INSPECTION
| INSPECTION |
| CYLINDER BLOCK |
Visually check for cracks and damage. Especially, inspect the important parts by means of red lead check.
Check the oil passages for clogging.
Inspect the crankcase surface that mates with cylinder head for warping by using a straight edge, and correct by grinding if necessary.
Warping limit:
0.025 mm (0.00098 in)
Grinding limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Standard height of cylinder block:
201.0 mm (7.91 in)
| CYLINDER AND PISTON |
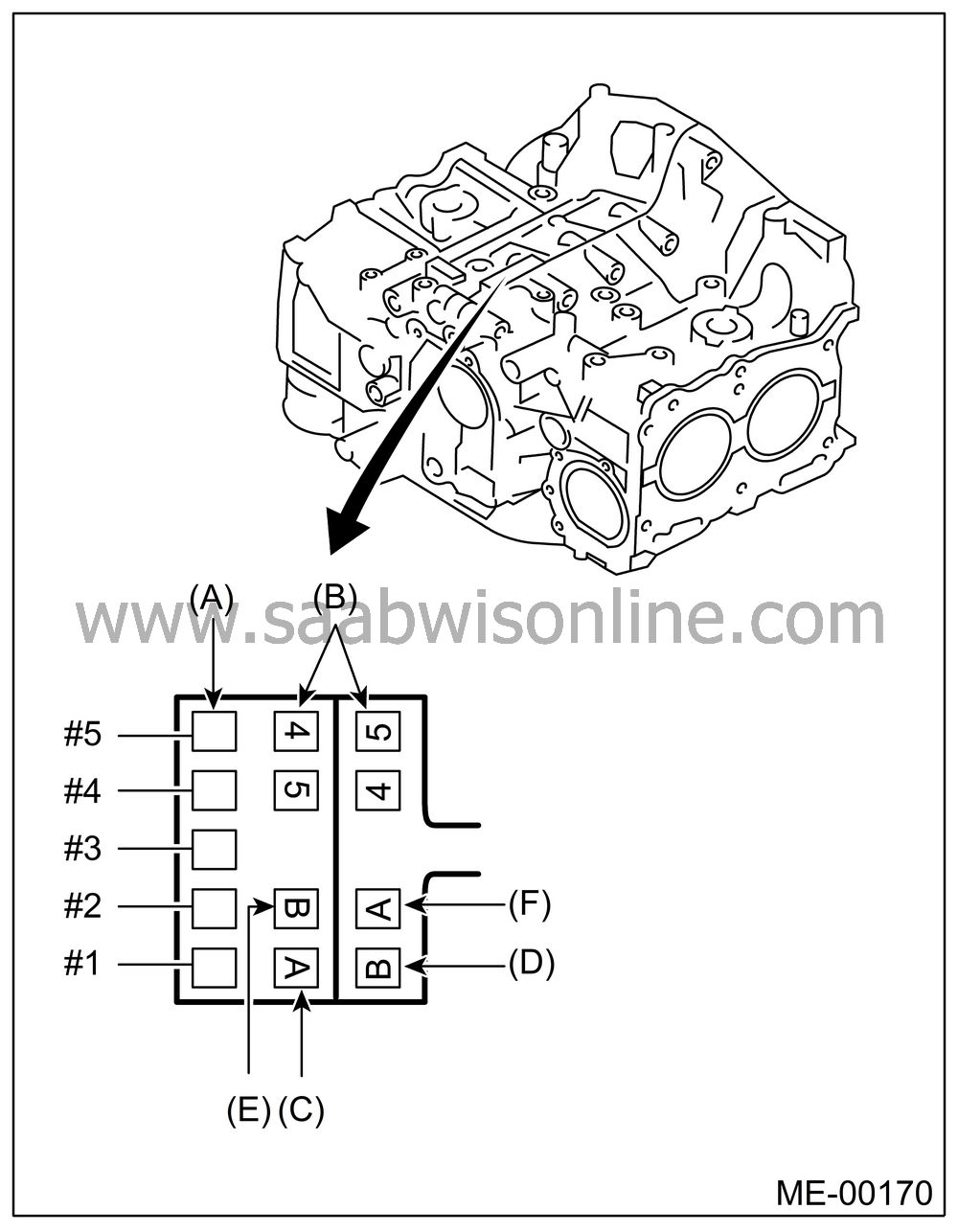
The cylinder bore size is stamped on cylinder block’s front upper surface.
| Note | ||
| • |
Measurement should be performed at a temperature of
20°C (68°F).
|
|
| • |
Standard sized pistons are classified into two grades, “A” and “B”.
These grades should be used as a guide line in selecting a standard
piston.
|
|
Standard diameter:
A: 92.005 — 92.015 mm (3.6222 — 3.6226 in)
B: 91.995 — 92.005 mm (3.6218 — 3.6222 in)
|
(A)
|
Main journal
size mark
|
|
(B)
|
Cylinder
block (RH)-(LH) combination mark
|
|
(C)
|
#1
cylinder bore size mark
|
|
(D)
|
#2
cylinder bore size mark
|
|
(E)
|
#3
cylinder bore size mark
|
|
(F)
|
#4
cylinder bore size mark
|
How to measure the inner diameter of each cylinder:
Measure the inner diameter of each cylinder in both the thrust and piston pin directions at the heights shown in the figure, using a cylinder bore gauge.
| Note | ||
|
Measurement should be performed at a temperature of 20°C (68°F). |
Taper:
Standard
0.015 mm (0.0006 in)Out-of-roundness:
Standard
0.010 mm (0.0004 in)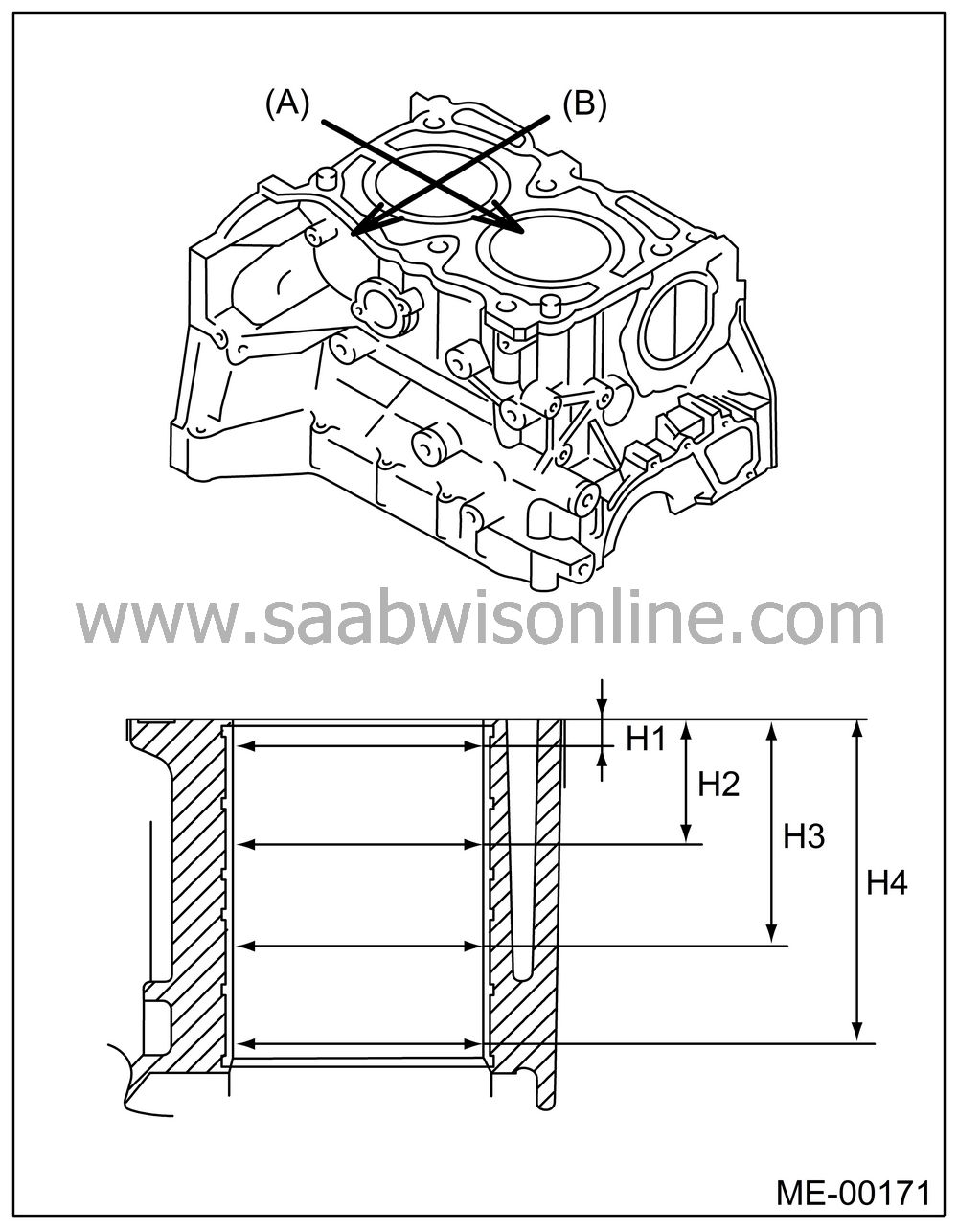
|
(A)
|
Piston
pin direction
|
|
(B)
|
Thrust
direction
|
|
H1:
|
10 mm (0.39
in)
|
|
H2:
|
45 mm (1.77
in)
|
|
H3:
|
80 mm (3.15
in)
|
|
H4:
|
115 mm
(4.53 in)
|
When the piston is to be replaced due to general or cylinder wear, determine a suitable sized piston by measuring the piston clearance.
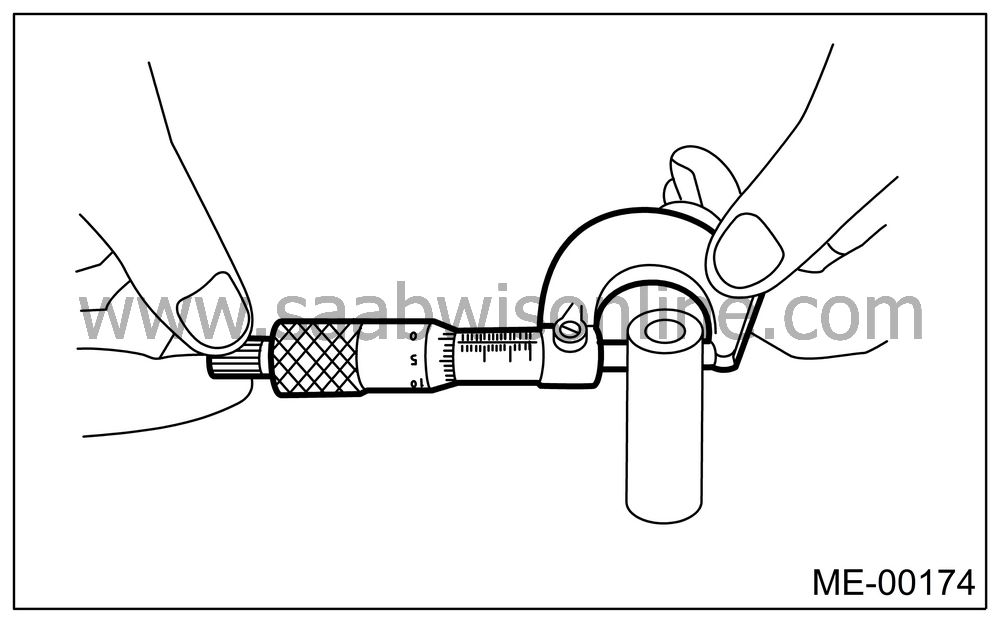
How to measure the outer diameter of each piston:
Measure the outer diameter of each piston at the height shown in the figure. (Thrust direction)
| Note | ||
|
Measurement should be performed at a temperature of 20°C (68°F). |
Piston grade point H:
40.0 mm (1.57 in)
Piston outer diameter:
Standard
A: 91.985 — 91.995 mm (3.6214 — 3.6218 in)B: 91.975 — 91.985 mm (3.6211 — 3.6214 in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
92.225 — 92.235 mm (3.6309 — 3.6313 in)0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
92.475 — 92.485 mm (3.6407 — 3.6411 in)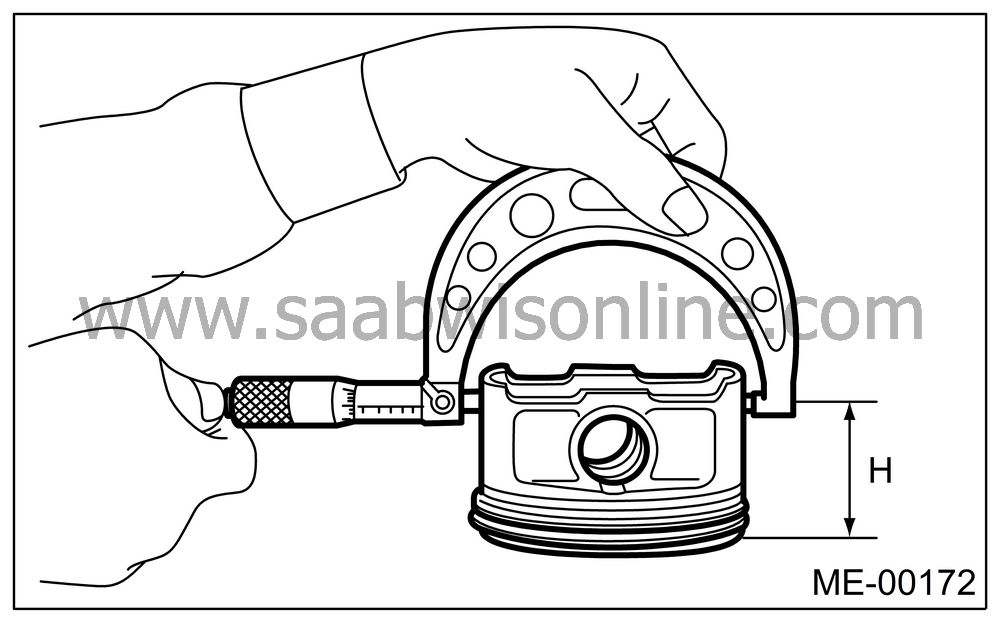
Calculate the clearance between cylinder and piston.
| Note | ||
|
Measurement should be performed at a temperature of 20°C (68°F). |
Cylinder to piston clearance at 20°C (68°F):
Standard
0.010 — 0.030 mm (0.0004 — 0.0012 in)Boring and honing:
If the value of taper, out-of-roundness, or cylinder-to-piston clearance measured exceeds the standard or if there is any damage on the cylinder wall, reboring it to use an oversize piston.
| Important | ||
|
When any of the cylinders needs reboring, all other cylinders must be bored at the same time, and use oversize pistons. Do not perform boring on one cylinder only, nor use an oversize piston for one cylinder only. |
||
If the cylinder inner diameter exceeds the limit after boring and honing, replace the crankcase.
| Note | ||
|
Immediately after reboring, the cylinder diameter may differ from its real diameter due to temperature rise. Thus, pay attention to this when measuring the cylinder diameter. |
Limit of cylinder enlarging (boring):
0.5 mm (0.020 in)
| PISTON AND PISTON PIN |
Check the pistons and piston pins for damage, cracks, and wear and the piston ring grooves for wear and damage. Replace if defective.
Measure the piston-to-cylinder clearance at each cylinder.
 If any of the clearances
is not within specification, replace the piston or bore the cylinder
to use an oversize piston.
If any of the clearances
is not within specification, replace the piston or bore the cylinder
to use an oversize piston.
Make sure that the piston pin can be inserted into the piston pin hole with a thumb at 20°C (68°F). Replace if defective.
Standard clearance between piston pin and hole in piston:
Standard
0.004 — 0.008 mm (0.0002 — 0.0003 in)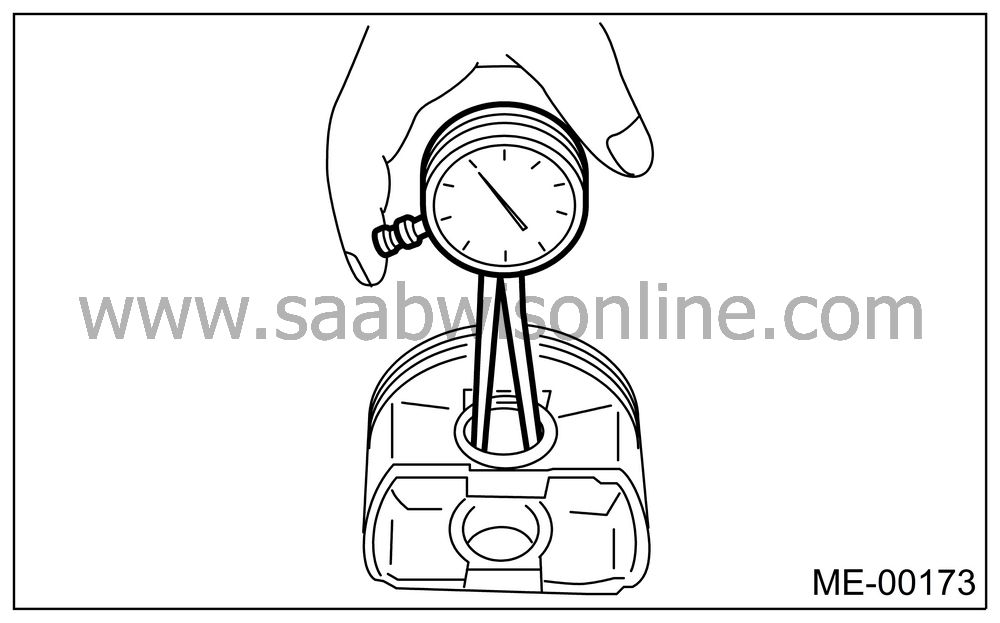
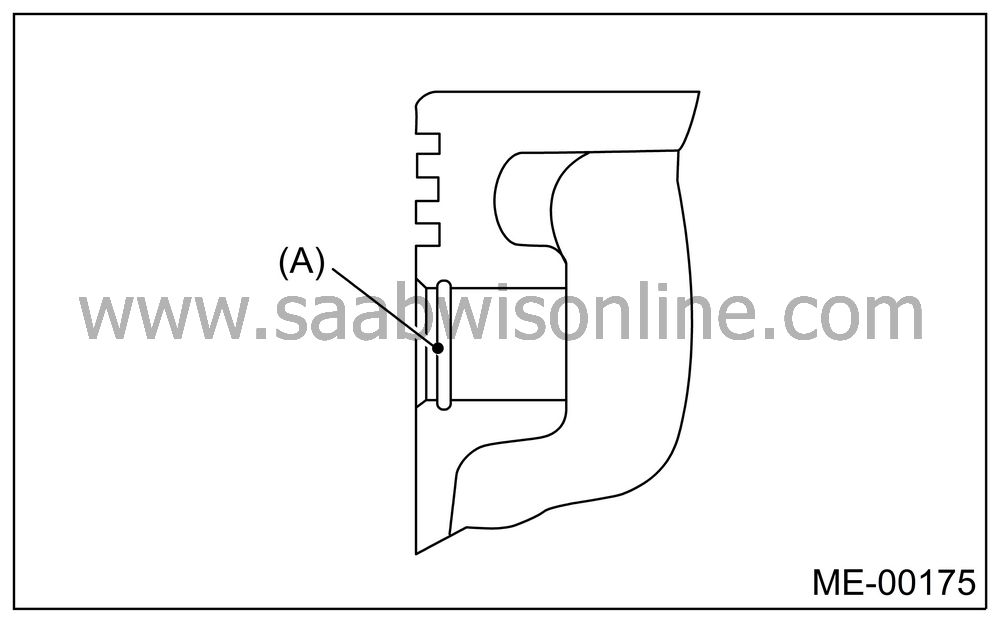
Check the snap ring installation groove on piston for burr (A). If necessary, remove the burr from groove so that the piston pin can lightly move.
Check the piston pin snap ring for distortion, cracks and wear.
| PISTON RING |
If the piston ring is broken, damaged, or worn, or if its tension is insufficient, or when the piston is replaced, replace the piston ring with a new one of the same size as the piston.
| Important | ||
| • |
Marks are shown on the end of
top and second rings. When installing the rings to piston, face
this mark upward.
|
|
| • |
Oil ring consists of upper rail, expander and lower
rail. When installing on piston, be careful of each rail’s
direction.
|
|
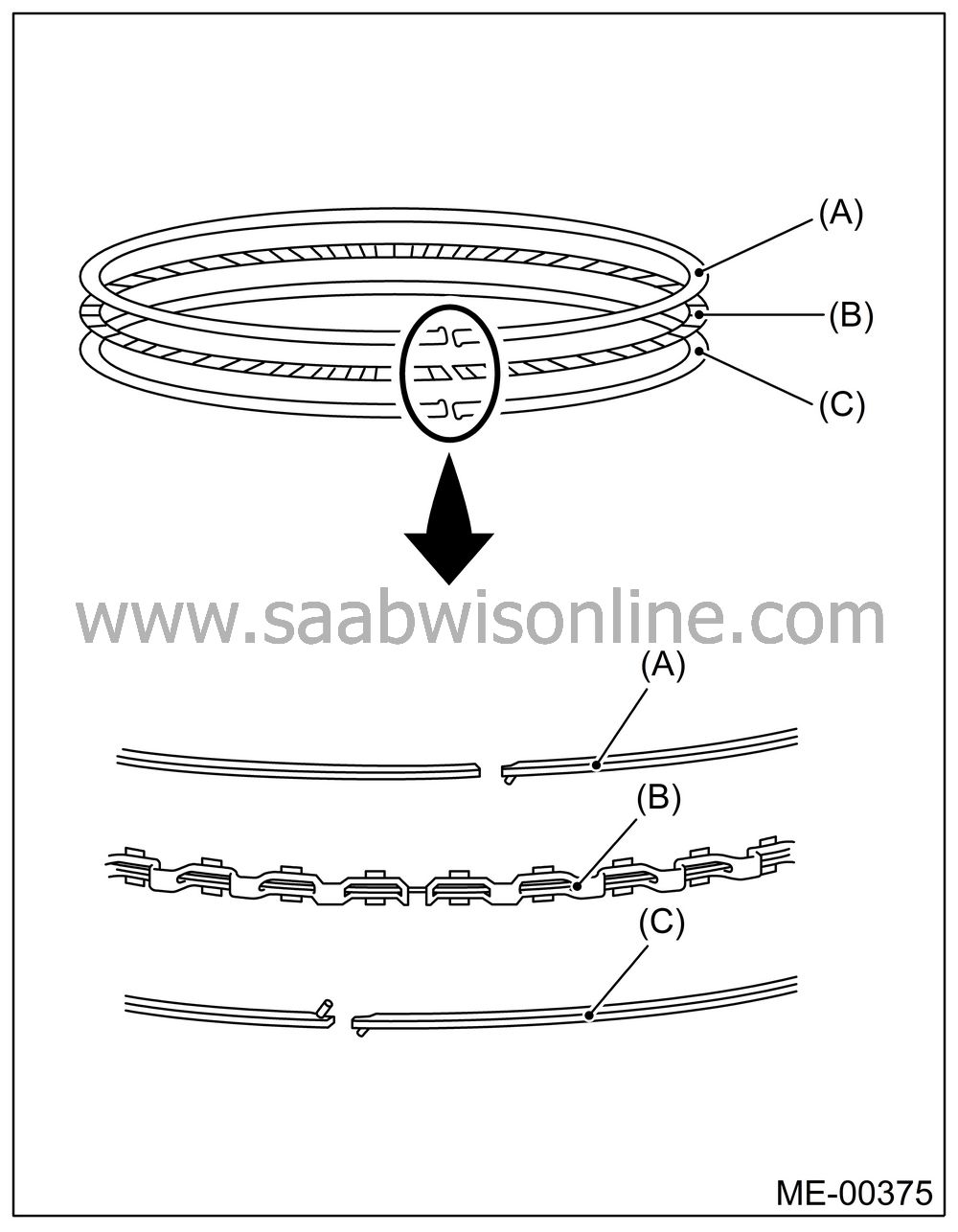
|
(A)
|
Upper rail
|
|
(B)
|
Expander
|
|
(C)
|
Lower rail
|
Squarely place the piston ring and oil ring in cylinder, and then measure the piston ring gap with a thickness gauge.
|
Unit:
mm (in)
|
||
|
Standard
|
||
|
Piston ring gap
|
Top
ring
|
0.20 — 0.25
(0.0079 — 0.0098) |
|
Second ring
|
0.40 — 0.50
(0.0157 — 0.0197) |
|
|
Oil
ring rail
|
0.20 — 0.50
(0.0079 — 0.0197) |
|
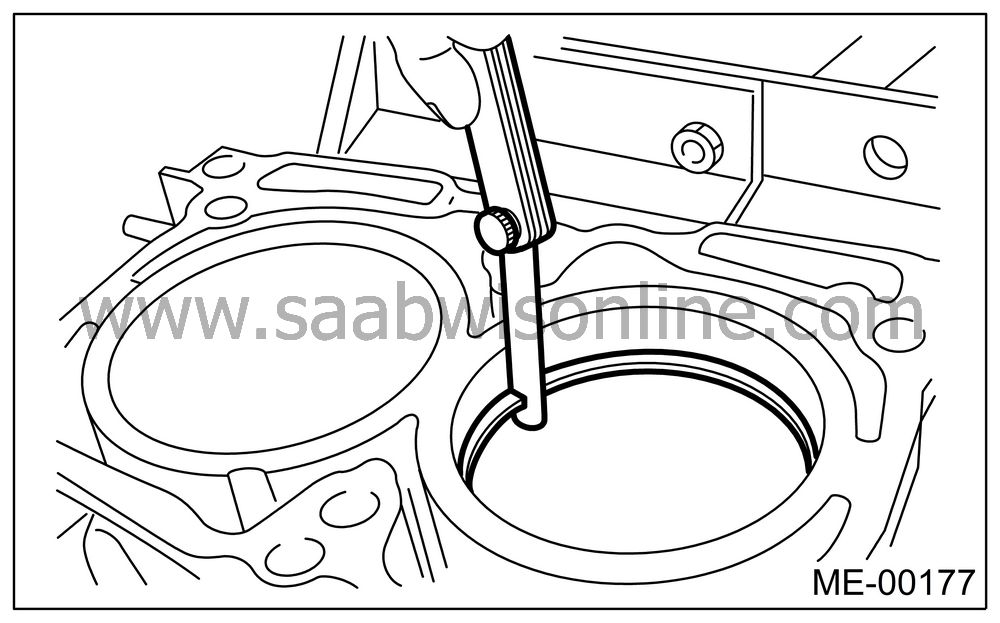
Measure the clearance between piston ring and piston ring groove with a thickness gauge.
| Note | ||
|
Before measuring the clearance, clean the piston ring groove and piston ring. |
|
Unit:
mm (in)
|
||
|
Standard
|
||
|
Clearance between piston ring and piston ring groove
|
Top
ring
|
0.040 — 0.080
(0.0016 — 0.0031) |
|
Second ring
|
0.030 — 0.070
(0.0012 — 0.0028) |
|
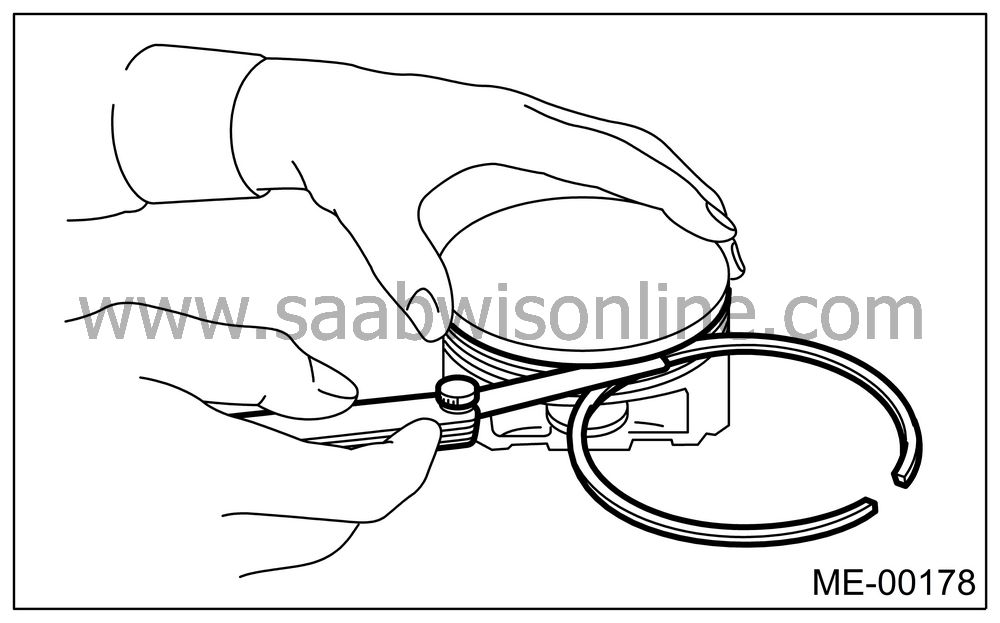
| CONNECTING ROD |
Replace the connecting rod, if the large or small end thrust surface is damaged.
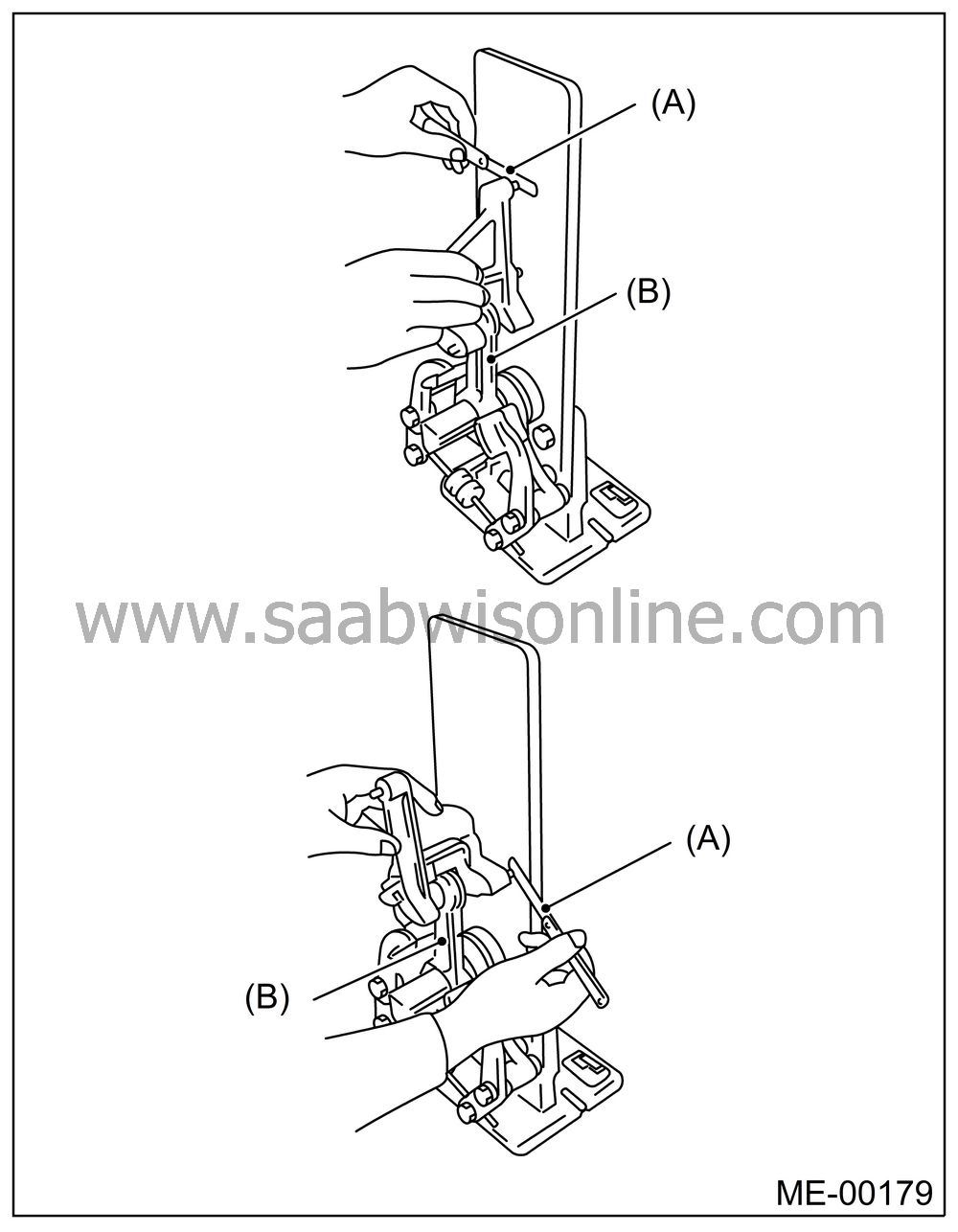
Check for bend or twist using a connecting rod aligner. Replace the connecting rod if the bend or twist exceeds the limit.
Limit of bend or twist per 100 mm (3.94 in) in length:
0.10 mm (0.0039 in)
|
(A)
|
Thickness
gauge
|
|
(B)
|
Connecting
rod
|
Install the connecting rod fitted with bearing to crankshaft, and then measure the side clearance (thrust clearance). Replace the connecting rod if the side clearance exceeds the specified limit.
Connecting rod side clearance:
Standard
0.070 — 0.330 mm (0.0028 — 0.0130 in)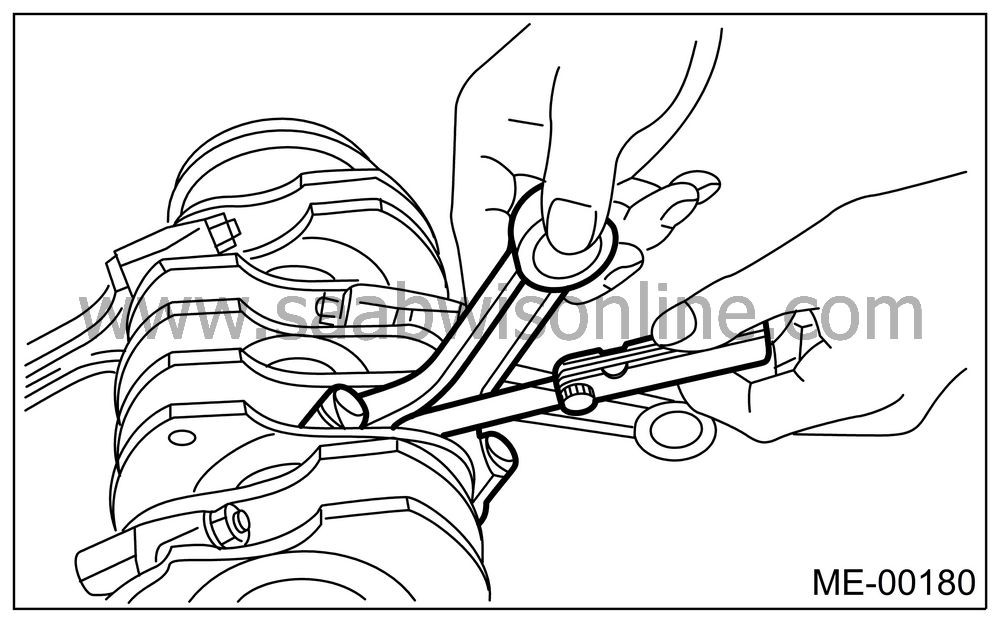
Inspect the connecting rod bearing for scar, peeling, seizure, melting, wear, etc.
Measure the oil clearance on individual connecting rod bearings by means of plastigauge. If any oil clearance is not within specification, replace the defective bearing with a new one of standard size or undersize as necessary. (See the table below.)
Connecting rod oil clearance:
Standard
0.026 — 0.052 mm (0.0010 — 0.0020 in)|
Unit: mm (in)
|
||
|
Bearing
|
Bearing
size
(Thickness at center) |
Outer
diameter of crank pin
|
|
Standard
|
1.486 — 1.498
(0.0585 — 0.0590) |
51.984 — 52.000
(2.0466 — 2.0472) |
|
0.03 (0.0012)
undersize |
1.504 — 1.512
(0.0592 — 0.0595) |
51.954 — 51.970
(2.0454 — 2.0461) |
|
0.05 (0.0020)
undersize |
1.514 — 1.522
(0.0596 — 0.0599) |
51.934 — 51.950
(2.0447 — 2.0453) |
|
0.25 (0.0098)
undersize |
1.614 — 1.622
(0.0635 — 0.0639) |
51.734 — 51.750
(2.0368 — 2.0374) |
Inspect the bushing at connecting rod small end, and replace if worn or damaged. Also measure the piston pin clearance at connecting rod small end.
Clearance between piston pin and bushing:
Standard
0 — 0.022 mm (0 — 0.0009 in)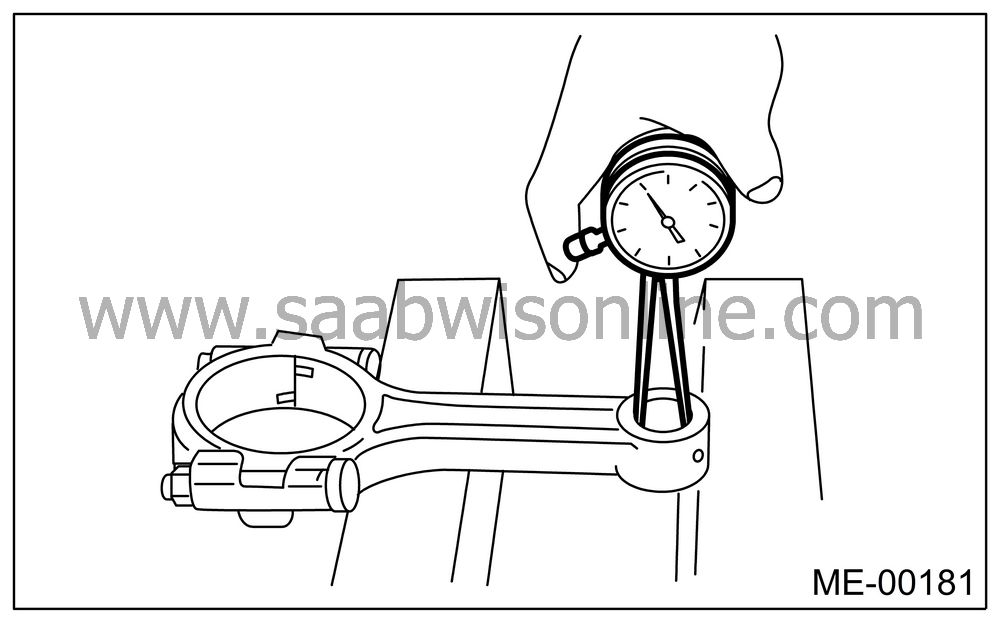

Replacement procedure is as follows:
Remove the bushing from connecting rod with ST and press.
Press the bushing with ST after applying oil on the periphery of bushing.
ST 32005122 CONNECTING ROD BUSHING REMOVER AND INSTALLER
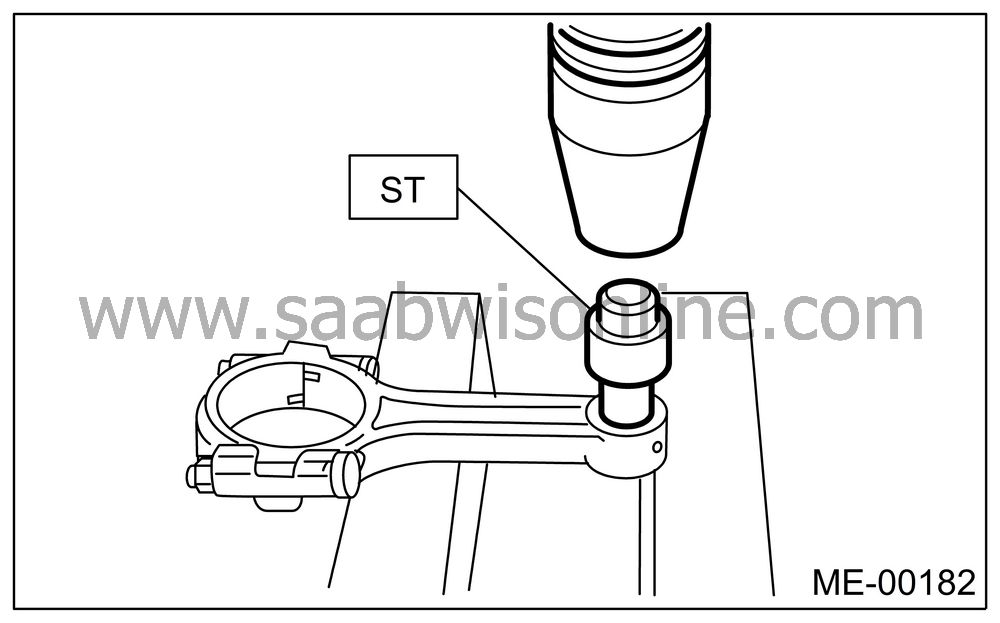
Make two 3 mm (0.12 in) holes in bushing. Ream the inside of bushing.
After the completion of reaming, clean the bushing to remove chips.
| CRANKSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT BEARING |
Clean the crankshaft completely and check for cracks by means of red lead check etc., and replace if defective.
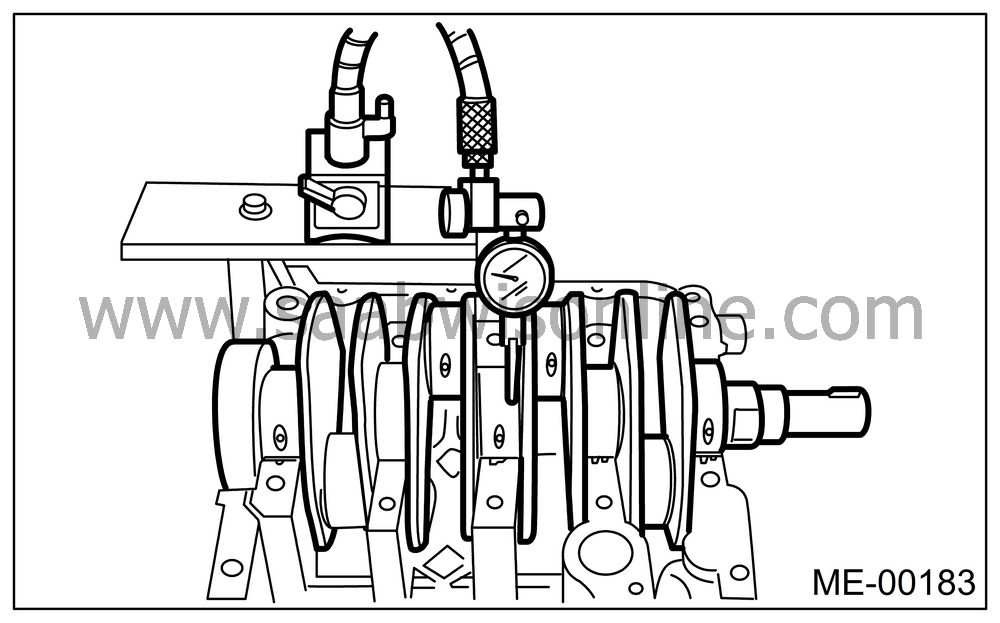
Measure the crankshaft bend, and correct or replace if it exceeds the limit.
| Note | ||
|
If a suitable V-block is not available, install the #1 and #5 crankshaft bearing on cylinder block, position the crankshaft on these bearings and measure the crankshaft bend using a dial gauge. |
Crankshaft bend limit:
0.035 mm (0.0014 in)
Inspect the crank journal and crank pin for wear. If they are not within the specifications, replace the bearing with a suitable (undersize) one, and then replace or recondition the crankshaft as necessary. When grinding the crank journal or crank pin, finish them to specified dimensions according to the undersize bearing to be used.
Crank pin and crank journal:
Out-of-roundness
0.005 mm (0.0002 in) or lessTaper limit
0.006 mm (0.00024 in)Crank pin grinding limit (diameter)
51.750 mm (2.0374 in)Crank journal grinding limit (diameter)
59.750 mm (2.3524 in) or less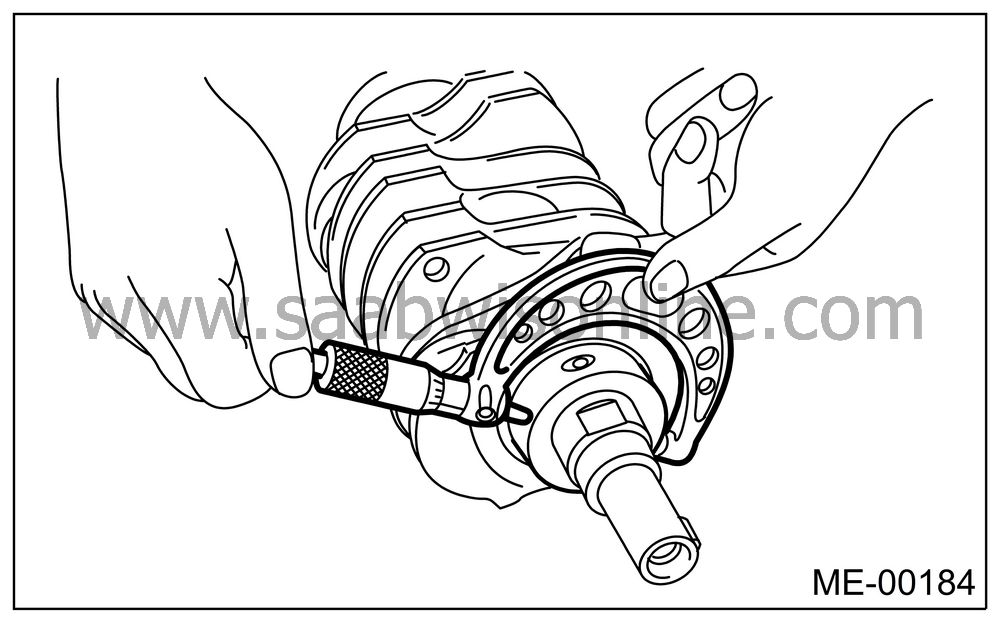
|
Unit: mm (in)
|
||||
|
Crank journal diameter
|
Crank pin diameter
|
|||
|
#1, #3, #5
|
#2, #4
|
|||
|
Standard
|
Journal
O.D.
|
59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625) |
59.992 — 60.008
(2.3619 — 2.3625) |
51.984 — 52.000
(2.0466 — 2.0472) |
|
Bearing
size
(Thickness at center) |
1.998 — 2.011
(0.0787 — 0.0792) |
2.000 — 2.013
(0.0787 — 0.0793) |
1.486 — 1.498
(0.0585 — 0.0590) |
|
|
0.03 (0.0012)
undersize |
Journal
O.D.
|
59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613) |
59.962 — 59.978
(2.3607 — 2.3613) |
51.954 — 51.970
(2.0454 — 2.0461) |
|
Bearing
size
(Thickness at center) |
2.017 — 2.020
(0.0794 — 0.0795) |
2.019 — 2.022
(0.0795 — 0.0796) |
1.504 — 1.512
(0.0592 — 0.0595) |
|
|
0.05 (0.0020)
undersize |
Journal
O.D.
|
59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605) |
59.942 — 59.958
(2.3599 — 2.3605) |
51.934 — 51.950
(2.0447 — 2.0453) |
|
Bearing
size
(Thickness at center) |
2.027 — 2.030
(0.0798 — 0.0799) |
2.029 — 2.032
(0.0799 — 0.0800) |
1.514 — 1.522
(0.0596 — 0.0599) |
|
|
0.25 (0.0098)
undersize |
Journal
O.D.
|
59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527) |
59.742 — 59.758
(2.3520 — 2.3527) |
51.734 — 51.750
(2.0368 — 2.0374) |
|
Bearing
size
(Thickness at center) |
2.127 — 2.130
(0.0837 — 0.0839) |
2.129 — 2.132
(0.0838 — 0.0839) |
1.614 — 1.622
(0.0635 — 0.0639) |
|
O.D.: Outer Diameter
Measure the thrust clearance of crankshaft at center bearing. If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the bearing.
Crankshaft thrust clearance:
Standard
0.030 — 0.115 mm (0.0012 — 0.0045 in)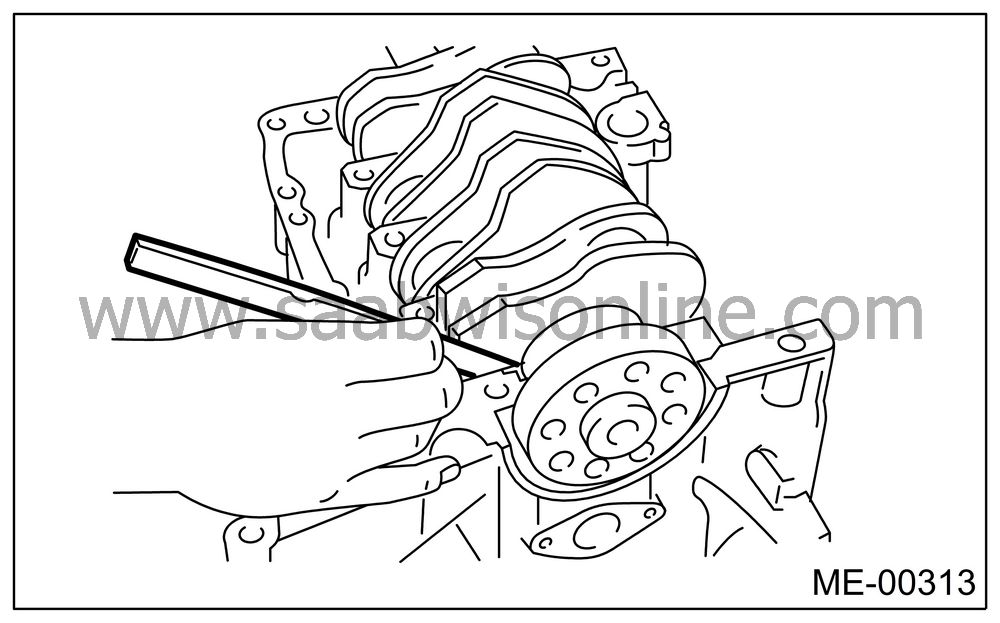
Inspect individual crankshaft bearings for signs of flaking, seizure, melting, and wear.
Measure the oil clearance on each crankshaft bearing by means of plastigauge. If the measurement is not within the specification, replace the defective bearing with an undersize one, and replace or recondition the crankshaft as necessary.
Crankshaft oil clearance:


