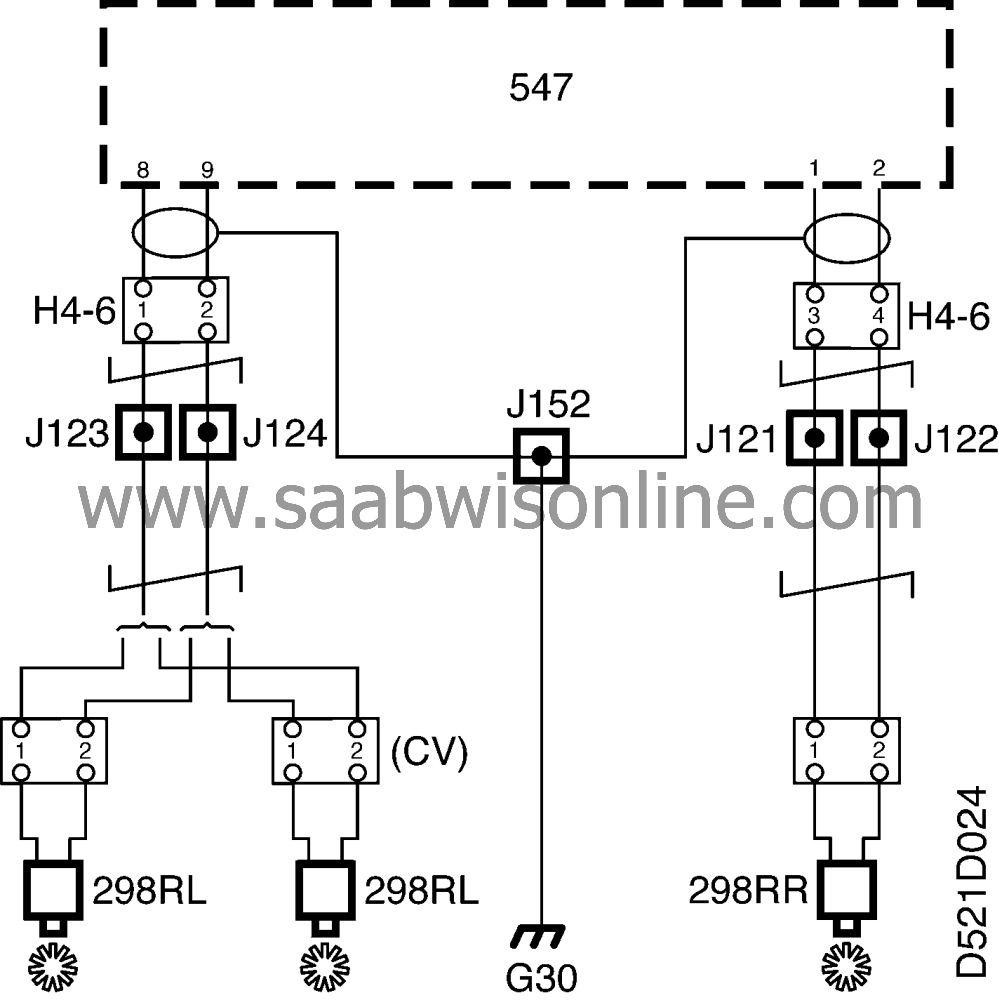
The electronic control module receives wheel speed information from the rear left wheel sensor at pin 9. The sensor is grounded at pin 8.
The electronic control module receives wheel speed information from the rear right sensor at pin 2. The sensor is grounded at pin 1.
The wheel sensors are integrated into the wheel hubs and consist of an inductive sensor with 29 teeth.
The inductive sensor works like a small alternator, the sine-wave voltage of which increases with increasing wheel speed. The sine-wave voltage alternates between negative and positive polarity, which is achieved by alternate teeth and gaps on the toothed wheel.
The wheel sensors are designed differently from the front wheel sensors and are not as sensitive to wheel bearing play. Using a multimeter set at AC attached to the two conductors of the sensor it should be possible to register a voltage of >100 mV when the wheel is rotated 1 turn per second.
A wheel speed of 20 km/h will produce about 5V∼.
If the sensor should fail, or an open-circuit occurs in the circuit the ABS function disengages and the ABS lamp comes on.